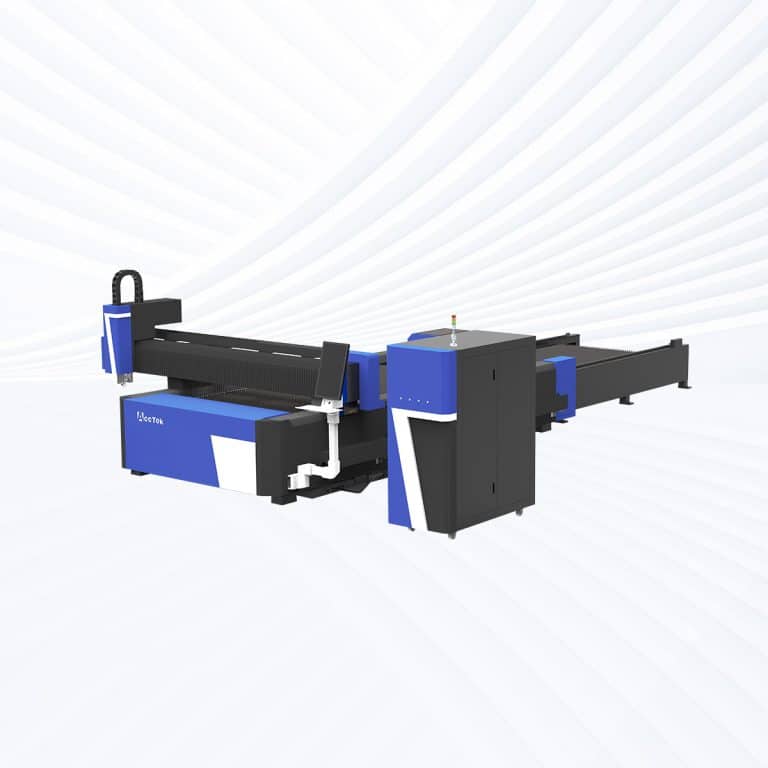
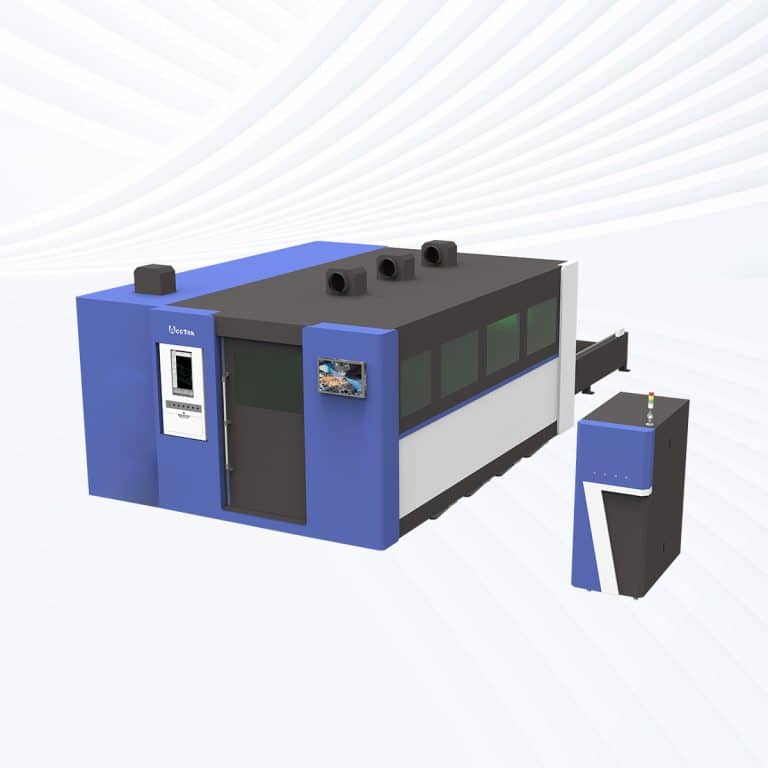
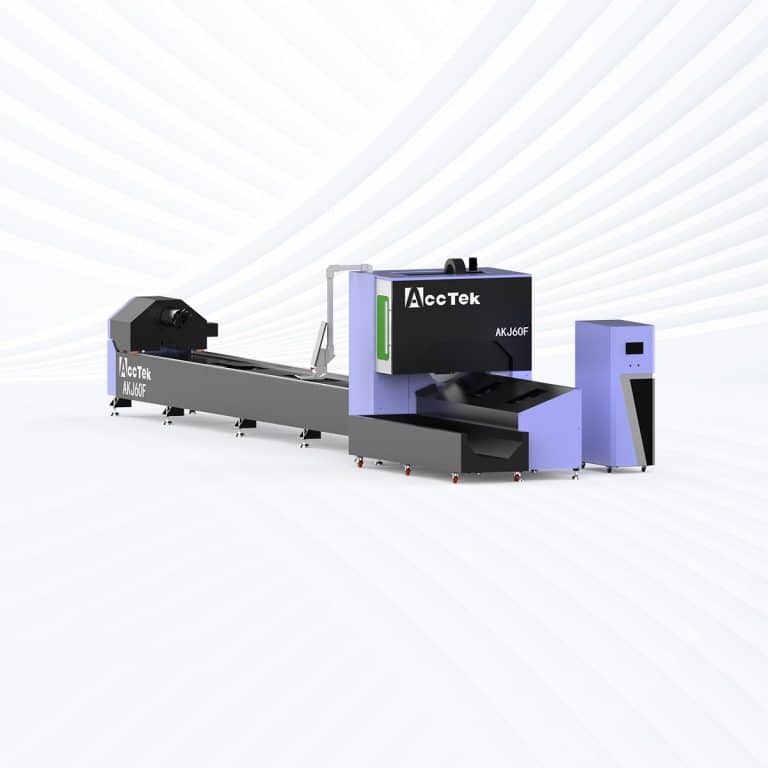
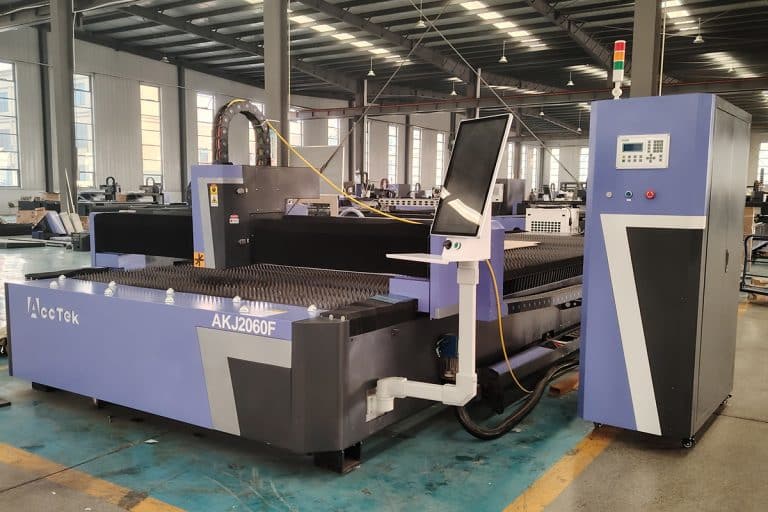
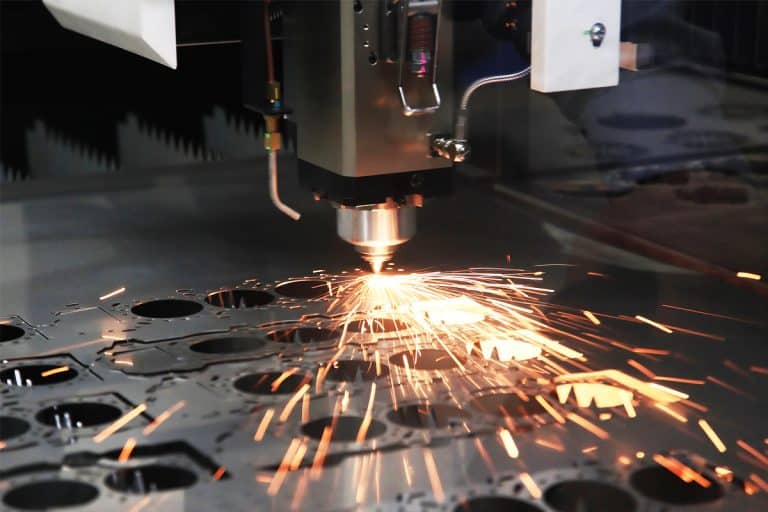
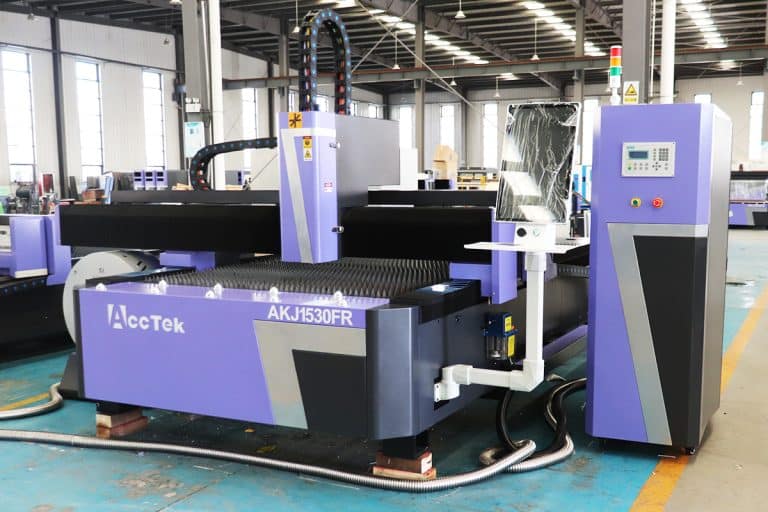
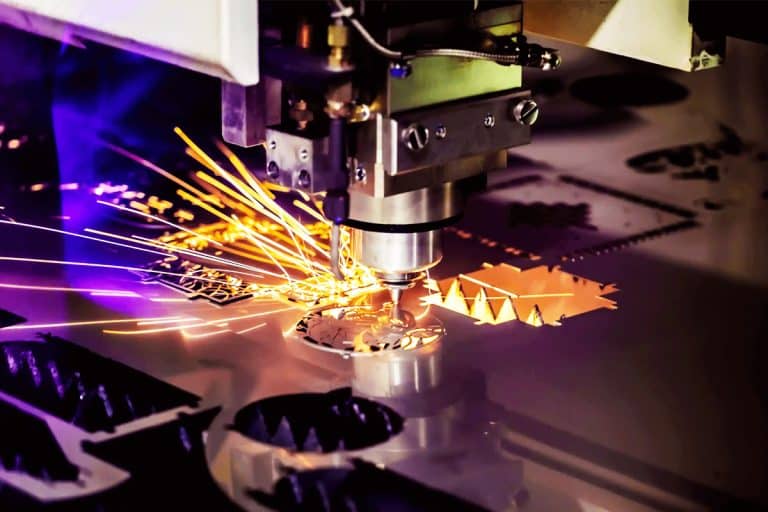
Product Introduction
30kW Laser Cutting Capacity
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Focus Position (mm) | Cutting Height (mm) | Gas | Nozzle (mm) | Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 5 | 24-30 | 0 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 3 | 8 |
| 6 | 25-28 | -0.5 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 3 | 8 | |
| 8 | 18-22 | -1 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 3 | 8 | |
| 10 | 14-17 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 12 | 11-13 | -2 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 14 | 8.0-10.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 4 | 8 | |
| 16 | 7.5-8.5 | -4 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 5 | 8 | |
| 18 | 5.5-6.5 | -6 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 6 | 10 | |
| 20 | 5.0-5.5 | -8 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 6 | 10 | |
| 25 | 3.0-3.5 | -12 | 0.5 | N2/Air | 6 | 10 | |
| 10 | 2.0-2.3 | +8 | 0.8 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 12 | 1.8-2.0 | +9 | 0.8 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 14 | 1.6-1.8 | +10 | 0.8 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.4 | 0.6 | |
| 16 | 1.6-1.8 | +11 | 0.8 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.4 | 0.6 | |
| 20 | 1.5-1.6 | +12 | 0.8 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.6 | 0.6 | |
| 22 | 1.4-1.5 | +13 | 0.5 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.4 | 0.7 | |
| 25 | 1.2-1.4 | +13 | 0.4 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.5 | 1.0 | |
| 30 | 1.2-1.3 | +13.5 | 0.4 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.5 | 1.2 | |
| 40 | 0.6-0.9 | +14 | 0.4 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.6 | 1.4 | |
| 40 | 0.3-0.6 | +13 | 2 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| 50 | 0.3-0.5 | +13 | 2 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| 50 | 0.6-0.8 | +14 | 0.4 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| 60 | 0.2-0.25 | +13.5 | 2 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| 70 | 0.18-0.2 | +13.5 | 2 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.7 | |
| 80 | 0.12-0.15 | +14 | 2 | O2 (Negative Focal) | 1.8 | 1.8 | |
| 12 | 3.2-3.5 | -10 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.6 | 1 | |
| 14 | 3.0-3.2 | -10 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.6 | 1 | |
| 16 | 3.0-3.1 | -12 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.6 | 1 | |
| 20 | 2.8-3.0 | -12 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.6 | 1.2 | |
| 25 | 2.6-2.8 | -14 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.8 | 1.3 | |
| 30 | 2.2-2.6 | -14 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 1.8 | 1.4 | |
| 35 | 1.4-1.6 | -15 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 2P | 1.4 | |
| 40 | 1.0-1.4 | -15 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 2.5 | 1.5 | |
| 45 | 0.8-0.9 | -17 | 1.5 | O2 (Positive Focal) | 2.5 | 1.6 | |
| Stainless Steel | 1 | 50-60 | 0 | 1 | N2 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | 50-60 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 8 | |
| 3 | 40-50 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 4 | 35-40 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 5 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 8 | |
| 6 | 22-25 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 8 | 18-22 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 5 | 8 | |
| 10 | 14-18 | -1.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 8 | |
| 12 | 12-14 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 6 | 8 | |
| 14 | 8.0-10.0 | -4 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 8 | |
| 16 | 7.5-8.5 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 8 | |
| 18 | 6.0-7.0 | -6 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 8 | |
| 20 | 5.0-6.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 12 | |
| 25 | 2.0-3.0 | -12 | 0.3 | N2 | 7 | 12 | |
| 30 | 1.5-2.0 | -16 | 0.3 | N2 | 7 | 12 | |
| 40 | 0.6-0.8 | -16 | 0.3 | N2 | 7 | 16 | |
| 50 | 0.4-0.6 | -18 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 16 | |
| 60 | 0.15-0.2 | +11 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 70 | 0.1-0.13 | +11 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 80 | 0.08-0.1 | +11 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 90 | 0.05-0.06 | +11 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 100 | 0.04-0.05 | +11 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 1 | 50-60 | 0 | 1 | Air | 2 | 8 | |
| 2 | 50-60 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 3 | 40-50 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 4 | 35-40 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 5 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 6 | 22-25 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 3.5 | 8 | |
| 8 | 18-22 | 0 | 0.5 | Air | 3.5 | 10 | |
| 10 | 14-18 | -1.5 | 0.3 | Air | 3.5 | 10 | |
| 12 | 12-14 | -4 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 14 | 10-12 | -6 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 16 | 8.0-9.0 | -7 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 18 | 6.0-7.0 | -8 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 20 | 5.0-6.0 | -9 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 25 | 2.5-3.0 | -13 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 30 | 1.5-2.0 | -17 | 0.3 | Air | 5 | 10 | |
| 40 | 0.8-1.2 | -16 | 0.3 | Air | 7 | 16 | |
| 50 | 0.6-0.8 | -18 | 0.3 | Air | 8 | 16 | |
| 60 | 0.15-0.2 | -20 | 0.3 | Air | 8 | 20 | |
| 70 | 0.1-0.13 | -25 | 0.3 | Air | 8 | 20 | |
| Aluminum | 1 | 55-60 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | 40-45 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 8 | |
| 3 | 30-35 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 10 | |
| 4 | 25-30 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |
| 5 | 18-25 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 6 | 18-20 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 8 | 15-18 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 14 | |
| 10 | 12-15 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 14 | |
| 12 | 10-12 | -6 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 16 | |
| 14 | 8.0-10.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 16 | |
| 16 | 6.0-8.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 16 | |
| 18 | 3.0-4.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 16 | |
| 20 | 2.0-3.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 18 | |
| 25 | 1.5-2.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 18 | |
| 30 | 0.8-1.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7 | 20 | |
| 40 | 0.5-0.8 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 7 | 20 | |
| 50 | 0.4-0.6 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| 60 | 0.2-0.3 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8 | 20 | |
| Brass | 1 | 40-45 | 0 | 1 | N2 | 2 | 12 |
| 2 | 35-40 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 28-30 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 4 | 20-25 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |
| 5 | 18-20 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 6 | 15-18 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 8 | 10-15 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 10 | 8.0-10.0 | -1 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 14 | |
| 12 | 5.0-8.0 | -2 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 14 | |
| 14 | 3.0-5.0 | -3 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 16 | |
| 16 | 1.5-2.0 | -3 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 18 | |
| 18 | 1.2-1.5 | -4 | 0.3 | N2 | 5 | 18 | |
| 20 | 0.8-1 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6 | 18 | |
| Copper | 1 | 25-30 | 0 | 1 | O2 | 2 | 5 |
| 2 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.5 | O2 | 2 | 5 | |
| 3 | 20-25 | 0 | 0.5 | O2 | 2 | 6 | |
| 4 | 18-20 | -1 | 0.5 | O2 | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 5 | 15-18 | -1 | 0.5 | O2 | 2.5 | 8 | |
| 6 | 10-15 | -2 | 0.5 | O2 | 3 | 8 | |
| 8 | 6.0-10.0 | -3 | 0.5 | O2 | 3 | 10 | |
| 10 | 2.0-3.5 | -4 | 0.5 | O2 | 3.5 | 12 | |
| 12 | 2.0-2.5 | -5 | 0.5 | O2 | 3.5 | 12 | |
| 14 | 1.5-2.0 | -6 | 0.5 | O2 | 3.5 | 12 | |
| Titanium | 1 | 10.1-15.9 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 7.9-11.9 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 6.2-9.2 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 4.0-6.0 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 5 | 2.8-4.2 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 6 | 2.2-3.3 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 8 | 1.8-2.6 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 16 | |
| 10 | 1.4-2.1 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 16 | |
| 12 | 1.1-1.7 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 16 | |
| 14 | 0.9-1.3 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 16 | 0.6-0.9 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 18 | 0.4-0.6 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.26-0.4 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 25 | 0.18-0.26 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 4 | 18 | |
| Galvanized Steel | 1 | 48.0-72.0 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 |
| 2 | 24.0-36.0 | -1 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 | |
| 3 | 12.0-18.0 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 8.0-12.0 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 5 | 6.0-9.0 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 6 | 4.8-7.2 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 8 | 3.2-4.8 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 10 | 2.4-3.6 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 12 | 1.6-2.4 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 14 | 1.2-1.8 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 16 | 1.0-1.4 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 18 | 0.8-1.2 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.6-1.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| 25 | 0.4-0.6 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 16 | |
| 30 | 0.3-0.4 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5 | 18 | |
| 40 | 0.15-0.2 | -5 | 0.4 | N2 | 3.5 | 18 | |
| Nickel-Alloy | 1 | 19.2-28.8 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 |
| 2 | 7.7-11.5 | -0.8 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 | |
| 3 | 3.8-5.8 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 4 | 2.6-3.8 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 5 | 1.9-2.9 | -1.8 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 6 | 1.5-2.3 | -1.8 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 8 | 1.0-1.4 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.2 | 16 | |
| 10 | 0.6-1.0 | -2.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2.2 | 16 | |
| 12 | 0.4-0.7 | -3.2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.2 | 16 | |
| 14 | 0.3-0.5 | -3.2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.6 | 18 | |
| 16 | 0.25-0.4 | -3.2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.6 | 18 | |
| 18 | 0.2-0.3 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.6 | 18 | |
| 20 | 0.15-0.2 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.6 | 18 | |
| 25 | 0.1-0.15 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 18 |
Compatible Materials
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Tool Steel
- Bronze
- Zinc
- Inconel
- Hastelloy
- Waspaloy
- Rene alloys
- Stellite
- Galvanized Steel
- Chrome-Plated Steel
- Aluminized Steel
Application of 30kW Laser Cutting Machines








Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Cutting Technologies
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting | Flame Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Precision | Very high (±0.05 mm) | Medium (±0.5 mm) | Very high (±0.1 mm) | Low (±1–2 mm) |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, minimal post-processing | Rougher, may need grinding | Excellent, no heat effect | Rough edges, heavy finishing |
| Material Range | Metals, reflective materials | Conductive metals only | Almost all materials (metal, stone, glass, composites) | Ferrous metals only |
| Max Cutting Thickness | Up to 50 mm (with high-power lasers) | Up to 150 mm | Up to 200+ mm | Up to 300 mm (steel) |
| Cutting Speed (Thin Sheets) | Fastest for <20 mm | Fast for medium-thick plates | Slower | Slow |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Very small | Medium | None | Large |
| Operating Cost | Low (energy-efficient, minimal consumables) | Medium (electrodes, gas) | High (abrasive, water, pump) | Low (fuel and oxygen) |
| Initial Investment | Medium to high | Low to medium | Very high | Low |
| Maintenance | Low (fiber lasers are reliable) | Medium (torch wear, consumables) | High (pump, nozzle, abrasive lines) | Low |
| Automation Compatibility | Excellent (CNC, software-driven) | Good | Good | Limited |
| Surface Finish | Clean, ready-to-use | Requires secondary finishing | Excellent | Poor |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no chemicals, low waste) | Moderate (fumes, slag) | High (abrasive waste disposal) | High (fumes, CO₂) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (especially fiber lasers) | Moderate | Low (energy-intensive pumps) | Moderate |
| Noise Levels | Low | High | High | High |
| Best Use Case | Precision sheet/plate cutting, prototyping, high-quality parts | Structural steel, medium-to-thick plates | Ultra-thick, exotic, or non-metal materials | Heavy plate cutting, construction |
| Industry Adoption | Automotive, aerospace, fabrication, electronics, signage | Shipbuilding, repair, construction | Aerospace, defense, custom fabrication | Heavy industry, construction |
Why Choose Us
Advanced Technology
Our laser cutting machines feature high-speed, precision cutting with the latest laser technology, ensuring smooth edges, minimal waste, and superior efficiency across various materials and thicknesses.
Reliable Quality
Each machine undergoes rigorous quality control and durability testing to ensure long-term stability, low maintenance, and consistent high performance, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Comprehensive Support
We provide full technical support, including installation guidance, operator training, and after-sales service, ensuring smooth machine operation and minimal downtime for your business.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Our machines offer high performance at competitive prices, with customizable options to fit different production needs, helping businesses maximize their investment without compromising on quality.
Related Resources

What Safety Measures Should Be Taken When Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article teaches the basic safety measures for operating a laser cutting machine, including hazard awareness, engineering controls, PPE, fire prevention, ventilation, training, and emergency response drills.

Addressing the Challenges of Fiber Laser Cutting: Common Problems and Solutions
This article explores common challenges in fiber laser cutting, including material-related issues, machine performance, and operator-related problems, offering practical solutions to optimize cutting quality and efficiency.

Precautions for Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article provides a detailed overview of basic precautions for operating laser cutting machines, covering safety risks, proper setup, operating guidelines, maintenance procedures, and emergency preparedness.

Is Laser Cutting Fume Toxic
This article explains what laser cutting fumes are, how they form, their health and environmental risks, and the safety measures needed for proper fume control and extraction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do 30kW Laser Cutting Machines Cost?
- Open Laser Cutting Machine ($120,000-$122,000): The most basic option, open-frame designs are less expensive but provide minimal operator protection. While powerful, these systems expose operators to sparks, fumes, and laser radiation, requiring strict PPE and advanced workshop ventilation. They are best for businesses prioritizing cutting power at a lower cost.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine ($126,000-$128,000): Enclosed models provide far greater safety and dust control. The cutting chamber contains sparks and radiation, while integrated fume extraction keeps the environment clean. This configuration is preferred in professional environments where compliance and operator safety are non-negotiable.
- Open Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($127,000-$129,000): This model adds an exchange worktable to the open design, allowing operators to load one sheet while the machine cuts another. It boosts productivity but still lacks the safety advantages of an enclosed system.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($134,000-$136,000): This type combines enclosure safety with high throughput provided by exchange worktables. It is ideal for high-volume production lines, balancing productivity with strict operator protection.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine ($133,000-$135,000): These machines handle both flat sheets and tubes, offering versatility for industries like construction, energy, and transportation. While the open design is cost-effective, it requires strong safety management.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($140,000-$142,000): This system merges tube-sheet flexibility with exchange worktable efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale workshops that need speed, variety, and high throughput in their production cycles.
- Enclosed Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($147,000-$149,000): At the premium end of the 30kW range, this machine offers maximum power, versatility, safety, and productivity. The enclosure ensures compliance with laser safety standards, the exchange worktable reduces downtime, and the tube-sheet capability makes it suitable for the broadest range of industrial tasks. This is the ultimate choice for 24/7 industrial operations.
What Is The Power Consumption Of 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Generator Power (≈90,000W): The generator is the primary energy consumer, requiring about 90kW of electrical input to produce 30kW of optical laser power. The additional demand covers conversion losses in laser diodes and power electronics. This alone accounts for the majority of the machine’s total energy draw.
- Chiller Power (≈27,620W): At such a high cutting capacity, the laser source and optics generate immense heat. A large-capacity industrial chiller consumes nearly 28kW to maintain stable operating temperatures, ensuring system safety and extending component lifespan. This is the second-largest load and runs continuously during machine operation.
- Driver Power (≈9450W): Servo motors and motion drivers consume close to 9.5kW, enabling rapid acceleration, precise positioning, and smooth operation across the X, Y, and Z axes. Power requirements increase when handling thick plates at high speeds or processing complex cutting paths.
- Draught Fan Power (≈5500W): The draught fan clears smoke, dust, and fine particulates from the cutting zone. While less demanding than the generator or chiller, it is critical for workplace safety, protecting optics, and maintaining cutting consistency. At 5.5kW, it represents a significant share of the machine’s supporting systems.
How Can I Buy 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Identify Application Needs: 30kW laser cutting machines are ideal for cutting very thick plates (40-60 mm and above) and for operations that prioritize maximum speed. Buyers should confirm that their production requires this level of power, as lower-wattage systems may suffice for thinner materials.
- Evaluate Machine Specifications: Compare cutting speed, maximum thickness capacity, positional accuracy, and automation features. Machine rigidity, cooling systems, and CNC controls should be reviewed to ensure long-term stability under heavy loads.
- Choose the Right Supplier: Reputable manufacturers and authorized distributors should be prioritized. Check their track record, certifications, and ability to provide installation, training, and after-sales support.
- Consider Automation and Integration: High-power lasers are often paired with automatic nozzle changers, pallet exchangers, and robotic material handling. Buyers should assess how well the machine integrates into existing production lines and future automation plans.
- Check Assist Gas Systems: 30kW cutting consumes large volumes of oxygen or nitrogen at high pressures. Ensure gas supply infrastructure is adequate, and review operating costs linked to gas usage.
- Assess Service and Support: Reliable technical service, fast spare part delivery, and operator training are essential for minimizing downtime. Strong support networks often outweigh small differences in machine price.
- Calculate Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the purchase price, factor in electricity, assist gas consumption, consumables, and maintenance. Buyers should ensure that production gains justify long-term costs.
- Financing and Procurement: Explore purchase, lease, or financing options. Some suppliers also offer trade-in programs for upgrading from lower-wattage systems.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Using 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- High Purchase Cost: These machines are among the most expensive in the laser cutting market. The investment includes not only the machine but also heavy-duty cooling, extraction, and gas systems.
- Very High Operating Costs: 30kW lasers consume more electricity and larger volumes of assist gas than lower-wattage machines. Nitrogen and oxygen usage, in particular, can drive up operating expenses significantly.
- Excessive Power for Thin Materials: While excellent for thick plates, 30kW laser cutting systems may be inefficient for thin or medium sheets. Lower-power machines (6-12kW) can cut thinner materials just as well, but at lower cost.
- Increased Maintenance Demands: Optics, nozzles, and protective windows wear more quickly at high power levels. This increases the frequency of consumable replacements and the need for stricter maintenance routines.
- Heat-Related Cutting Issues: The extreme energy can cause warping, wider kerf, or taper in thin or heat-sensitive materials. Operators must carefully adjust parameters to avoid poor edge quality.
- Complex Operation Requirements: Despite modern automation, 30kW laser cutting systems demand highly trained operators. Incorrect parameter settings can lead to material waste, downtime, or even equipment damage.
- Infrastructure Limitations: These machines require reinforced floors, stable high-capacity power, and advanced cooling and ventilation systems. Smaller facilities may struggle to accommodate them.
Is It Safe To Use 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Radiation: A 30kW laser is a Class 4 laser, meaning even brief direct or reflected exposure can cause permanent eye or skin injury. Machines are typically fully enclosed, but laser safety glasses are mandatory during servicing or maintenance when the beam path could be exposed.
- Fire and Heat Hazards: At such high power, sparks, molten spatter, and heat buildup can ignite flammable materials or cause localized fires. Fire suppression systems, proper extraction, and flame-resistant surroundings are essential.
- Fume and Particulate Emissions: Cutting metals releases fumes, vapors, and particulates that can be harmful to operators. Robust fume extraction and filtration systems are required to maintain safe air quality.
- High-Pressure Assist Gases: 30kW laser cutting machines rely heavily on oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air at very high pressures. Leaks, improper handling, or equipment failure can cause explosions or health hazards.
- Electrical and Cooling Systems: The electrical load of a 30kW laser cutting machine is significant. Stable, high-capacity power supply and properly maintained chillers are required to prevent electrical hazards, overheating, or machine shutdown.
- Material Handling Risks: These machines are built for cutting large, thick plates, which require automated handling or skilled lifting. Improper handling can lead to operator injury or material damage.
- Operator Training and Procedures: Safe operation depends on trained personnel following strict procedures for startup, shutdown, maintenance, and emergency responses. Safety protocols must be reinforced through regular training.
What Training Is Required To Operate 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Machine Operation and Controls: Operators must learn CNC interfaces, CAD/CAM software integration, and parameter adjustments such as speed, power, gas pressure, and focus settings. Training ensures they can load and run programs efficiently.
- Material-Specific Training: Different materials and thicknesses require precise adjustments. Operators must understand how to optimize parameters for steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and other alloys, especially when cutting thick plates.
- Laser Safety Protocols: As Class 4 lasers, 30kW laser cutting systems pose severe hazards. Operators require laser safety training covering PPE use, enclosure protocols, fire prevention, and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Assist Gas Handling: Operators must be trained in safe handling and monitoring of high-pressure oxygen, nitrogen, and compressed air systems. Knowledge of gas selection for specific applications is essential for both safety and cut quality.
- Cooling and Electrical Systems: Training includes monitoring chiller systems, checking coolant purity, and recognizing warning signals related to power or cooling instability. Understanding safe interaction with high-capacity electrical systems is also important.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Operators should be trained to perform routine maintenance such as cleaning optics, inspecting nozzles, clearing slag beds, and checking gas flow. Basic troubleshooting helps minimize downtime before technicians are called.
- Quality Inspection: Training must include evaluating cut edges, kerf widths, burrs, and dross. Operators should know how to adjust parameters to correct defects and maintain consistent quality.
- Certification and Compliance: Depending on region and workplace, operators may require formal certifications, such as OSHA laser safety training or manufacturer-provided operator certification.
What Is The Lifespan Of 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Source (Fiber Module): The core laser source in 30kW laser cutting machines typically lasts 80,000-100,000 operating hours under normal use. This long lifespan is one of the main advantages of fiber lasers compared to CO2 tubes, which require more frequent replacement or servicing.
- Optics and Cutting Head: Protective windows, lenses, and nozzles wear quickly at such high power due to spatter and heat exposure. These consumables usually last hundreds to thousands of cutting hours and require frequent replacement to maintain cut quality.
- Assist Gas Systems: With proper filtration and handling, regulators, valves, and gas lines can last many years. Poor gas quality or contamination shortens their lifespan and negatively affects cut quality.
- Motion and Mechanical Systems: Linear rails, guides, and servo motors typically last 5-10 years with routine lubrication and cleaning. Heavy-duty 24/7 operation may reduce this range, while lighter workloads can extend it.
- Cooling Systems: Chillers and coolant circuits generally last 8-10 years, provided water purity and filter maintenance are maintained. Poor upkeep can lead to premature failure and reduced laser lifespan.
- Electronics and Control Systems: Controllers, drives, and software often last 10+ years, though upgrades may be required sooner for compatibility with newer production systems.
- Overall Machine Lifespan: With consistent preventive maintenance and professional servicing, 30kW laser cutting machines can reliably operate for 10-15 years in an industrial environment. Continuous heavy use will shorten its lifespan, while careful maintenance and moderate workloads can extend it further.
How Should I Maintain 30kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Optics and Cutting Head: Protective lenses, windows, and nozzles must be inspected and cleaned frequently. At such high power, even minor contamination can reduce beam quality, cause thermal damage, or shorten component life. Worn or damaged parts should be replaced immediately.
- Cooling System: Stable water cooling is essential. Operators must regularly monitor coolant purity, levels, and temperature. Filters and coolant should be replaced on schedule to prevent scaling, corrosion, or overheating.
- Assist Gas System: Gas lines, regulators, and valves should be inspected for leaks and purity. High-pressure nitrogen, oxygen, and compressed air systems must be maintained carefully to ensure stable cutting and reduce gas waste.
- Motion and Mechanical Systems: Linear guides, servo motors, and bearings must be cleaned and lubricated routinely. Heavy-duty cutting creates dust and slag that can interfere with smooth motion and reduce cutting accuracy.
- Dust and Slag Removal: The cutting bed should be cleared of slag buildup, while extraction and filtration systems must be inspected regularly. Failure to maintain them can increase fire risks and reduce cut quality.
- Electrical and Control Systems: Power connections, circuit boards, and sensors should be kept clean and dry. Stable power supply and periodic software updates prevent failures and improve performance reliability.
- Preventive Maintenance Schedule: Manufacturers recommend structured daily, weekly, and monthly checks—including nozzle cleaning, optics inspection, coolant monitoring, gas system checks, and calibration. Annual professional servicing ensures optimal performance.
- Operator Involvement: Operators should be trained not only in machine use but also in basic maintenance tasks and recognizing early warning signs, such as unusual cut quality, noise, or system alerts.