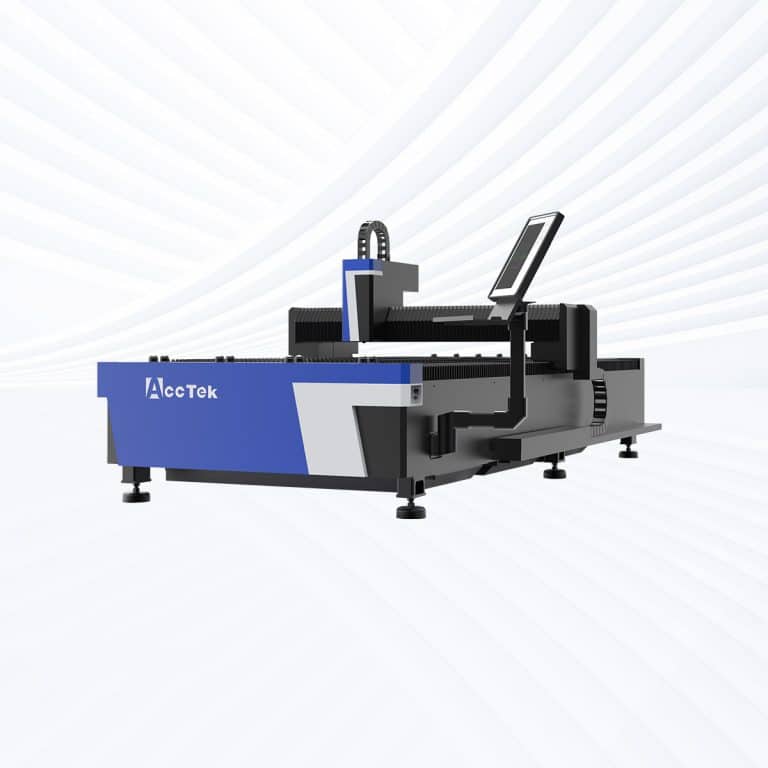
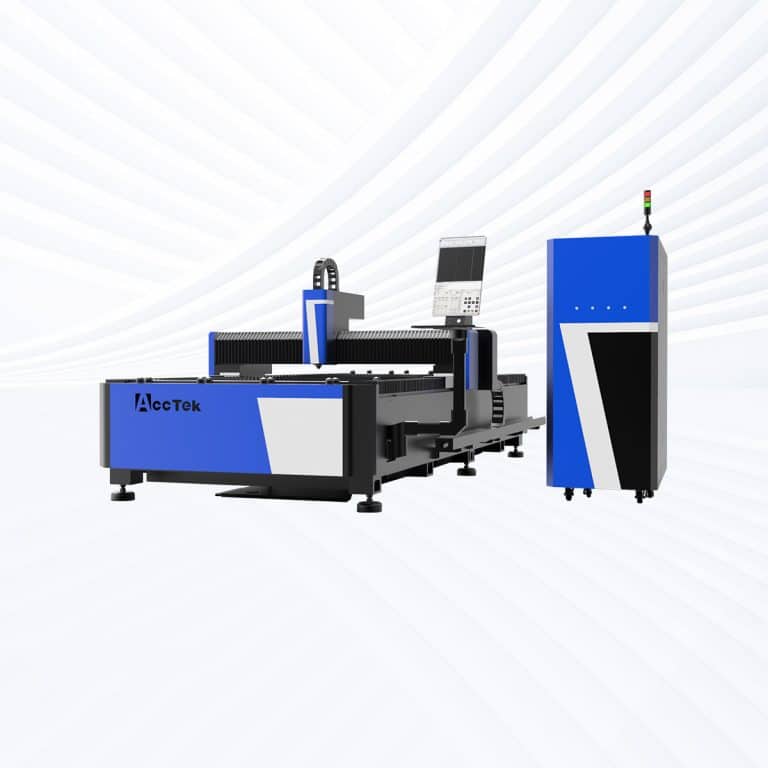
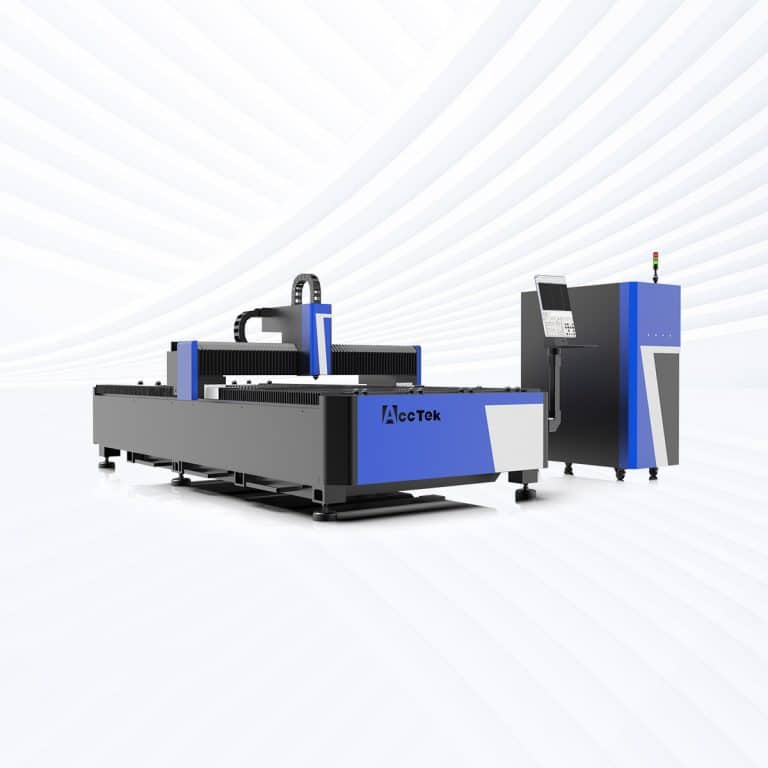
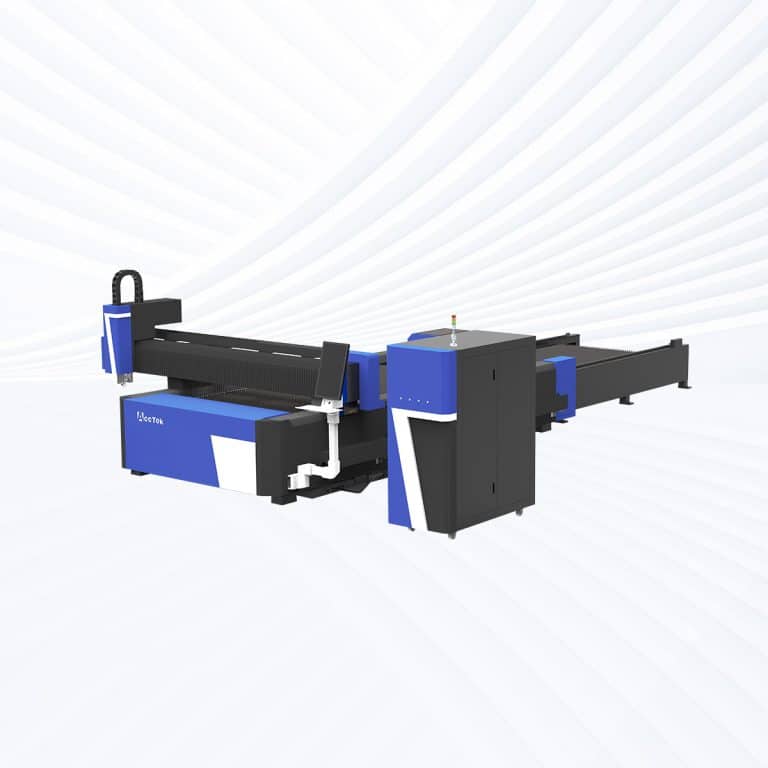
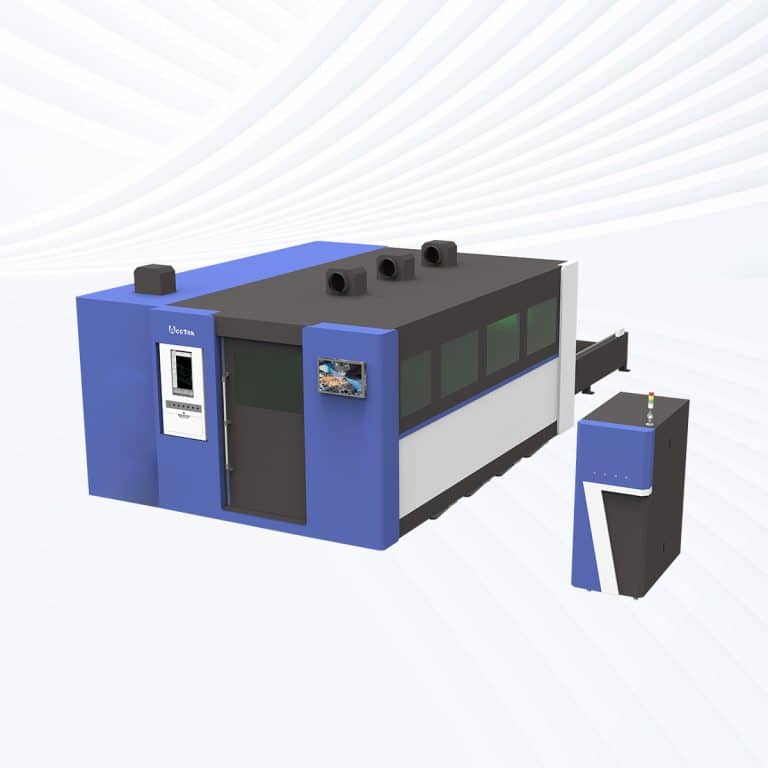
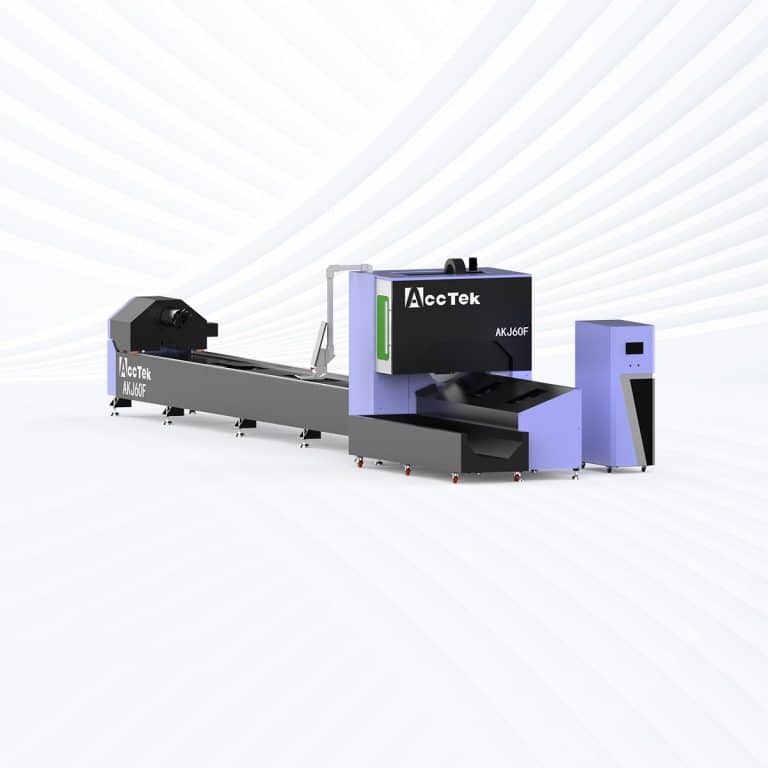
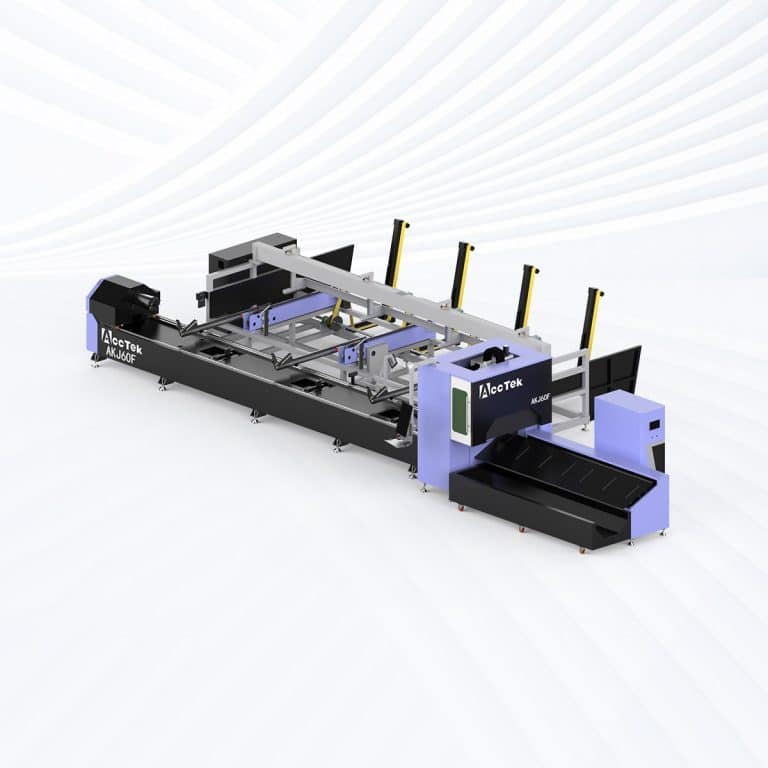
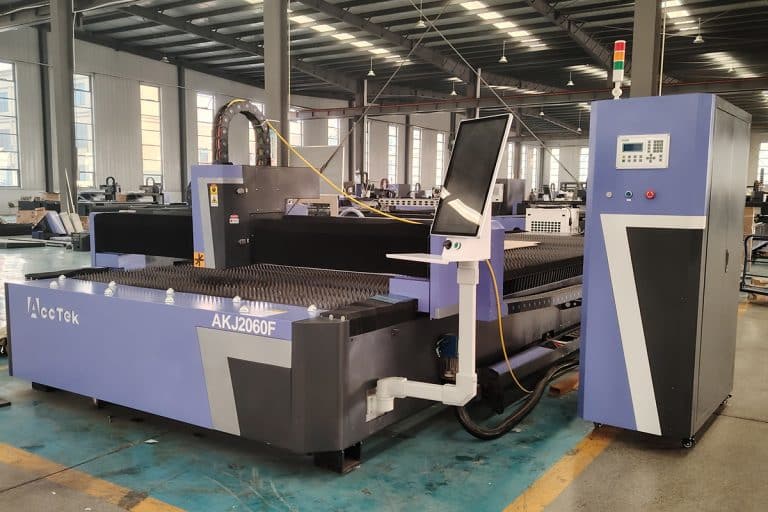
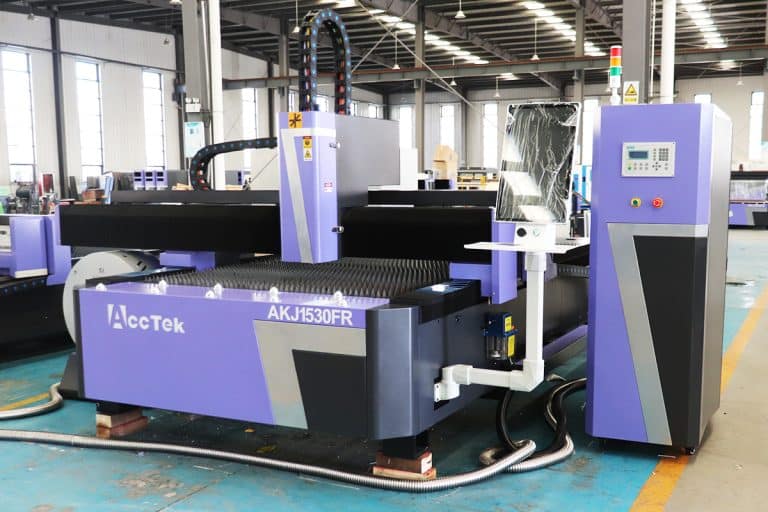
Product Introduction
4kW Laser Cutting Capacity
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Focus Position (mm) | Cutting Height (mm) | Gas | Nozzle (mm) | Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 1 | 28-35 | 0 | 1 | N2/Air | 1.5 | 10 |
| 2 | 12-15 | -1 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 2 | 10 | |
| 3 | 8.0-12.0 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 2 | 10 | |
| 3 | 4.0-4.5 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 4 | 3.0-3.5 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 5 | 2.5-3.0 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 6 | 2.5-2.8 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 8 | 2.0-2.3 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 10 | 1.8-2.0 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 12 | 1.0-1.2 | +2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 3 | 0.5 | |
| 14 | 0.9-1.0 | +2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 3.5 | 0.5 | |
| 16 | 0.7-0.9 | +2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 3.5 | 0.5 | |
| 18 | 0.6-0.7 | +2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 4 | 0.5 | |
| 20 | 0.55-0.65 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 4 | 0.5 | |
| 22 | 0.5-0.6 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 4.5 | 0.5 | |
| 25 | 0.5 | +3 | 0.8 | O2 | 5 | 0.5 | |
| Stainless Steel | 1 | 30-40 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5 | 10 |
| 2 | 15-20 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 10-12 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 4 | 6.0-7.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |
| 5 | 4.0-4.5 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 6 | 3.0-3.5 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 8 | 1.5-1.8 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 10 | 1.0-1.2 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 4 | 16 | |
| 12 | 0.8 | -6 | 0.5 | N2 | 4 | 16 | |
| Aluminum | 1 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 16-20 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 10-13 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 6.0-7.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 5 | 4.0-5.0 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 6 | 2.5-3.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 8 | 1.0-1.3 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 10 | 0.8 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 16 | |
| Brass | 1 | 25-28 | 0 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 12-15 | -1 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 | |
| 3 | 7.0-8.0 | -1 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 4.0-5.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 5 | 2.5-3.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 6 | 2.0-2.5 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 8 | 0.8-1.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| Titanium | 1 | 3.8-5.7 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 2.9-4.3 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 2.2-3.2 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 1.7-2.5 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 5 | 1.1-1.6 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 6 | 0.8-1.2 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 8 | 0.6-0.9 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 16 | |
| Galvanized Steel | 1 | 13.0-20.0 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 |
| 2 | 6.7-10.0 | -1 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 | |
| 3 | 3.4-5.0 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 2.2-3.3 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 5 | 1.7-2.5 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 6 | 1.3-2.0 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 8 | 0.9-1.3 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 10 | 0.7-1.0 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 12 | 0.4-0.7 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 14 | 0.3-0.5 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 16 | 0.2-0.4 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| Nickel-Alloy | 1 | 5.8-8.6 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 |
| 2 | 2.3-3.5 | -0.8 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 | |
| 3 | 1.2-1.7 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 4 | 0.8-1.2 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 5 | 0.6-0.9 | -1.8 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 6 | 0.5-0.7 | -1.8 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 8 | 0.3-0.4 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.2 | 16 |
Compatible Materials
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Tool Steel
- Bronze
- Zinc
- Inconel
- Hastelloy
- Waspaloy
- Rene alloys
- Stellite
- Galvanized Steel
- Chrome-Plated Steel
- Aluminized Steel
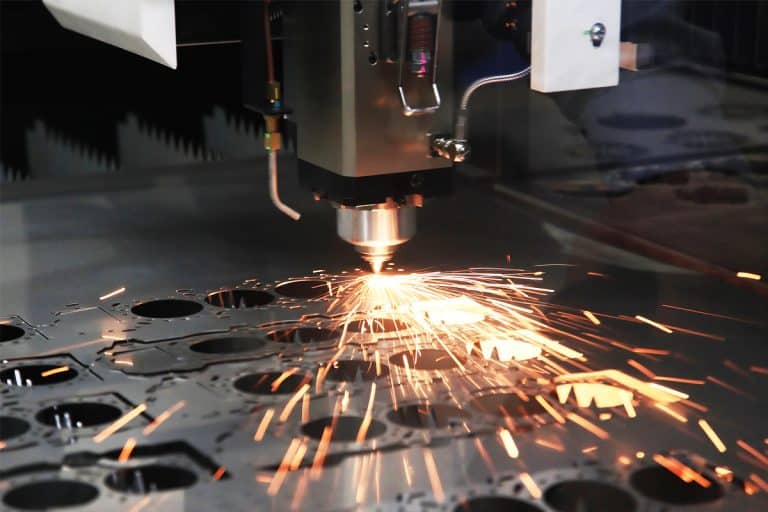
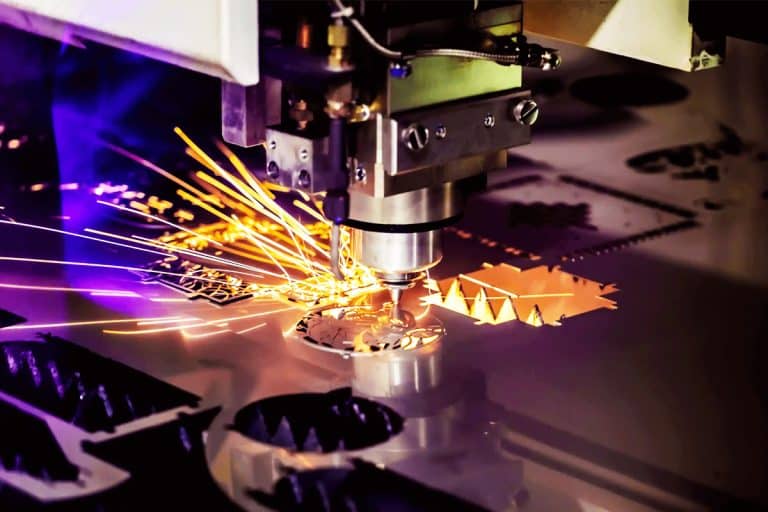
Application of 4kW Laser Cutting Machines






Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Cutting Technologies
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting | Flame Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Precision | Very high (±0.05 mm) | Medium (±0.5 mm) | Very high (±0.1 mm) | Low (±1–2 mm) |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, minimal post-processing | Rougher, may need grinding | Excellent, no heat effect | Rough edges, heavy finishing |
| Material Range | Metals, reflective materials | Conductive metals only | Almost all materials (metal, stone, glass, composites) | Ferrous metals only |
| Max Cutting Thickness | Up to 50 mm (with high-power lasers) | Up to 150 mm | Up to 200+ mm | Up to 300 mm (steel) |
| Cutting Speed (Thin Sheets) | Fastest for <20 mm | Fast for medium-thick plates | Slower | Slow |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Very small | Medium | None | Large |
| Operating Cost | Low (energy-efficient, minimal consumables) | Medium (electrodes, gas) | High (abrasive, water, pump) | Low (fuel and oxygen) |
| Initial Investment | Medium to high | Low to medium | Very high | Low |
| Maintenance | Low (fiber lasers are reliable) | Medium (torch wear, consumables) | High (pump, nozzle, abrasive lines) | Low |
| Automation Compatibility | Excellent (CNC, software-driven) | Good | Good | Limited |
| Surface Finish | Clean, ready-to-use | Requires secondary finishing | Excellent | Poor |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no chemicals, low waste) | Moderate (fumes, slag) | High (abrasive waste disposal) | High (fumes, CO₂) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (especially fiber lasers) | Moderate | Low (energy-intensive pumps) | Moderate |
| Noise Levels | Low | High | High | High |
| Best Use Case | Precision sheet/plate cutting, prototyping, high-quality parts | Structural steel, medium-to-thick plates | Ultra-thick, exotic, or non-metal materials | Heavy plate cutting, construction |
| Industry Adoption | Automotive, aerospace, fabrication, electronics, signage | Shipbuilding, repair, construction | Aerospace, defense, custom fabrication | Heavy industry, construction |
Why Choose Us
Advanced Technology
Our laser cutting machines feature high-speed, precision cutting with the latest laser technology, ensuring smooth edges, minimal waste, and superior efficiency across various materials and thicknesses.
Reliable Quality
Each machine undergoes rigorous quality control and durability testing to ensure long-term stability, low maintenance, and consistent high performance, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Comprehensive Support
We provide full technical support, including installation guidance, operator training, and after-sales service, ensuring smooth machine operation and minimal downtime for your business.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Our machines offer high performance at competitive prices, with customizable options to fit different production needs, helping businesses maximize their investment without compromising on quality.
Related Resources

What Safety Measures Should Be Taken When Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article teaches the basic safety measures for operating a laser cutting machine, including hazard awareness, engineering controls, PPE, fire prevention, ventilation, training, and emergency response drills.

Addressing the Challenges of Fiber Laser Cutting: Common Problems and Solutions
This article explores common challenges in fiber laser cutting, including material-related issues, machine performance, and operator-related problems, offering practical solutions to optimize cutting quality and efficiency.

Precautions for Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article provides a detailed overview of basic precautions for operating laser cutting machines, covering safety risks, proper setup, operating guidelines, maintenance procedures, and emergency preparedness.

Is Laser Cutting Fume Toxic
This article explains what laser cutting fumes are, how they form, their health and environmental risks, and the safety measures needed for proper fume control and extraction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do 4kW Laser Cutting Machines Cost?
- Open Laser Cutting Machine ($26,000-$61,500): Open-frame machines are the most affordable 4kW laser cutting systems. They provide good cutting performance for sheets but lack enclosures, which expose operators to sparks, fumes, and laser radiation. Because of this, proper ventilation and PPE are essential. These models are attractive for workshops focused on cost savings but willing to manage safety independently.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine ($30,000-$64,000): Enclosed machines are safer and cleaner to operate. The housing contains sparks and radiation, while integrated exhaust systems help manage fumes. They are preferred in professional environments where compliance with safety standards is important. The price reflects added protections and automation.
- Open Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($30,500-$64,500): Adding an exchange worktable allows operators to load and unload material while the machine continues cutting. This reduces downtime and boosts efficiency, especially in production environments. These models retain the open design, so operators must still take extra safety precautions.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($34,500-$68,500): This type combines the efficiency of an exchange table with the safety of a fully enclosed machine. It is ideal for mid- to large-scale workshops that require both productivity and operator protection. The cost is higher, but the balance of speed, safety, and reliability makes it a strong investment.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine ($39,000-$73,000): Tube-sheet machines can cut both flat metal sheets and round or square tubes, providing more flexibility for industries like construction, furniture, and automotive. The open-frame design keeps costs lower than enclosed models but requires additional safety measures.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($43,500-$77,500): These machines combine multitasking capabilities with exchange worktables to increase efficiency and throughput. They are well-suited for workshops handling mixed production needs. The higher price reflects the additional tube-handling system and automated table switching.
- Enclosed Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($48,000-$82,000): At the top end of the 4kW range, this configuration offers maximum productivity, safety, and versatility. The enclosure ensures operator protection, while the exchange worktable reduces downtime, and tube-sheet compatibility allows broader applications. This setup is designed for industrial-scale operations with demanding workloads.
What Is The Power Consumption Of 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Generator Power (≈12,000W): The generator converts electricity into a high-energy cutting beam. To output 4kW of laser power, it requires around 12kW of electrical input, accounting for conversion inefficiencies in the laser diodes. This makes the generator the largest single consumer of energy in the system.
- Chiller Power (≈5120W): Running a 4kW laser creates substantial heat in the generator, optics, and electronics. A heavy-duty water chiller maintains stable temperatures to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability. Consuming more than 5kW, the chiller is the second-largest load, operating continuously while the machine is in use.
- Driver Power (≈4850W): Servo motors and precision drive systems move the cutting head and worktable. At nearly 5kW, this subsystem supports rapid acceleration, smooth positioning, and accurate cuts across multiple axes. Driver power demand increases with thicker materials and high-speed cutting.
- Draught Fan Power (≈3000W): The draught fan removes smoke, dust, and particulates generated during cutting. While it doesn’t influence cutting speed directly, it is vital for operator safety, clean optics, and maintaining a stable environment. At 3kW, it is a significant part of the machine’s total energy usage.
How Can I Purchase 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Define Your Requirements: Before reaching out to suppliers, determine your production needs. Consider factors such as material types (steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper), thickness ranges, expected cutting volumes, and whether you need special features like an exchange worktable or tube-sheet cutting capability. This helps you choose the right configuration and avoid overspending.
- Research Reliable Manufacturers: Look for established brands or OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) with a strong reputation in fiber laser cutting. Check case studies, customer reviews, and industry certifications (like ISO or CE) to ensure credibility. Well-known suppliers also offer longer warranties and better spare part availability.
- Compare Machine Options: 4kW laser cutting machines come in different formats: open vs. enclosed designs, flatbed vs. tube-sheet, with or without exchange worktables. Enclosed models provide better operator safety and dust control, while open models are easier to access and maintain. Comparing these configurations allows you to balance cost, efficiency, and safety.
- Request Quotes and Demonstrations: Contact multiple suppliers and request detailed quotations that include not only the machine price but also shipping, installation, training, and warranty. If possible, schedule an on-site or virtual demonstration to see the machine in operation. This helps verify cut quality, speed, and ease of use before committing.
- Check After-Sales Support: A good machine is only as reliable as the service behind it. Ensure that the supplier provides operator training, remote technical support, local service teams (if available), and fast delivery of spare parts. This reduces downtime and keeps your production running smoothly.
- Consider Financing and Delivery: For larger purchases, many manufacturers or distributors offer financing options, leasing, or staged payments. Delivery times can vary from stock availability (a few weeks) to custom orders (several months), so align your purchase with production schedules.
- Finalize Purchase and Installation: Once you select the supplier, confirm the terms of sale, warranty period, and installation timeline. Prepare your workshop with the necessary infrastructure—power supply, ventilation, and space for loading/unloading materials—before delivery.
Are 4kW Laser Cutting Machines Easy To Operate?
- Control Systems and Software: Most 4kW laser cutting machines come equipped with advanced CNC controllers and touchscreen interfaces. These systems often include built-in material libraries, automated parameter settings, and cutting path optimization. For new operators, this reduces the need for manual adjustments and minimizes errors.
- Automation and Smart Features: Many 4kW models integrate features such as automatic nozzle centering, autofocus for varying material thicknesses, and real-time monitoring of cutting conditions. Machines with exchange worktables further simplify production by allowing materials to be prepared while cutting continues, improving efficiency without adding complexity.
- Training Requirements: Although the machines are easier to operate than older systems, proper training is essential. Operators must learn how to adjust cutting parameters, handle assist gases, monitor optics, and manage maintenance tasks. Fortunately, most suppliers include hands-on training sessions, and once trained, operators typically adapt quickly.
- Safety Considerations: Ease of operation also ties to safety. Enclosed 4kW laser cutting machines with protective housings offer a safer working environment by reducing exposure to sparks, fumes, and laser radiation. Open models are still straightforward to use but demand greater attention to PPE, ventilation, and workshop safety protocols.
- Learning Curve: For beginners, the first challenge is understanding material-specific parameters and maintenance routines. However, once mastered, 4kW laser cutting machines are far easier to operate consistently than traditional cutting tools. Automated diagnostics and error alerts further simplify troubleshooting.
What Assist Gases Can Be Used With 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is commonly used for cutting carbon steel. It reacts with the hot metal in an exothermic process, which increases cutting speed while reducing laser power requirements. However, this process leaves an oxidized edge that may need additional finishing if a clean surface is required. Oxygen is ideal for thick plates where productivity is more important than cosmetic edge quality.
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is used when a clean, oxide-free edge is essential, such as in stainless steel, aluminum, and high-end sheet metal fabrication. Instead of reacting with the metal, nitrogen simply blows away molten material. This produces smooth, burr-free edges but requires much higher gas flow and pressure, which increases operating costs. For industries like food processing, aerospace, or medical equipment manufacturing, nitrogen is often the preferred choice.
- Compressed Air: Compressed air, a cost-effective alternative, contains about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. It can be used for cutting thin stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel. While it’s cheaper than pure nitrogen, the presence of oxygen may cause slight oxidation on the edges, making it suitable for non-decorative or functional parts where a perfect edge finish isn’t critical.
- Argon (Ar): Though less commonly used due to high cost, argon is an inert gas that prevents oxidation entirely. It is occasionally used in specialized applications, such as titanium cutting or high-value alloys, where edge protection is critical.
- Gas Pressure Considerations: For thinner sheets, higher gas pressures are typically required to achieve clean cuts and prevent dross buildup. In thicker materials, gas consumption increases significantly, making efficient supply systems essential.
What Are The Environmental Requirements For Using 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser cutting generates fumes, especially when cutting materials like metals, plastics, or composite materials. These fumes contain particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and potentially harmful gases such as ozone. An effective fume extraction system is essential to capture and filter these emissions, maintaining both air quality and worker safety. Proper ventilation prevents toxic fumes from accumulating and helps maintain a comfortable work environment.
- Room Temperature and Humidity Control: Laser cutting machines operate best in environments where ambient temperatures are stable and within the range of 18°C to 25°C (64°F to 77°F). High humidity can cause moisture buildup inside the machine, leading to rust, corrosion, or inaccurate performance. Dry, well-ventilated conditions are ideal to keep electrical components functioning properly and to avoid condensation inside sensitive parts. A chiller unit is often used to maintain the cooling system at an optimal temperature.
- Electrical and Power Supply Requirements: A stable power supply is critical for the proper functioning of 4kW laser cutting machines. Voltage fluctuations can cause instability in the machine’s performance or even damage sensitive components like the laser source or CNC controls. Additionally, surge protectors and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are recommended to safeguard against power spikes and interruptions. Depending on the region, a three-phase power supply may be required to ensure the machine operates efficiently.
- Safety and Radiation Shielding: Fiber laser cutting machines are generally safer than CO2 lasers in terms of radiation exposure, but they still require safety precautions. Laser enclosures and protective barriers should be in place to prevent exposure to laser radiation, particularly when the machine operates at high power. Warning signs, interlocks, and safety goggles are essential safety measures for operators working with the machine.
- Space Requirements: 4kW laser cutting machines can be large, and the workspace needs to accommodate the machine size, as well as allow for material loading and unloading. It is recommended to have at least 3 meters of clearance around the machine to ensure adequate airflow and prevent obstruction of the cooling system, gas flow, and ventilation systems. The work area should also be free of dust, as dust buildup can interfere with optics and the overall performance of the machine.
- Waste Disposal and Recycling: The cutting process generates waste materials, including metal slag, scrap material, and dust. A well-organized system for collecting and disposing of waste is important for maintaining a clean and efficient workspace. Many materials cut by fiber lasers (especially metals) can be recycled. It’s also essential to ensure that filters from the fume extraction system are disposed of properly to prevent contamination.
How Should I Maintain 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Regular Cleaning
- Laser Optics: The mirrors and lenses should be cleaned regularly to ensure the laser beam remains focused and efficient. Dust, smoke, and residue can accumulate and reduce cutting quality or even damage the optics. Use a soft, lint-free cloth with a gentle laser optic cleaner, and clean both sides of the lenses.
- Air Assist and Nozzles: Check and clean the air assist nozzles regularly, as debris can obstruct the airflow, reducing the cutting quality. Use compressed air or a soft brush to clean the nozzle and surrounding areas.
- Guide Rails: Clean the rails where the laser head moves, removing dust and debris. Use a vacuum or a cloth to wipe them down to maintain smooth operation and prevent wear.
- Cooling System Maintenance
- Chiller Unit: The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal temperature levels for the laser tube. Check the chiller’s coolant level regularly and ensure the cooling fluid is replaced as per the manufacturer’s recommendation. Dirty or old coolant can cause overheating, which may damage the laser tube.
- Clean Radiator and Filters: Clean the radiator and filters of the chiller unit periodically. This will help prevent the system from overheating, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and maintaining the performance of the machine.
- Water Quality: Maintain the water’s quality, keeping it free of contaminants like rust or scale buildup. Use distilled or deionized water to prevent mineral deposits from accumulating.
- Check and Maintain the Laser Tube
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the laser tube for any cracks, discoloration, or leaks. A faulty tube can lead to poor beam quality and potential safety hazards.
- Voltage Checks: Ensure the high-voltage power supply is working correctly. A drop in power can lead to inconsistencies in the cutting process or cause the tube to overheat.
- Laser Tube Alignment: Ensure the laser tube is properly aligned with the rest of the optical system. Misalignment can cause inefficient cutting, poor beam focus, and potential damage to other components.
- Focus and Alignment
- Laser Head Alignment: Align the laser head properly to ensure the beam remains focused on the material surface. A misaligned laser head can lead to uneven cuts and poor quality.
- Focus Lens: Ensure the focus lens is correctly positioned, and adjust it based on the material thickness. Also, inspect the lens for any scratches or marks that could affect the cutting quality.
- X and Y Axis Alignment: Check the alignment of the X and Y axis motors and rails to avoid uneven motion. Misalignment can cause distortions in the cutting path.
- Lubrication and Mechanical Maintenance
- Motion System: Regularly lubricate the gantry, rails, and other moving parts of the machine to minimize friction and ensure smooth operation. Use the recommended lubrication products as outlined by the manufacturer.
- Check Belts and Chains: Inspect belts and chains for wear or tension issues. Tighten or replace them as necessary to prevent any misalignment during operation.
- Motor Maintenance: Regularly inspect the motors for signs of wear or overheating. Ensure they are clean and free from debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Air Assist System
- Inspect Air Compressor: The air assist system helps blow debris and smoke away from the cutting area, improving cut quality and preventing fires. Regularly check the air compressor for proper functioning and ensure the air pressure is maintained at optimal levels.
- Replace Air Filters: Replace any air filters as needed to prevent contaminants from entering the cutting area, which could affect the cut quality or cause the machine to malfunction.
- Software and Control Systems
- Update Software: Ensure that the control software is regularly updated to avoid bugs and to take advantage of any new features that might improve cutting performance.
- Check Communication and Calibration: Periodically check the machine’s software communication and calibration with the hardware to ensure accurate cutting. If the machine starts cutting inaccurately or is not responsive to settings changes, it could be a software or calibration issue.
- Safety Features
- Interlocks and Emergency Stops: Test all safety interlocks and emergency stop buttons to ensure they function properly in case of an emergency.
- Fume Extraction System: Ensure the fume extraction system is working well, especially when cutting materials that produce toxic fumes. Regularly check for clogging, leaks, or damage to the exhaust ducts.
- Protective Equipment: Make sure that all operators are trained to use the machine safely, including wearing appropriate protective gear (goggles, gloves, etc.), and regularly inspect safety shields and windows for cracks or damage.
- Documentation and Logs
- Maintenance Log: Keep a maintenance log for tracking all routine checks, repairs, and replacements performed on the machine. This log helps you keep track of service intervals and identify potential recurring issues.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance intervals, troubleshooting guides, and replacement schedules for parts like the laser tube, lenses, and bearings.
- Scheduled Professional Servicing
- Professional Inspections: Schedule professional servicing at regular intervals, ideally annually or biannually, depending on the intensity of usage. A professional technician can perform deep maintenance like inspecting the electrical system, laser source, and ensuring that the machine is running at its full potential.
What PPE Is Required To Operate 4kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Safety Glasses: Fiber lasers emit light at wavelengths typically around 1µm, which can cause serious damage to the eyes. Protective eyewear with a specific optical density (OD) for the wavelength of the laser should always be worn. The glasses must cover both direct and scattered laser light. The OD value must be suitable to protect against the specific laser power, such as 4kW, to avoid eye injury.
- Protective Clothing: Wear flame-resistant and non-reflective clothing that covers the body, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants. This helps reduce the risk of burns or skin exposure to stray laser light. High-visibility or reflective workwear should be avoided, as it can reflect laser beams. Protective aprons made from durable materials are recommended in some instances.
- Gloves: Thick, heat-resistant gloves made from materials like leather or specialized textiles should be worn to protect against burns from hot surfaces, especially when handling materials or tools near the laser cutter. Gloves also provide protection when handling workpieces after cutting, as these can become very hot.
- Foot Protection: Steel-toed boots or heavy-duty work shoes are necessary to protect against falling objects, heavy tools, or components. Footwear should also be slip-resistant to prevent accidents while moving around the work area.
- Hearing Protection: Fiber laser cutting machines, especially high-power ones like 4kW, can generate high noise levels due to the operation of exhaust fans, air-assist systems, and cutting processes. Earplugs or earmuffs should be worn to protect hearing in noisy environments.
- Respiratory Protection: Depending on the materials being cut, fumes and particulate matter may be generated, particularly when cutting plastics, metals, or composites. Fume extraction systems are crucial, but in some environments, additional respiratory protection, such as a respirator, may be required to prevent inhalation of toxic gases, dust, or fumes. For example, cutting metals may release fine particles or hazardous gases like ozone, which are harmful if inhaled.
- Face Shield or Visor: A full-face shield or visor may be necessary in certain situations, especially when the operator is directly interacting with the laser machine or performing maintenance tasks. This additional protection shields against any laser reflections or accidental exposure, particularly if the operator needs to adjust settings or handle materials near the cutting area.
- Proper Ventilation and Exhaust Systems: Although not technically PPE worn by the operator, proper ventilation and fume extraction systems are critical in the workspace to protect the operator’s health. Adequate ventilation helps remove harmful fumes, especially when cutting materials like plastics and metals that can release dangerous vapors when heated.