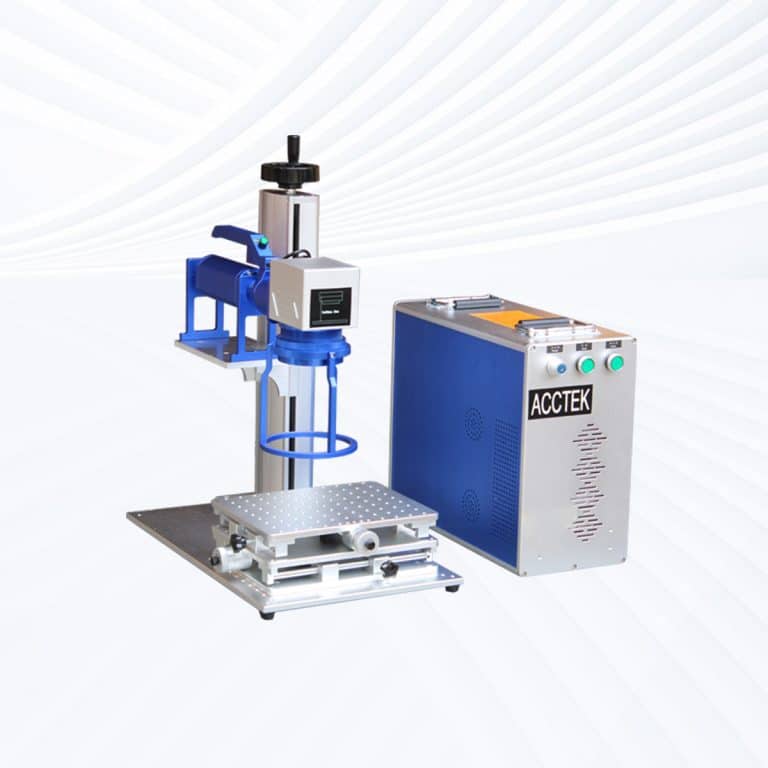
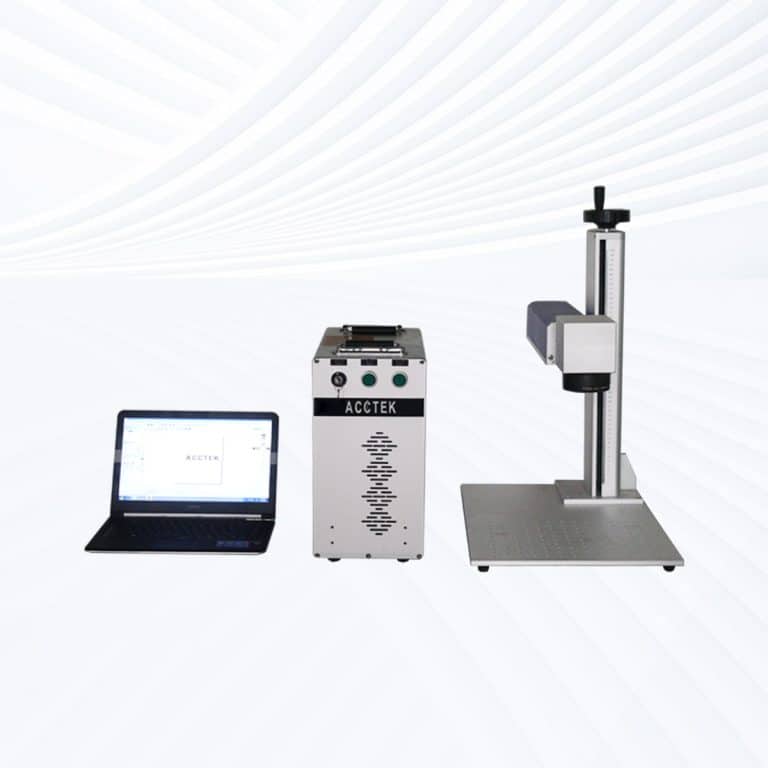
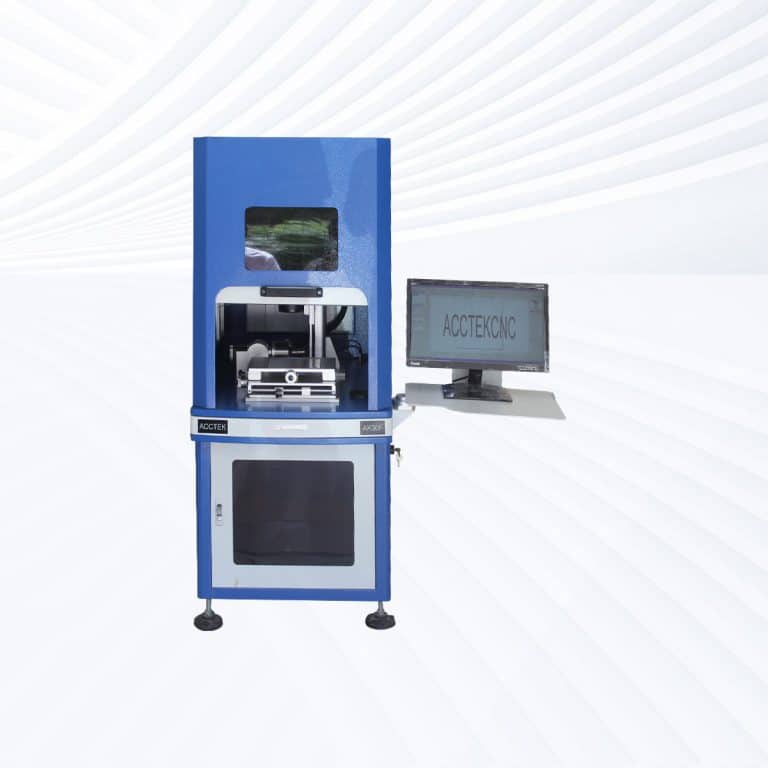
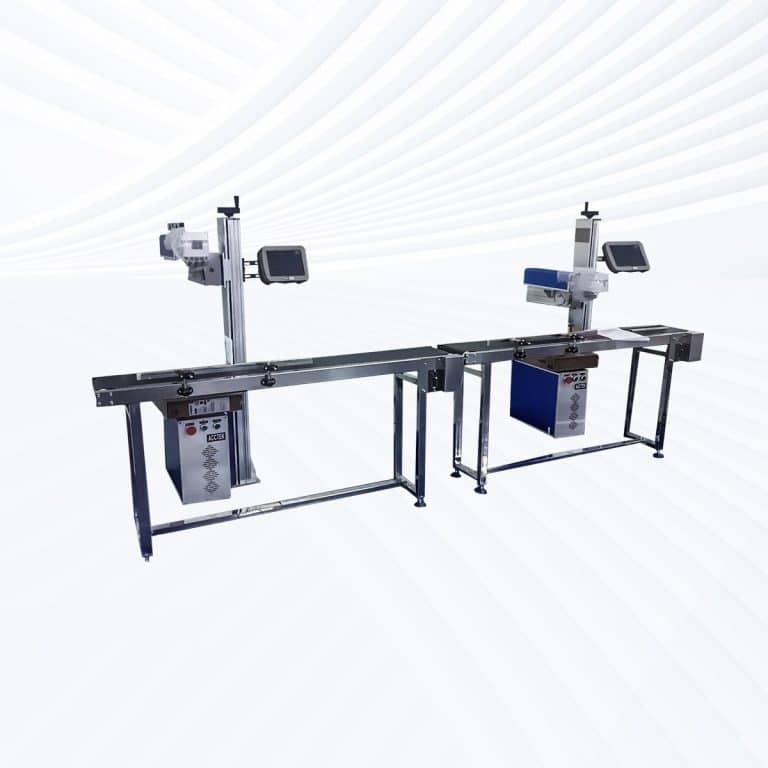
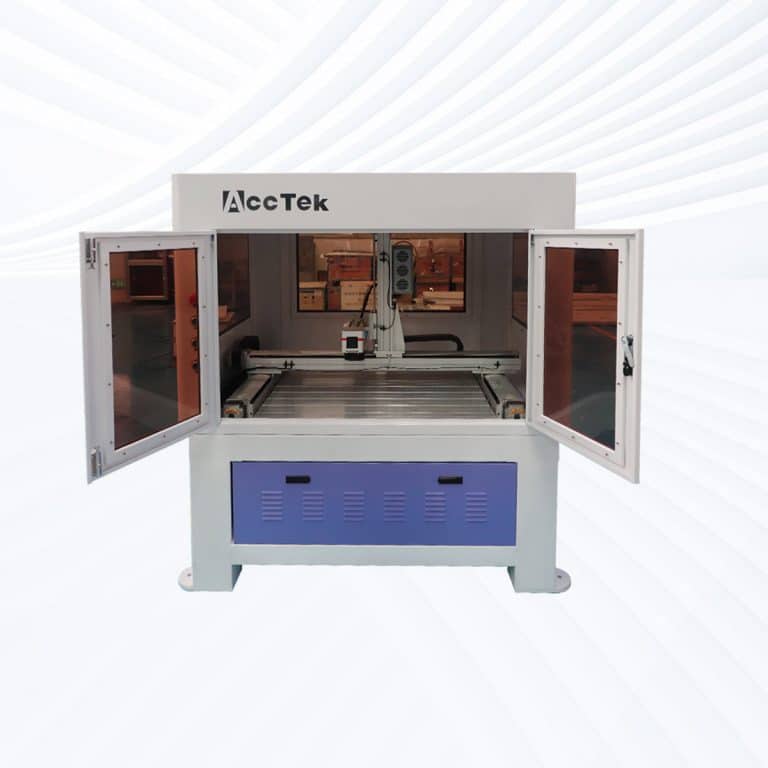
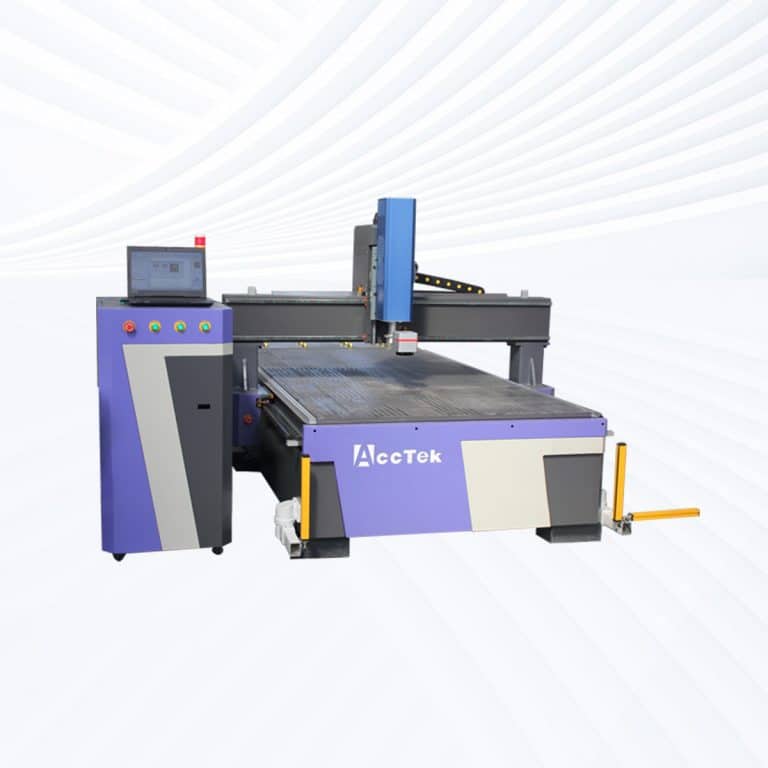
Product Introduction
Benefits of Laser Marking Wood
High Precision and Detail
Laser marking delivers fine lines and intricate designs with exceptional accuracy, even on small or curved wooden surfaces. It's ideal for detailed logos, text, and decorative patterns that require clean, consistent, and professional-quality results.
Permanent and Natural Finish
The laser etches directly into the wood surface, creating marks that won't fade, peel, or wear off. The resulting finish blends naturally with the wood grain, giving a rustic, authentic appearance without the need for additives.
Contact-Free and Damage-Free
As a non-contact process, laser marking avoids physical pressure or abrasion, preserving the surface integrity of delicate wood materials. This ensures smooth edges and eliminates the risk of cracks, splinters, or mechanical wear during marking.
No Inks or Chemicals Needed
Laser marking uses only focused light—no inks, solvents, or consumables. This makes the process cleaner, more environmentally friendly, and cost-effective over time, with minimal waste and no need for ongoing supply management.
Versatile Material Compatibility
Works on a wide variety of wood types, including softwood, hardwood, MDF, plywood, bamboo, and cork. Whether raw, varnished, or coated, the laser adapts to different surfaces and finishes without compromising quality.
Fast and Repeatable Production
Laser systems can operate at high speeds with excellent repeatability, making them suitable for both one-off custom pieces and large-scale production runs. Designs can be saved and reused, ensuring consistent branding and marking across batches.
Compatible Wood Materials
- Pine
- Oak
- Maple
- Cherry
- Walnut
- Birch
- Ash
- Mahogany
- Teak
- Beech
- Cedar
- Redwood
- Poplar
- Hickory
- Alder
- Basswood
- Bamboo
- Fir
- Spruce
- Sycamore
- Eucalyptus
- Rosewood
- Acacia
- Ebony
- Olive Wood
- Balsa Wood
- Ipe
- Larch
- Douglas Fir
- Wenge
- Zebrawood
- Plywood
- MDF
- HDF
- Veneered Wood
- Engineered Wood Panels
- Particle Board
- Cork
- Laminated Wood
- Painted or Coated Wood
Application of Wood Laser Marking Machines








Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Marking Technologies
| Feature | Laser Marking | Screen Printing | Pad Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Quality | High precision, clean lines, excellent detail | Good quality but less detailed on grainy wood | Moderate, less suited for wood | Good detail but not as durable |
| Durability | Permanent, burn-etched into the wood | Can wear off with friction or moisture | Short lifespan on porous wood | Susceptible to fading or peeling |
| Material Compatibility | Works on all wood types and composites | Works best on smooth, treated surfaces | Limited to small, flat surfaces | Requires coated or treated wood |
| Contact with Surface | Non-contact process | Direct contact | Direct contact | Minimal contact |
| Surface Adaptability | Adapts to curved, textured, or uneven surfaces | Best on flat, even surfaces | Limited flexibility on wood | Mostly flat surfaces |
| Setup Time | Minimal – software-driven | High – screen prep required | High – pad setup and alignment needed | Moderate – printhead setup required |
| Customization Speed | Instant digital updates, no retooling | Slow – new screens needed | Moderate – pad/tooling changes needed | Fast digital file updates |
| Marking Depth | Adjustable depth – surface or deep engraving | Surface ink only | Surface ink only | Surface-level color only |
| Repeatability | Excellent – identical results every time | Varies with screen condition and pressure | Can vary slightly between prints | Consistent if surface is flat and uniform |
| Tool Wear | None – laser has no physical contact | Screens degrade with use | Pads wear down and require replacement | Low tool wear |
| Maintenance Needs | Very low – minimal moving parts | Frequent screen cleaning and ink handling | Regular pad and ink maintenance | Moderate maintenance of printheads |
| Environmental Impact | Clean – no inks, solvents, or waste | Uses chemical inks and screens | Generates waste from inks and pads | Uses inks and energy, moderate impact |
| Cost per Mark (Long-Term) | Low – no consumables, minimal upkeep | Medium to high – screens and inks required | High – frequent consumables | Medium – ongoing ink and equipment costs |
| Speed for Batch Work | High-speed with automation capability | Slower due to setup and screen changes | Moderate speed, limited by tooling | Fast for short runs, slower for large batches |
| Automation Integration | Easily integrated into production lines | Difficult to automate | Limited automation | Moderate automation compatibility |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

Can Lasers Be Used For Marking On Curved or Irregular Surfaces
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of laser marking, including how it works, key technologies, applications, costs, and factors that determine when it is the right marking solution.

What Types of Laser Marking Machines Are There
This article explains the main types of laser marking machines, covering laser sources, marking methods, materials, applications, and how to choose the right system for production needs.
What Safety Precautions Are Required For Laser Marking
This article outlines essential safety precautions required for laser marking, including equipment safety, operator training, emergency protocols, and routine maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations.

How to Achieve High Contrast in Laser Marking
This article comprehensively covers the technologies, parameters, materials, and process controls required for consistent, high-contrast laser marking in industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Wood Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- Entry-Level Systems ($3,500–$7,000): These are usually desktop CO2 laser engravers with power ratings between 40W and 80W, suitable for small-scale businesses, hobbyists, or light commercial work. They can mark and lightly engrave on woods such as birch, pine, MDF, and bamboo. Most come with basic motion control, a limited work area (e.g., 300mm*500mm), and manual focus adjustment.
- Mid-Range Machines ($7,000–$15,000): These models offer higher power output (up to 100W or more), larger work areas (up to 900mm*600mm), and improved marking speed. They may include auto-focus, enhanced software, and rotary attachments for cylindrical objects like wood cups or dowels. This tier is ideal for custom woodworking shops, personalization businesses, and sign makers handling moderate to high volumes.
- High-End Industrial Machines ($15,000–$25,000): At the top of the range, you’ll find precision CO2 galvo systems and large-format flatbed laser engravers. These machines offer advanced control software, high-speed scanning heads, and continuous-duty cooling systems for reliable 24/7 operation. They are designed for the mass production of engraved wood panels, art pieces, packaging, or branded items with intricate detail and repeatability.
- Key Price Factors:
- Laser Power: Higher wattage enables deeper engraving and faster throughput, but increases cost.
- Work Area Size: Larger bed sizes allow for processing bigger wood pieces or multiple parts in one pass.
- Cooling System: Basic machines use air cooling; higher-end models may include water chillers for better thermal regulation during heavy use.
- Motion Control and Precision: Industrial-grade machines offer faster motors, smoother motion, and better resolution for fine detail work.
- Accessories: Add-ons such as rotary tools, fume extractors, autofocus sensors, and vision alignment systems can significantly affect pricing.
Which Laser Marking Machine is Best for Marking Wood?
- Wood and Wood-Based Products: CO2 lasers mark and engrave hardwoods, softwoods, plywood, MDF, and veneer with clean results. Lighter woods like birch or maple darken well under the laser, producing a crisp, burned appearance. Hardwoods may require more power but yield excellent depth and texture. To avoid scorching or smoke buildup, proper air assist and ventilation are essential.
- Acrylic and Plastics: CO2 lasers also work well on materials often combined with wood in signage or crafts. Acrylics, especially cast PMMA, produce clear, flame-polished edges when cut. Other plastics vary in cut quality and fume output. Always check plastic compatibility to avoid releasing harmful gases—PVC should never be processed.
- Paper and Cardboard: For packaging or prototyping, CO2 lasers cleanly mark and cut paper, chipboard, and cardboard. These materials are thin and flammable, so constant supervision and a reliable exhaust system are critical.
- Leather and Fabrics: Natural leather marks well with CO2 lasers, as do many textiles like cotton or felt. These materials are often used in wood-and-fabric crafts or furniture branding. However, synthetic leathers and vinyls may emit hazardous fumes and should be tested or avoided unless verified safe.
- Rubber: Laser-safe rubbers can be used for custom stamp production or inlays for wood crafts. Be cautious with unknown rubbers, especially those containing chlorine, as they release noxious gases.
- Foam: EVA foam and polyethylene foam are often used for wood packaging or tool inserts. CO2 lasers cut these well but pose a fire risk if left unsupervised, especially during longer runs.
- Glass and Ceramics (Engraving Only): While not wood, glassware is often paired with engraved wood products. CO2 lasers can etch the surface of glass and ceramic, allowing for matching designs across materials.
- Thin Non-Ferrous Metals (with limitations): Though CO2 lasers can’t engrave bare metals efficiently, they can mark coated or anodized metals—sometimes found on wood hardware or fixtures—if painted or pre-treated.
How Do I Remove Laser Markings from Wood?
- Sanding: For most wood types, light to moderate sanding is the primary method to remove laser markings. Use fine to medium-grit sandpaper (e.g., 120 to 220 grit) and sand in the direction of the wood grain.
- Shallow surface markings can often be removed with a few passes by hand or using a palm sander.
- Deeper engravings may require coarser grit followed by finer grit to restore a smooth finish.
- Always re-seal or re-finish the surface after sanding to match the original look.
- Scraping and Surface Shaving: On softwoods or thin veneers where sanding may cause uneven surfaces, a sharp wood scraper or chisel can be used to gently shave off the marked area.
- Use caution to avoid gouging or lifting the grain.
- This method is useful for small logos, initials, or burned edges that need spot correction.
- Chemical Wood Bleach: For surface discoloration or light burn marks that don’t penetrate deeply, apply a two-part wood bleach (usually oxalic acid-based) to lighten the darkened area.
- Effective for restoring contrast on light-colored woods like birch or maple.
- Always test on a scrap piece or hidden area first, as bleaching can alter the wood’s tone.
- Heat Gun and Light Resurfacing: For mild laser burns or smudging on softwoods, applying a heat gun at a low setting and then wiping with a clean cloth may lift the charred layer slightly. Follow up with light sanding to blend the area.
- This method should be used cautiously and is not suitable for deep or wide engravings.
- Filler and Re-Staining (for Deep Engravings): If the laser engraving is too deep to sand out cleanly, fill the carved area with wood filler or a wood putty that matches the surrounding tone. Once dry, sand flush with the surface and re-stain to match the original finish.
- This approach works best on painted or dark-stained wood, where blending is easier.
- Limitations and Considerations:
- On veneered wood or plywood, aggressive sanding may wear through the surface layer.
- If the wood was sealed or finished before engraving, you’ll likely need to refinish the entire surface after mark removal.
- Burn marks around the laser path can often be reduced by masking wood before engraving—helpful for future prevention.
What are The Disadvantages of Laser Marking Wood?
- Charring and Burn Marks: Laser engraving on wood works by burning away the surface layer, which naturally produces charred edges and dark marks. While this is often desirable for contrast, some woods—especially softwoods and plywood—can leave excess soot or uneven burns.
- Proper ventilation and air assist can reduce but not eliminate this effect.
- Additional cleaning or sanding may be required post-marking to achieve a clean finish.
- Inconsistent Results Across Wood Types: Different woods react differently to laser energy.
- Hardwoods like oak or maple engrave more cleanly but require more power and time.
- Softwoods like pine or fir can burn unpredictably due to resin content, leading to splotchy or uneven marks.
- Engineered woods like MDF or plywood may contain glues or fillers that smoke excessively or produce poor contrast.
- Limited Depth Control: CO2 lasers can engrave wood to various depths, but precise depth control is limited without high-end systems.
- Deeper engraving often results in more burning and smoke, which may obscure fine detail.
- Shallow marking works better for intricate designs, but can lack durability on surfaces that get worn or handled.
- Surface Damage Risk: Laser energy can warp or dry out thin or delicate wood surfaces, especially veneers or lightweight woods.
- Repeated passes can scorch the surrounding area or weaken the structure.
- High heat also increases the chance of ignition, particularly if the laser is left in one spot too long or if air assist is not used.
- Fume Generation and Cleanup: Wood laser engraving produces visible smoke and potentially harmful particles, especially from resin-rich or treated woods.
- Adequate fume extraction and filtration are essential to prevent health risks and buildup inside the machine.
- Post-engraving cleanup may be needed to remove soot, ash, or resin residue, especially on light-colored woods.
- Not Ideal for All Finishes: Laser marking is best on unfinished or lightly finished wood. Varnishes, paints, or sealers can:
- Interfere with laser absorption
- Bubble, flake, or discolor under heat
- Release toxic fumes when burned
- Fire Hazard: Wood is flammable. Laser engraving always carries a fire risk, especially during long jobs or if debris builds up inside the work area.
- Machines must be monitored constantly, and fire suppression equipment should be nearby in high-use environments.
How Should I Choose Wood Laser Marking Machines?
- Wood and Wood-Based Products: CO2 lasers can engrave or cut hardwood, softwood, plywood, MDF, and veneer with clean results. Different wood types react differently:
- Softwoods (pine, fir): Mark easily but may char quickly, requiring lower power and careful control.
- Hardwoods (oak, maple): Offer cleaner engraving but need more laser power.
- Engineered woods (MDF, plywood): Mark well, but adhesive content can create excess smoke and may shorten laser tube life.
- Power Output and Engraving Depth: Laser wattage determines how quickly and deeply the machine can mark or engrave.
- 40W to 60W: Suitable for light engraving and marking on thin wood sheets or softwoods.
- 80W to 100W: Offers faster speeds and deeper engravings on most wood types.
- 130W or higher: Recommended for heavy-duty work, large projects, or combining engraving and cutting tasks in one pass.
- Work Area Size: Consider the dimensions of your wood pieces. Standard bed sizes range from:
- 300*500 mm for small jobs and crafts
- 600*900 mm for medium signs and panels
- 1300*900 mm or larger for furniture parts, large signage, or batch production
- Motion System and Precision: Look for machines with stable gantry systems and smooth motion control for accurate marking, especially for intricate artwork, logos, or fine text. Higher-end machines may use servo motors or belt-driven mechanisms for better repeatability and speed.
- Cooling System: Most CO2 lasers require cooling.
- Water cooling (especially for lasers over 60W) ensures stable operation and prolongs tube life.
- Air cooling may be enough for lower-power desktop units, but not for continuous operation.
- Air Assist and Exhaust System: Proper airflow is essential when marking wood.
- Air assist reduces scorching and helps keep the work surface clean.
- A fume extractor or external exhaust removes smoke and particulates generated during burning, protecting optics and the work environment.
- Control Software and Usability: Choose a system with user-friendly software (like Ruida or LightBurn) that supports vector and raster engraving and common file types (SVG, DXF, BMP, AI). Important features to look for:
- Adjustable speed, power, and focus control
- Layered job control (e.g., different settings for engraving and cutting)
- Rotary tool support for marking cylindrical wood objects
- Build Quality and Support: Ensure the frame and components are durable—steel or aluminum chassis offer better rigidity than plastic casings. Machines with reliable customer support, a clear warranty, and available spare parts are more cost-effective over time.
How Should I Maintain Wood Laser Marking Machines?
- Daily Maintenance Tasks
- Clean the Optics (Lenses and Mirrors): Dust and smoke from wood can coat lenses and mirrors, reducing beam quality. Use lens-safe cleaning solution and lint-free wipes. Inspect them before each session and clean as needed.
- Wipe Down the Work Area: Wood residue, ash, and sap can build up quickly. Clean the cutting bed, rails, and surrounding areas to prevent debris from interfering with airflow or motion.
- Check Air Assist and Ventilation: Ensure the air assist is working properly to blow debris and smoke away from the laser path. Also, verify that the exhaust fan and ducting are free of blockages and functioning to clear fumes.
- Weekly Maintenance Tasks
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply light machine oil or manufacturer-recommended lubricant to guide rails and linear bearings. This keeps the gantry movement smooth and reduces wear from accumulated wood dust.
- Check Alignment of Optics: Laser mirrors can get knocked out of alignment from vibration or regular use. Use a target test to ensure the beam is hitting the right spots from the laser tube to the lens. Misalignment reduces power and can scorch material unevenly.
- Inspect and Clean the Fume Extractor Filters: Wood marking produces fine particulate matter. If you use a fume extraction system, check and clean or replace filters regularly to ensure safe operation and optimal airflow.
- Monthly Maintenance Tasks
- Examine the Laser Tube: Look for signs of wear or discoloration. CO₂ tubes lose power over time—if your marks are inconsistent or weak despite correct settings, the tube may need recalibration or replacement.
- Check Cooling System: If your machine uses water cooling, inspect the water level, clarity, and flow. Replace old water and clean the reservoir and tubing. Overheated tubes can crack or degrade faster.
- Tighten Belts and Check Tension: Loose belts reduce precision and can cause wobbling or skipping during engraving. Adjust belt tension according to your machine’s specs.
- Additional Best Practices
- Use the Right Wood: Avoid resin-heavy or oily woods like pine, which leave behind more residue and fumes.
- Keep a Maintenance Log: Track when tasks are completed. This helps prevent neglect and makes troubleshooting easier.
- Update Software and Firmware: Ensure your machine’s software is current. Bug fixes and improvements can enhance efficiency and reliability.
What Training is Required to Operate Wood Laser Marking Machines?
- Wood and Wood-Based Products: To operate a wood laser marking machine, users must be trained to handle materials like hardwood, softwood, MDF, plywood, and veneer. Each wood type reacts differently under laser exposure—hardwoods may require higher power settings, while softwoods can scorch easily. Trainees learn to adjust speed, power, and air assist to balance quality and safety. Charring, ignition risk, and resin buildup are common concerns, so training emphasizes proper ventilation, material placement, and fire prevention techniques.
- Design Software and File Preparation: Operators need hands-on training in vector and raster design software such as LightBurn, CorelDRAW, or Adobe Illustrator. This includes creating artwork, converting images to engravable formats, and setting correct layer parameters. Understanding how resolution, DPI, and grayscale values affect laser output is essential for clean, legible marks. The operator also learns to export files in the correct format for the machine’s control software.
- Laser Machine Operation and Settings: Training covers how to start up, calibrate, and safely shut down the laser system. Operators are taught how to focus the laser lens manually or with auto-focus tools, align mirrors (if applicable), and input correct job settings. Speed, power, frequency, and pass count all affect the depth and clarity of the mark. Training includes how to run test grids and adjust parameters to optimize results for specific wood types.
- Safety and Environmental Controls: Laser marking wood creates smoke and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Operators are trained to use air assist systems to prevent flare-ups and to monitor proper exhaust flow for effective smoke removal. Safety training also includes laser classification awareness (CO2 lasers are Class 4), proper eyewear use, emergency stop procedures, and fire extinguisher handling.
- Material Handling and Job Setup: Wood can warp, bow, or contain hidden defects. Training includes selecting flat, untreated boards, securing them properly on the workbed, and using masking tape or jigs when necessary. Operators are also taught to visually inspect wood for glue lines, knots, or finishes that might interfere with marking or produce hazardous fumes.
- Routine Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Proper maintenance keeps the laser in top shape. Training includes cleaning the lens and mirrors, checking and replacing filters, inspecting belts and rails, and managing the water cooling or chiller systems. Operators are trained to diagnose common issues like loss of beam strength, misalignment, or inconsistent engraving, and take corrective steps without damaging the machine.
What is the Lifespan of Wood Laser Marking Machines?
- Laser Tube Lifespan: The CO2 laser tube is the primary component subject to wear. Standard glass-sealed tubes typically last 1,500 to 3,000 hours of active use. High-end metal or ceramic RF (radio frequency) tubes can last 15,000 to 30,000 hours, but they come at a higher cost. Once a tube reaches the end of its life, marking power declines, and output becomes inconsistent, requiring replacement.
- Motion System and Optics: Precision components like mirrors, lenses, and linear rails can last for many years if cleaned regularly and kept free from wood dust and resin buildup. However, lenses and mirrors may need replacement every 6 to 18 months, depending on workload and cleanliness. Belt systems and bearings also experience wear and may require replacement every few years to maintain smooth gantry movement.
- Electronics and Control Systems: The control boards, power supplies, and cooling systems are designed for long-term use. These components often outlast the laser tube, provided the machine is operated in a dust-free, climate-controlled environment. Power surges and overheating are the main threats to these parts, so using voltage regulators and maintaining coolant quality are essential.
- Maintenance Impact: Machines that receive regular maintenance—such as cleaning optics, aligning mirrors, checking exhaust flow, and replacing filters—tend to reach the upper end of their lifespan. Neglected machines often fail much sooner due to resin buildup, overheating, and component misalignment.






