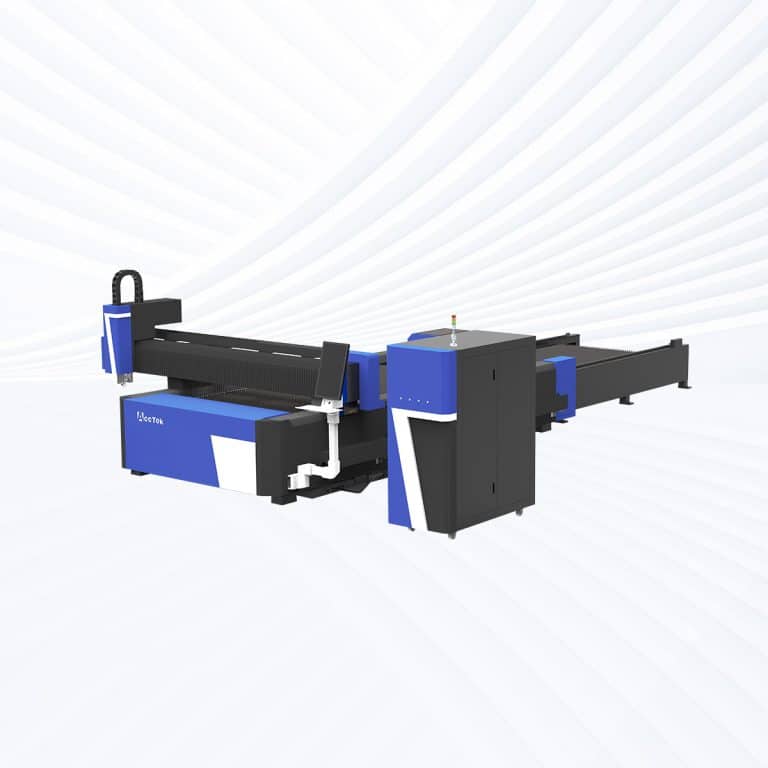
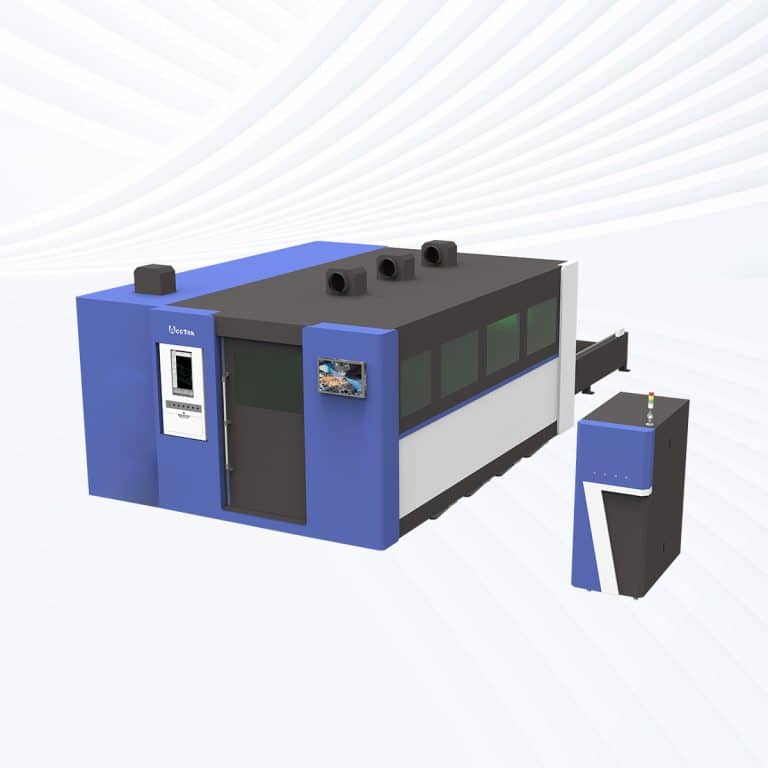
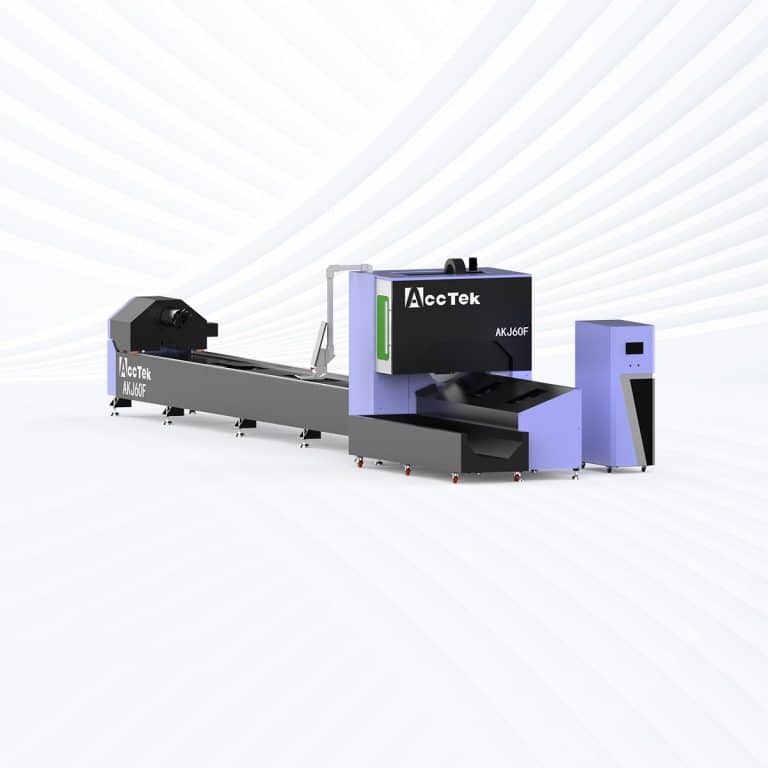
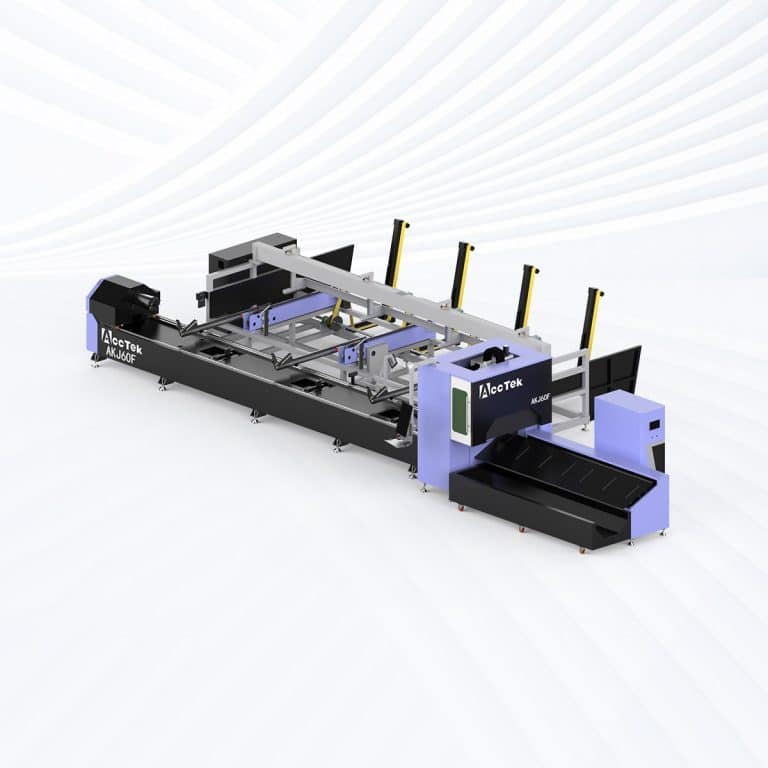
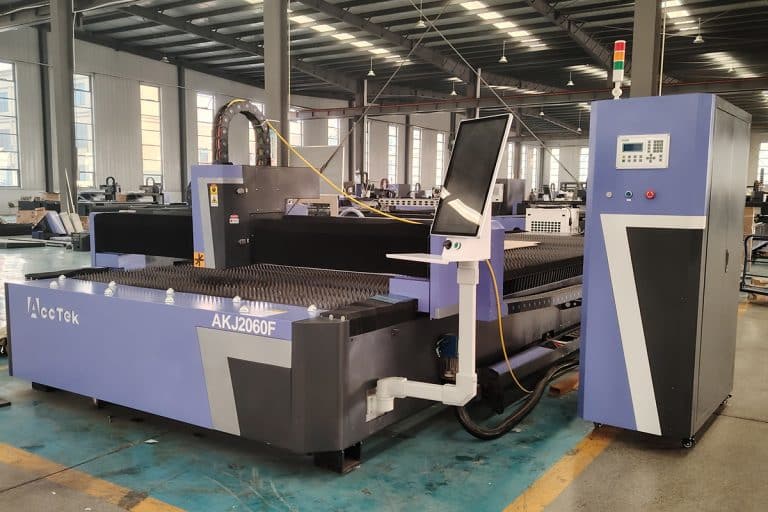
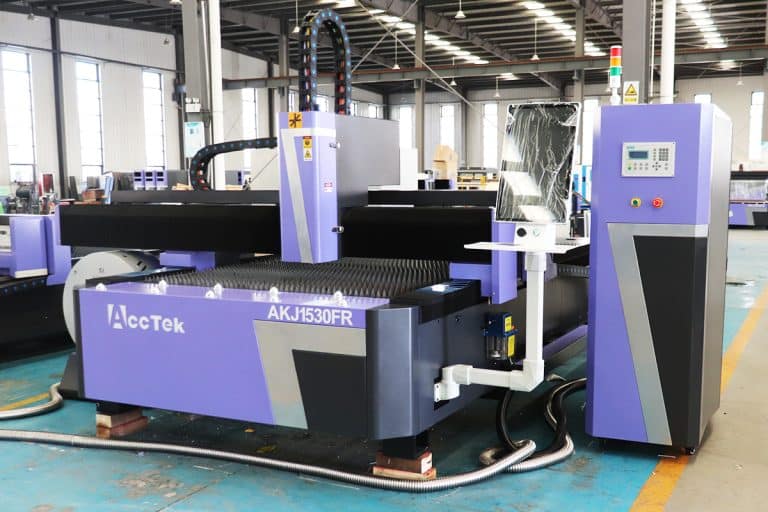
Product Introduction
1.5kW Laser Cutting Capacity
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Focus Position (mm) | Cutting Height (mm) | Gas | Nozzle (mm) | Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 1 | 20 | 0 | 1 | N2/Air | 1.5 | 10 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 2 | |
| 3 | 3.6 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 4 | 2.5 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 5 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 6 | 1.4 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.5 | 0.6 | |
| 8 | 1.2 | 3 | 0.8 | O2 | 1.5 | 0.6 | |
| 10 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 2 | 0.6 | |
| 12 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | |
| 14 | 0.65 | 2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 3 | 0.6 | |
| 16 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 0.8 | O2 | 3 | 0.6 | |
| Stainless Steel | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5 | 10 |
| 2 | 7 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 4.5 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |
| 5 | 1.5 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 14 | |
| 6 | 0.8 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| Aluminum | 1 | 18 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 6 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 3 | 2.5 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| 4 | 0.8 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 3 | 16 | |
| Brass | 1 | 15 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 5 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 3 | 1.8 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5 | 14 | |
| Titanium | 1 | 1.4-2.1 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5 | 12 |
| 2 | 1.0-1.5 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 0.8-1.2 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| Galvanized Steel | 1 | 6.5-10.0 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 |
| 2 | 3.2-4.9 | -1 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.6 | 12 | |
| 3 | 1.6-2.4 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 4 | 1.1-1.6 | -1.5 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 5 | 0.8-1.2 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| 6 | 0.6-1.0 | -2 | 0.6 | N2 | 2 | 14 | |
| Nickel-Alloy | 1 | 3.0-4.5 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 |
| 2 | 1.2-1.8 | -0.8 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.4 | 14 | |
| 3 | 0.6-0.9 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 | |
| 4 | 0.4-0.6 | -1.2 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.8 | 16 |
Compatible Materials
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Tool Steel
- Bronze
- Zinc
- Inconel
- Hastelloy
- Waspaloy
- Rene alloys
- Stellite
- Galvanized Steel
- Chrome-Plated Steel
- Aluminized Steel
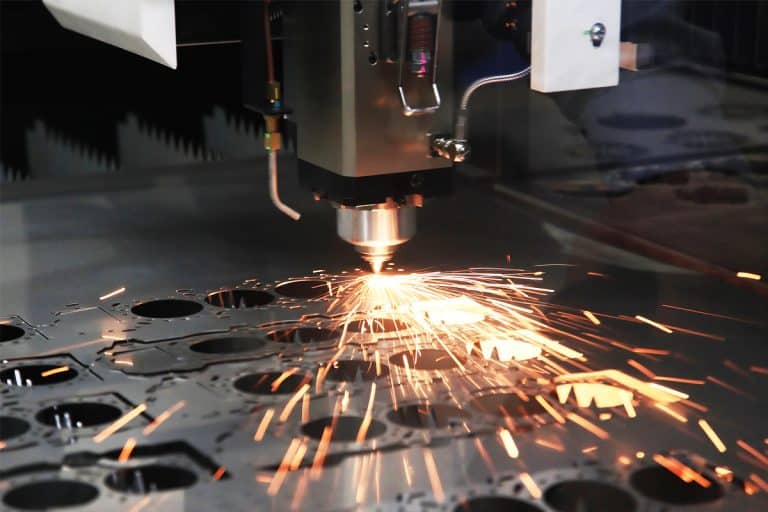
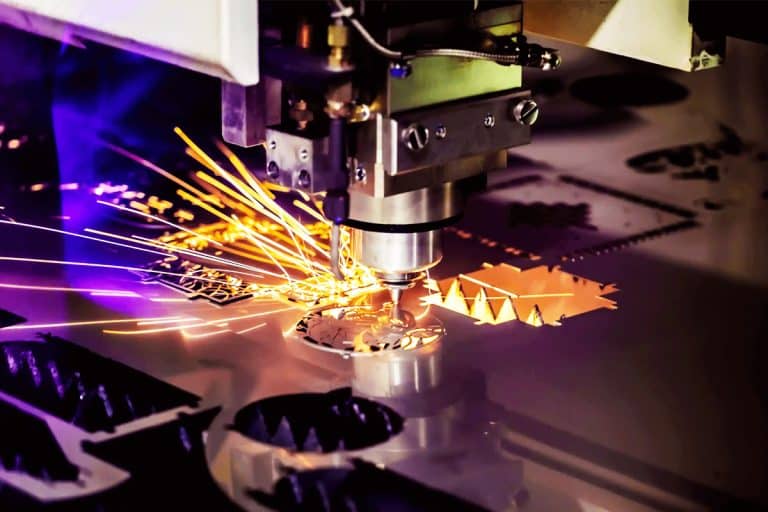
Application of 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines
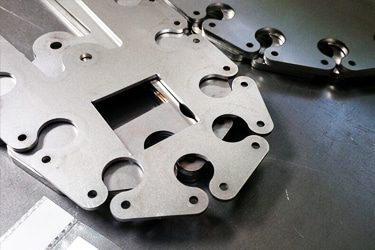






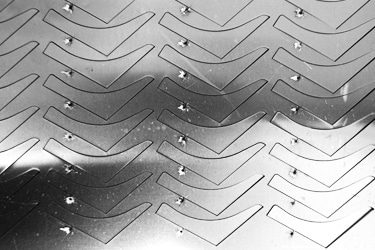
Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Cutting Technologies
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting | Flame Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Precision | Very high (±0.05 mm) | Medium (±0.5 mm) | Very high (±0.1 mm) | Low (±1–2 mm) |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, minimal post-processing | Rougher, may need grinding | Excellent, no heat effect | Rough edges, heavy finishing |
| Material Range | Metals, reflective materials | Conductive metals only | Almost all materials (metal, stone, glass, composites) | Ferrous metals only |
| Max Cutting Thickness | Up to 50 mm (with high-power lasers) | Up to 150 mm | Up to 200+ mm | Up to 300 mm (steel) |
| Cutting Speed (Thin Sheets) | Fastest for <20 mm | Fast for medium-thick plates | Slower | Slow |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Very small | Medium | None | Large |
| Operating Cost | Low (energy-efficient, minimal consumables) | Medium (electrodes, gas) | High (abrasive, water, pump) | Low (fuel and oxygen) |
| Initial Investment | Medium to high | Low to medium | Very high | Low |
| Maintenance | Low (fiber lasers are reliable) | Medium (torch wear, consumables) | High (pump, nozzle, abrasive lines) | Low |
| Automation Compatibility | Excellent (CNC, software-driven) | Good | Good | Limited |
| Surface Finish | Clean, ready-to-use | Requires secondary finishing | Excellent | Poor |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no chemicals, low waste) | Moderate (fumes, slag) | High (abrasive waste disposal) | High (fumes, CO₂) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (especially fiber lasers) | Moderate | Low (energy-intensive pumps) | Moderate |
| Noise Levels | Low | High | High | High |
| Best Use Case | Precision sheet/plate cutting, prototyping, high-quality parts | Structural steel, medium-to-thick plates | Ultra-thick, exotic, or non-metal materials | Heavy plate cutting, construction |
| Industry Adoption | Automotive, aerospace, fabrication, electronics, signage | Shipbuilding, repair, construction | Aerospace, defense, custom fabrication | Heavy industry, construction |
Why Choose Us
Advanced Technology
Our laser cutting machines feature high-speed, precision cutting with the latest laser technology, ensuring smooth edges, minimal waste, and superior efficiency across various materials and thicknesses.
Reliable Quality
Each machine undergoes rigorous quality control and durability testing to ensure long-term stability, low maintenance, and consistent high performance, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Comprehensive Support
We provide full technical support, including installation guidance, operator training, and after-sales service, ensuring smooth machine operation and minimal downtime for your business.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Our machines offer high performance at competitive prices, with customizable options to fit different production needs, helping businesses maximize their investment without compromising on quality.
Related Resources

What Safety Measures Should Be Taken When Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article teaches the basic safety measures for operating a laser cutting machine, including hazard awareness, engineering controls, PPE, fire prevention, ventilation, training, and emergency response drills.

Addressing the Challenges of Fiber Laser Cutting: Common Problems and Solutions
This article explores common challenges in fiber laser cutting, including material-related issues, machine performance, and operator-related problems, offering practical solutions to optimize cutting quality and efficiency.

Precautions for Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article provides a detailed overview of basic precautions for operating laser cutting machines, covering safety risks, proper setup, operating guidelines, maintenance procedures, and emergency preparedness.

Is Laser Cutting Fume Toxic
This article explains what laser cutting fumes are, how they form, their health and environmental risks, and the safety measures needed for proper fume control and extraction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines Cost?
- Open Laser Cutting Machine ($13,500-$30,000): These are the most affordable 1.5kW laser cutting machines, designed with an open-frame structure. They are suitable for workshops handling thin to mid-thickness sheet metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum. The trade-off is lower operator protection and more exposure to fumes and sparks, making proper ventilation and safety equipment essential.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine ($22,000-$33,000): Fully enclosed systems offer better safety and dust control, making them a more professional choice for industrial environments. The enclosure shields operators from laser radiation and reduces fume exposure. The higher cost reflects additional safety systems, automated doors, and enhanced air extraction units.
- Open Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($23,000-$33,000): Adding an exchange table increases efficiency by allowing one sheet to be loaded while another is being cut. This feature is valuable for workshops that need to maintain high throughput. These machines remain open-structured, so they share the same safety limitations as basic open models.
- Enclosed Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($27,000-$37,000): This configuration combines enclosure safety with exchange table efficiency. It is ideal for shops needing both high production speed and a controlled environment. The additional automation increases the cost slightly compared to non-exchange enclosed models, but the productivity gain offsets the investment.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine ($25,000-$35,000): Designed to cut both flat sheets and tubes, these systems provide greater versatility. They are widely used in industries like construction, furniture, and automotive, where both structural and flat components are needed. The dual-purpose capability adds to the price compared to sheet-only systems.
- Open Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($37,000-$47,500): This upgrade merges multitasking (sheet + tube) with the productivity of an exchange worktable. It’s a strong choice for workshops with mixed production needs and medium-to-high output requirements. The added cost reflects both the tube cutting hardware and the automated sheet handling system.
- Enclosed Tube-Sheet Laser Cutting Machine with Exchange Worktable ($41,500-$52,000): At the premium end of 1.5kW laser cutting systems, these machines combine maximum safety, productivity, and versatility. They are designed for industrial settings, handling a wide range of jobs at higher volumes. The enclosure protects operators, while exchange tables and tube-sheet compatibility deliver peak efficiency.
What Is The Power Consumption Of 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Generator Power (≈4500W): The laser generator is the core of the system, transforming electrical input into a focused cutting beam. To output 1.5kW of laser energy, it typically consumes around 4.5kW due to conversion losses in the diodes and power supply. Efficiency is higher than that of older CO2 lasers, but the input-to-output ratio still makes this the single largest power draw.
- Chiller Power (≈2660W): Heat is generated not only by the laser source but also by the optics and electronics. The chiller circulates coolant to stabilize these temperatures, preventing performance fluctuations and component damage. At about 2.6kW, the chiller represents a significant background load and runs continuously during machine operation.
- Driver Power (≈2650W): Servo motors and drive systems move the cutting head with speed and precision across multiple axes. High acceleration and precise positioning consume roughly 2.65kW. Motion system efficiency directly impacts both cut quality and operating costs, making proper lubrication and calibration essential for minimizing wasted energy.
- Draught Fan Power (≈1500W): The draught fan removes fumes, dust, and metal particles from the cutting chamber. This subsystem ensures a safe environment for operators while also keeping optics cleaner. At around 1.5kW, it is less energy-intensive than the generator or chiller but still necessary for safe, reliable cutting.
How Can I Purchase 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Direct from Manufacturers: Many buyers choose to purchase directly from machine manufacturers, particularly those based in China, where laser technology is highly competitive. Direct purchase often provides better pricing and customization options, but communication, shipping logistics, and import duties must be managed carefully.
- Authorized Distributors and Dealers: Local distributors or resellers offer easier communication, faster delivery, and hands-on demonstrations. They often provide installation services, training, and technical support. While prices are generally higher than factory-direct purchases, the added convenience and after-sales assistance make this a safer option for many businesses.
- Online Industrial Marketplaces: Platforms such as Alibaba, Made-in-China, and specialized machinery trading websites allow buyers to compare multiple suppliers. These sites offer transparent pricing ranges and buyer protections. However, thorough due diligence is critical to avoid unreliable vendors or hidden costs.
- Machine Configuration Choices: When purchasing, you’ll need to decide between open or enclosed designs, whether you need an exchange worktable, and if tube-sheet cutting is required. Each upgrade affects the final price and operational efficiency. Buyers should evaluate their production needs to avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
- Installation and Training: Most suppliers include remote or on-site installation services, along with operator training. This ensures your team understands machine setup, operation, and basic troubleshooting. It’s wise to confirm training availability before purchasing, especially for workshops new to laser technology.
- After-Sales Service and Warranty: A good warranty (typically 1-3 years for the laser source and machine parts) and responsive technical support are critical. Spare parts availability, online troubleshooting, and service agreements should be discussed before finalizing the purchase.
- Payment and Shipping: Machines can be purchased via wire transfer, letter of credit, or platform-secured payment systems. Buyers should account for shipping, customs clearance, and local taxes. Lead times may range from a few weeks to several months, depending on machine customization and supplier location.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Using 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Limited Cutting Capacity on Thick Metals: Although stronger than 1kW laser cutting systems, a 1.5kW laser cutting machine still struggles with very thick plates. For example, stainless steel over 8-10 mm or carbon steel above 14-16 mm may require slower speeds, multiple passes, or higher assist gas pressures. For heavy-duty industrial cutting, higher-power lasers (2-6kW and above) are more practical.
- High Power Consumption: 1.5kW laser cutting systems consume around 11-12 kW in total when accounting for the generator, chiller, motion system, and draught fan. This increases electricity costs, especially in high-volume operations. Businesses in regions with expensive energy must carefully evaluate long-term operating expenses.
- Initial Investment Costs: Compared to mechanical cutting or plasma systems, lasers require a higher upfront investment. Even entry-level open-frame models cost tens of thousands of dollars, while enclosed, tube-sheet machines can exceed $50,000. This makes them less accessible for small workshops with limited budgets.
- Material Limitations: Fiber lasers excel at cutting metals but are less versatile with non-metallic materials. Unlike CO2 lasers, they are not suitable for cutting wood, acrylic, leather, or many plastics. This makes them less flexible for businesses that work with a mix of organic and non-metallic materials.
- Maintenance Demands: Although fiber lasers are more reliable than CO2 laser cutting systems, they still require regular care. Optics must be kept clean, gas lines must be maintained, and the chiller must be serviced. Neglecting preventive maintenance can quickly lead to lower cutting quality, downtime, or costly repairs.
- Fume and Dust Management: Cutting metal generates hazardous fumes and fine particles that must be extracted effectively. Inadequate ventilation not only harms operator health but also contaminates machine optics and electronics, shortening their lifespan. This adds to infrastructure requirements.
- Learning Curve for Optimization: Basic operation is straightforward thanks to automation, but optimizing parameters (speed, focus, gas pressure) for new materials or complex cuts requires skill and experience. Without proper training, operators may face reduced cut quality, higher gas consumption, or wasted material.
What Training Is Required To Operate 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Basic Machine Operation: Operators must learn how to start up, shut down, and safely handle the system. This includes using the touchscreen interface, importing design files (such as DXF or CAD formats), setting parameters, and executing jobs. Training usually begins with supervised practice on simple cuts before moving to more advanced applications.
- Software and Programming Skills: Most 1.5kW laser cutting machines use CAD/CAM software for drawing, nesting, and toolpath generation. Operators should be trained in creating and editing designs, optimizing layouts for material efficiency, and adjusting cutting parameters within the software. This ensures smooth workflow from design to execution.
- Material Knowledge and Cutting Parameters: Training includes learning how different metals (stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, brass) respond to laser cutting. Operators must understand the impact of speed, focus, gas type, and pressure on cut quality. Mastering parameter adjustments is key to reducing defects like burrs, dross, or incomplete cuts.
- Safety Procedures: Since fiber lasers are Class 4 laser systems, safety training is critical. Operators are instructed on the use of laser safety glasses (for open systems), emergency stop protocols, gas handling, and fume extraction systems. Fire prevention measures, such as keeping extinguishers nearby and avoiding flammable materials, are also part of training.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Operators are taught daily maintenance routines such as cleaning optics, checking gas lines, inspecting nozzles, and monitoring coolant levels. They also learn basic troubleshooting skills to address common issues like poor cut quality, nozzle collisions, or software errors before escalating to technical service.
- Advanced Training (for Skilled Technicians): In larger operations, advanced training may be provided for technicians responsible for calibration, software customization, and optimizing production workflows. This goes beyond basic operation and focuses on improving efficiency, reducing consumables use, and maximizing machine uptime.
What Is The Service Life Of 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Source (100,000+ hours): One of the greatest advantages of fiber lasers over CO2 systems is the long lifespan of the laser generator. A high-quality 1.5kW fiber source typically lasts 80,000-100,000 working hours, equivalent to 8-10 years in continuous operation. Proper cooling and dust control are key to reaching maximum life expectancy.
- Optical Components (1-2 years for consumables): Protective lenses, nozzles, and focusing optics are exposed to spatter, fumes, and dust. These are considered consumables and may need replacement every few months to two years, depending on workload. Regular cleaning and inspection extend their usable life and ensure consistent cutting quality.
- Chiller System (5-8 years): The industrial chiller is designed to run continuously but requires periodic servicing. With proper maintenance—such as water quality control, filter cleaning, and pump checks—chillers typically last between 5-8 years before requiring major replacement or overhaul.
- Motion System (8-10 years): Rails, servo motors, and drive systems usually last as long as the machine’s overall lifespan when maintained properly. Regular lubrication, calibration, and protection against dust accumulation prevent premature wear. Neglect, however, can shorten their lifespan significantly.
- Electrical and Control Systems (7-10 years): The CNC controller, wiring, and electronics are generally reliable but vulnerable to voltage surges, humidity, or dust. With a stable power supply and environmental control, these systems can last as long as the laser source itself.
- Machine Frame and Structure (10+ years): The steel frame and body are extremely durable, often outlasting other components. As long as the structure is not exposed to excessive vibration, corrosion, or poor handling, it can support upgrades and continue working for more than a decade.
What PPE Is Required To Operate 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Laser Safety Glasses: For open-frame machines, certified laser safety glasses are mandatory. These glasses must match the wavelength of the fiber laser (typically 1064 nm) and provide adequate optical density to block harmful radiation. Even brief exposure to a Class 4 fiber laser can cause permanent eye injury, making protective eyewear the most critical PPE. Enclosed machines reduce this need, but should still have glasses available for maintenance or servicing.
- Respiratory Protection: Cutting metals produces fine particulates and potentially toxic fumes, such as zinc oxide from galvanized steel. While extraction systems handle most of this, operators may still require masks or respirators in poorly ventilated environments or during maintenance when filters are replaced. A P100 or N95-rated respirator is generally sufficient for particulate protection.
- Protective Clothing: Operators should wear flame-resistant clothing made of natural fibers like cotton or specialized workwear designed for welding and laser cutting. Synthetic fabrics (like polyester) can melt when exposed to sparks or hot spatter. Long sleeves and full-length pants are recommended to protect skin from burns and radiant heat.
- Gloves: Heat-resistant gloves protect operators when handling freshly cut parts, which can retain high surface temperatures. They also help during maintenance tasks like nozzle replacement or slag removal, where sharp edges are present. Gloves should not be bulky, as dexterity is needed for precision tasks.
- Hearing Protection: Fiber laser cutting machines themselves are not excessively loud, but auxiliary equipment such as exhaust fans, compressors, or high-pressure gas systems can create elevated noise levels. Earplugs or earmuffs may be required in workshops where continuous exposure exceeds safe limits.
- Safety Footwear: Steel-toe or reinforced work boots protect against heavy sheet metals falling during loading and unloading. Slip-resistant soles are recommended for safety in workshops where coolant or water from the chiller may spill on the floor.
What Assist Gases Can Be Used With 1.5kW Laser Cutting Machines?
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is widely used for cutting carbon steel. It reacts with the hot metal in an exothermic reaction, adding extra heat and allowing thicker plates to be cut at lower laser power. However, oxygen cuts leave an oxidized edge, which may require secondary processing like grinding or painting. For applications where edge appearance is less critical, oxygen is both economical and effective.
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is an inert gas that does not react with the metal. It is commonly used for stainless steel, aluminum, and other materials where a clean, oxide-free edge is required. Nitrogen cuts faster than oxygen on thin sheets but requires higher pressures and flow rates, increasing operating costs. It is the preferred gas for industries like food processing and medical equipment, where surface quality is crucial.
- Air: Compressed air can be used as a low-cost alternative to nitrogen for thin metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum. Air is composed of about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, so cuts are faster than with nitrogen alone but may have slight oxidation. This option reduces gas costs dramatically, making it ideal for workshops focused on cost efficiency over perfect edge quality.
- Argon (Ar): Argon is inert and heavier than air, providing strong protection against oxidation. It is sometimes used for highly reactive metals or special alloys, such as titanium. However, its high cost limits its use in everyday cutting. Argon is mostly chosen for niche, high-value applications where preventing even slight oxidation is critical.
- Mixed Gases: In some cases, suppliers offer custom gas blends (e.g., nitrogen-oxygen mixtures) to balance cutting speed, edge quality, and cost. These blends are less common for 1.5kW systems but may be used in specialized industrial settings.