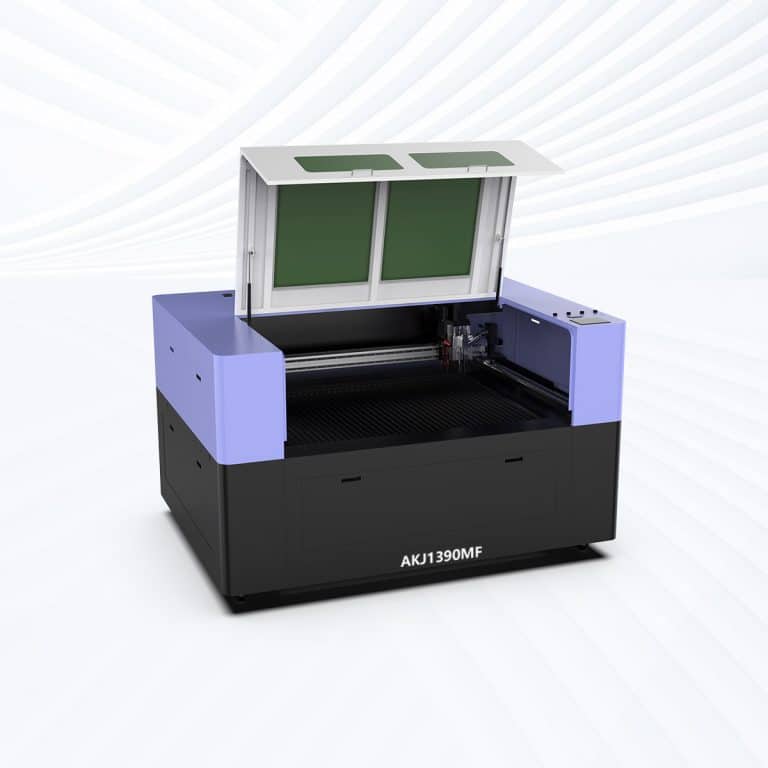
Product Introduction
Types of 2kW Laser Welding Machines
2kW Laser Welding Capacity
| Material Type | Welding Form | Thickness (mm) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Defocus Amount | Protective Gas | Blowing Method | Flow (L/min) | Welding Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (Q235B) | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 90~100 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 80~90 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 1.5 | 60~70 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 2 | 40~50 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 3 | 30~40 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 4 | 20~30 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Stainless Steel (SUS304) | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 100~110 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 90~100 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 1.5 | 70~80 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 2 | 50~60 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 3 | 40~50 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 4 | 30~40 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Brass | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 80~90 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 60~70 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 1.5 | 40~50 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 2 | 30~40 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 3 | 20~30 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| 1-3 Series Aluminum Alloys | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 90~100 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 80~90 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 1.5 | 70~80 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 2 | 40~50 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 3 | 20~30 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| 4-7 Series Aluminum Alloys | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 70~80 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 60~70 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 1.5 | 40~50 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Butt Welding | 2 | 30~40 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely | |
| Copper | Butt Welding | 0.5 | 60~70 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
| Butt Welding | 1 | 20~30 | -1~1 | Ar | Coaxial/Paraaxial | 5~10 | Welded Completely |
Compatible Materials
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Galvanized Steel
- High-Strength Steel
- Tool Steel
- Spring Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Cast Iron
- Aluminum
- Aluminum Alloys
- Copper
- Brass
- Bronze
- Titanium
- Titanium Alloys
- Nickel
- Nickel Alloys
- Inconel
- Monel
- Hastelloy
- Cobalt
- Cobalt Alloys
- Magnesium
- Magnesium Alloys
- Molybdenum
- Tantalum
- Zirconium
- Tungsten
- Gold
- Gold
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Electrical Steels
- Duplex Stainless Steel
- Super Duplex Stainless Steel
- Nitinol
- Low-Alloy Steels
- Clad Metals
- Bimetallic Joints
Application of 2kW Laser Welding Machines







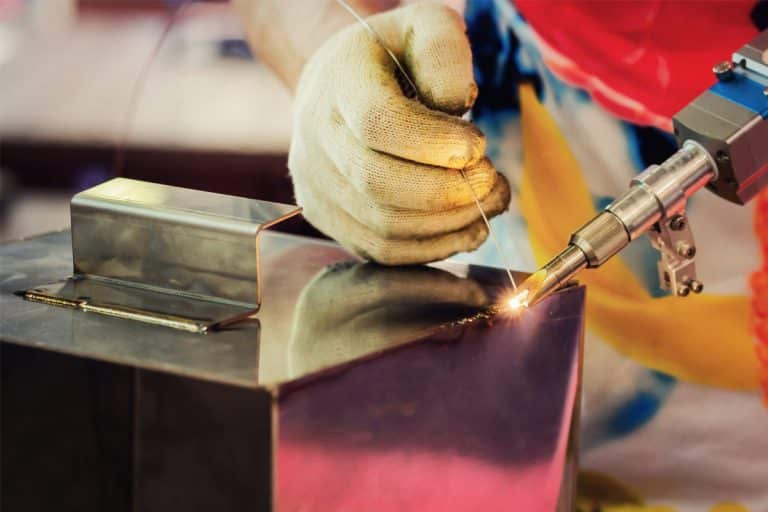
Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other WeldingTechnologies
| Features | Laser Welding | TIG Welding (GTAW) | MIG Welding (GMAW) | Plasma Arc Welding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weld Quality | Superior precision, smooth, minimal defects | Excellent, very clean | Good, but prone to spatter | High, may need post-finishing |
| Heat Input | Very low, minimal distortion | Moderate, localized | Higher, risk of warping | Higher than laser, less than MIG |
| Welding Speed | Very fast | Slow | Faster than TIG | Moderate |
| Penetration Depth | High, effective on thin and medium materials | Shallow to moderate | Moderate, strong on thicker parts | Deep penetration possible |
| Automation Compatibility | Excellent, robotics integration | Limited automation | Compatible, less precise | Good automation potential |
| Material Versatility | Wide: stainless, aluminum, copper, titanium, alloys | Wide, but struggles on thin sheets | Wide, best on medium/thick metals | Wide, effective on conductive metals |
| Setup Time | Short with presets, quick changeover | Long, requires skill | Moderate | Longer than MIG |
| Skill Requirement | Low–moderate, user-friendly | High, operator expertise needed | Moderate | High, requires trained operators |
| Maintenance | Low, few consumables | High (electrode wear, gas usage) | Medium (wire + shielding gas) | Higher (gas + electrodes) |
| Consumables Cost | Very low | High (tungsten electrodes, gas) | Medium (wire, gas) | Medium (gas, electrodes) |
| Operational Cost | Low, energy-efficient, less rework | Medium | Medium | High, more energy-intensive |
| Welding Thickness Range | Best for thin to medium sections | Thin to medium | Medium to thick | Medium to very thick |
| Spatter & Cleanup | None or negligible | Minimal | Significant spatter, cleanup needed | Some spatter |
| Safety Considerations | Enclosed systems reduce exposure | High UV/IR exposure | High arc light + fumes | High UV, PPE required |
| Suitability for Mass Production | Excellent, scalable for automation | Poor | Good, common in production | Moderate |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver accurate, clean welds with minimal heat input, reducing distortion and ensuring strong, consistent joints across a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
Easy Operation
Designed with intuitive controls and user-friendly interfaces, our systems allow both experienced operators and new users to achieve professional results with minimal training.
Durable & Reliable
Built with high-quality components and strict quality standards, our welding machines provide stable performance, long service life, and low maintenance requirements.
Custom Options
We offer a variety of models and customizable features to match specific production needs, helping businesses improve workflow and adapt to changing manufacturing demands.
Related Resources

Laser Welding VS Arc Welding
This article explores the key differences between laser welding and arc welding, comparing their processes, advantages, limitations, and ideal applications across various industries.

What Welding Defects Can Occur In Laser Welding
This article helps to understand common laser welding defects, their causes, and effective prevention strategies to ensure consistent welding quality across different materials and applications.

Laser Welding Brass Guide
This article is a comprehensive guide to brass laser welding, covering welding techniques, parameters, challenges, equipment selection, and best practices for achieving precise, high-quality welds.

Autogenous VS Filler Laser Welding
This article explains the differences between autogenous and filler laser welding, detailing their principles, processes, parameters, and applications in industrial manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do 2kW Laser Welding Machines Cost?
- Entry-Level Models: At the lower end of the range, around $5,700, basic models are designed for workshops or small businesses. These machines typically include standard functions, manual settings, and core safety features. They are suitable for thin to medium-thick materials, such as stainless steel and carbon steel.
- Mid-to-High-End Options: Machines priced closer to $6,600 usually offer advanced automation, such as touchscreen control panels, integrated wire feeders, and intelligent parameter adjustment systems. These higher-end models provide better precision, faster welding speeds, and enhanced productivity, making them well-suited for continuous production lines in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
- Additional Costs: Besides the machine itself, buyers should consider extra expenses such as assist gases (argon, nitrogen, or helium), laser safety equipment, fume extraction systems, and consumables like protective lenses and nozzles. Some suppliers may also charge for operator training, installation, or extended warranty services.
What Is The Power Consumption Of 2kW Laser Welding Machines?
- Laser Generator Power: The laser generator is the core of the machine, producing the focused high-energy beam needed for welding. 2kW laser welding machines typically have a laser generator power of around 6000W (6kW). This level of power supports deeper penetration and higher welding speeds, making it suitable for thicker materials and heavy-duty production tasks.
- Chiller Power: The cooling system prevents overheating by circulating coolant through the machine. The chiller power is approximately 2540W (2.54kW), ensuring stable operation and protecting sensitive internal components from thermal damage.
- Total Power Requirement: When combining both the laser generator and the chiller, the total electrical demand is roughly 8540W (8.54kW). A stable electrical supply is essential, and facilities should consider installing voltage stabilizers or circuit protection systems to avoid power fluctuations that could harm the machine.
Are 2kW Laser Welding Machines Easy To Operate?
- Simplified Controls: Most modern 2kW laser welding machines come equipped with touchscreen interfaces and preset welding modes. Operators can easily adjust settings such as power, speed, and focus without needing deep technical expertise. This helps reduce the learning curve, especially for small workshops or production facilities transitioning to laser welding.
- Automation and Precision: Features like automatic wire feeding and real-time monitoring systems help minimize manual errors while improving weld accuracy. This makes the machines suitable for precision industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing.
- Training Requirements: While operation is straightforward, basic training is still essential. Operators must learn about laser safety protocols, material handling techniques, and machine maintenance to prevent accidents and achieve optimal weld quality.
Do 2kW Laser Welding Machines Require Welding Wire?
- Wire-Free Welding (Autogenous Welding): For thin materials or joints with precise fit-up, 2kW laser welding machines can perform autogenous welding, which means no filler wire is used. The laser melts the base metals directly to form a strong joint. This method is common in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and precision manufacturing, where minimal heat input and a clean finish are essential.
- Welding with Wire: When working with thicker materials, larger gaps, or different metal types, welding wire becomes necessary. The filler wire helps bridge gaps between workpieces, improves joint strength, and reduces the risk of defects like cracks or porosity. It is especially useful in applications like automotive manufacturing, machinery production, and structural components.
- Wire Feeding Systems: Many 2kW laser welding machines come with optional or integrated automatic wire feeders. These systems ensure consistent wire delivery, improving productivity and the overall quality of the weld seam.
How Should I Choose 2kW Laser Welding Machines?
- Assess Welding Requirements: Start by considering the type of materials, their thickness, and the intended application. 2kW laser welding machines are ideal for medium-thickness metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum. For heavier-duty tasks or high-volume production, a higher-powered model may be required.
- Evaluate Machine Features: Look for features that enhance precision and ease of use, such as touchscreen controls, automatic wire feeding, and real-time monitoring systems. A reliable cooling system is also important to maintain stable performance and prevent overheating during continuous operation.
- Safety and Quality Standards: Ensure the machine meets international safety certifications, including built-in protection systems like emergency stop buttons and laser shielding. Machines with protective enclosures and efficient fume extraction systems are safer and comply with workplace safety regulations.
- Supplier Support and Warranty: Select a supplier who provides comprehensive after-sales services, including installation, operator training, and technical support. Access to spare parts and maintenance services will minimize downtime and protect your investment.
- Consider Total Cost: The price of 2kW laser welding machines typically ranges from $5,700 to $6,600. While cost is important, focus on overall value by weighing machine durability, included accessories, and warranty coverage.
What Problems May Occur When Using 2kW Laser Welding Machines?
- Welding Quality Problems: Poor parameter settings can lead to defects such as incomplete penetration, excessive burn-through, or weak joints. For example, if the laser power or speed is not correctly matched to the material thickness, the weld may be too shallow or too deep. Misaligned beams or dirty optical lenses can also cause inconsistent weld seams and reduced accuracy.
- Material Compatibility Issues: Reflective metals like aluminum, copper, and brass may reflect the laser beam, leading to unstable welding or damage to optical components. Contaminants such as oil, rust, or coatings on the workpiece surface can result in porosity, spatter, and poor weld strength.
- Machine Component Failures: If the cooling system fails, the laser source can overheat, causing performance drops or machine shutdowns. Worn protective lenses, clogged nozzles, or faulty sensors may reduce precision and increase the risk of costly repairs. Electrical issues, such as unstable voltage, can also disrupt machine operation.
- Safety and Environmental Concerns: Improper fume extraction may lead to the accumulation of hazardous gases and particles, endangering operator health. Additionally, failure to follow laser safety protocols can result in eye injuries or skin burns from laser radiation exposure.
What Is The Service Life Of 2kW Laser Welding Machines?
- Laser Source Lifespan: The laser source is the most critical and long-lasting component of the machine. On average, it can operate for 80,000 to 100,000 working hours under normal conditions. With proper care, this lifespan can span several years, even in high-volume production environments.
- Supporting Components: Other parts, such as the cooling system, optical lenses, nozzles, and electronic controls, generally have shorter service lives. These components require routine inspection and timely replacement to prevent performance decline and unexpected downtime.
- Impact of Usage and Maintenance: Machines used continuously or in harsh environments may experience faster wear. However, by following a regular maintenance schedule, including cleaning, alignment checks, and coolant replacement, operators can significantly extend the overall lifespan of the machine.
What Are The Environmental Requirements For 2kW Laser Welding Machines?
- Temperature and Humidity Control: The ideal operating temperature range is 10℃ to 40℃ (50℉–104℉). Extremely high temperatures can cause overheating, while very low temperatures may affect the cooling system and optical components. Humidity should be maintained below 70% to prevent condensation, which can damage electronics and sensitive optics.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser welding produces smoke, fumes, and potentially harmful gases, especially when welding coated or treated metals. A well-ventilated workspace with a proper fume extraction system is essential to maintain clean air and protect operator health. Good airflow also reduces contamination of the laser lens and welding area.
- Dust-Free, Clean Environment: Dust and debris can interfere with the laser beam, clog nozzles, and damage optical components. The machine should be placed in a clean, dust-free area, away from corrosive substances, oil mist, or chemical vapors.
- Stable Power Supply: 2kW laser welding machines have a total power requirement of approximately 8.54kW, including the laser generator and cooling system. A stable electrical supply with voltage regulation is necessary to avoid power fluctuations that can cause operational errors or damage sensitive electronics.
- Safety Space and Layout: Provide enough clearance around the machine for easy access during operation and maintenance. Laser-protective barriers or curtains should be installed to shield nearby workers from accidental exposure to laser radiation.


