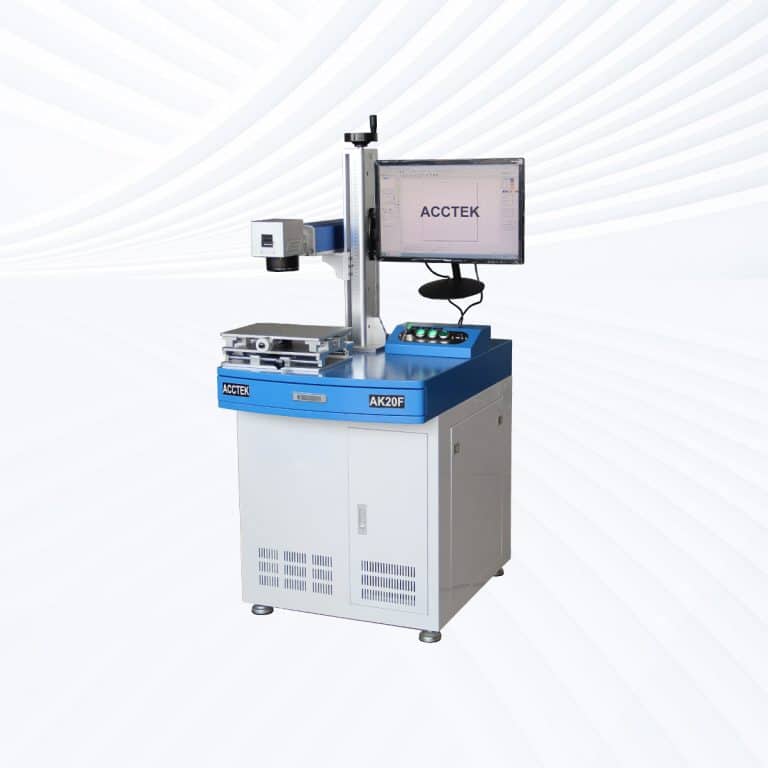
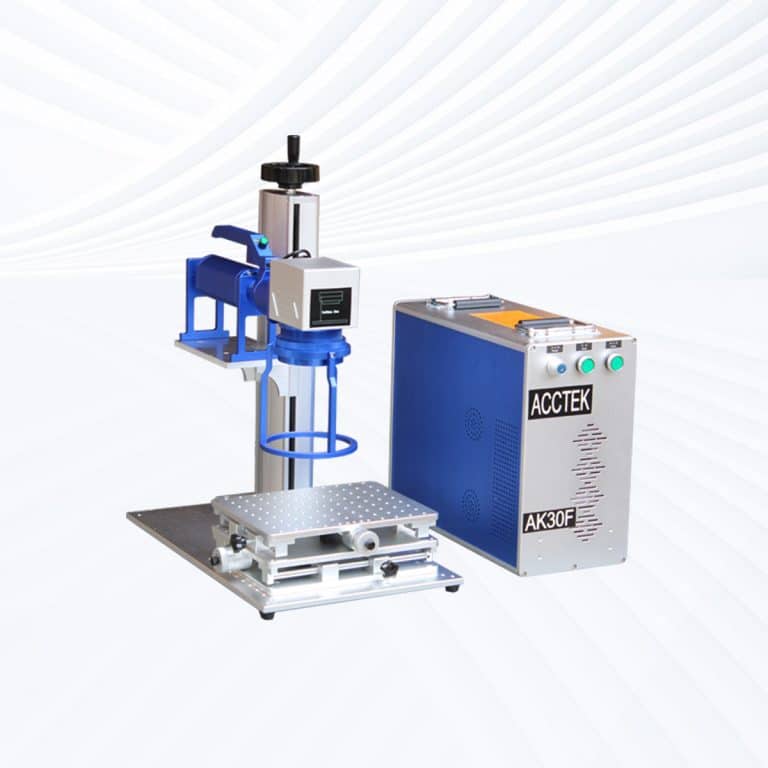
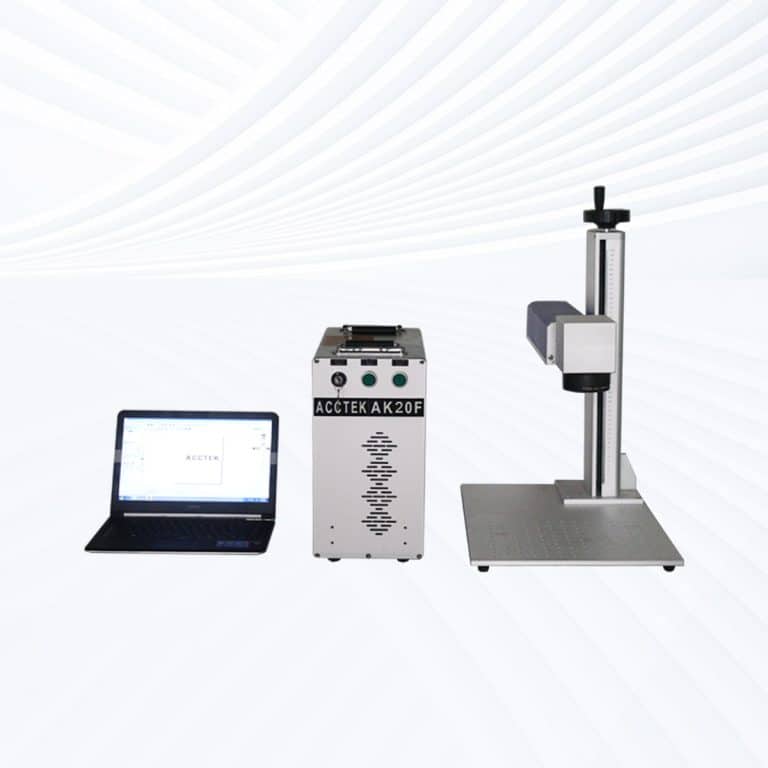
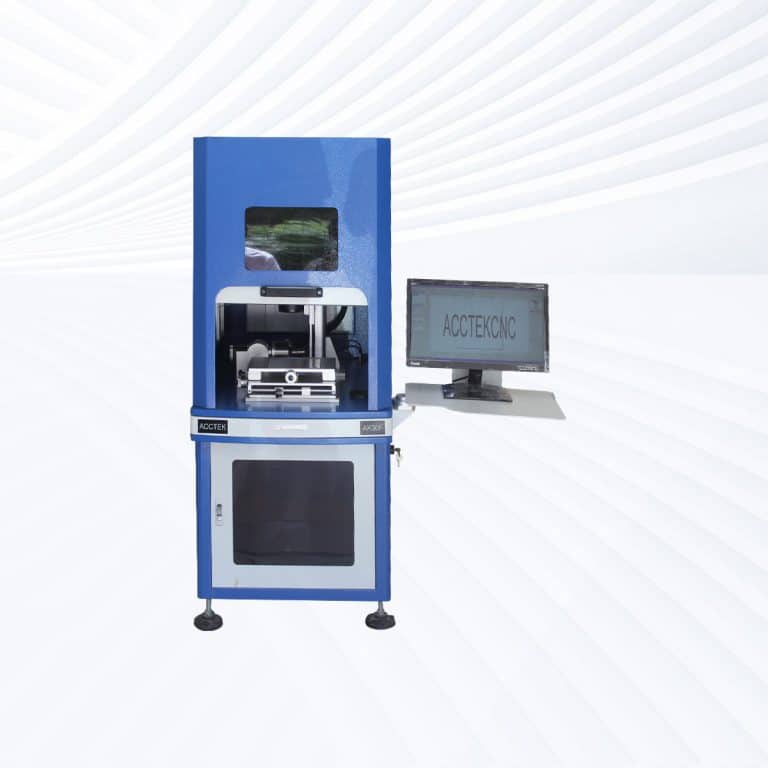
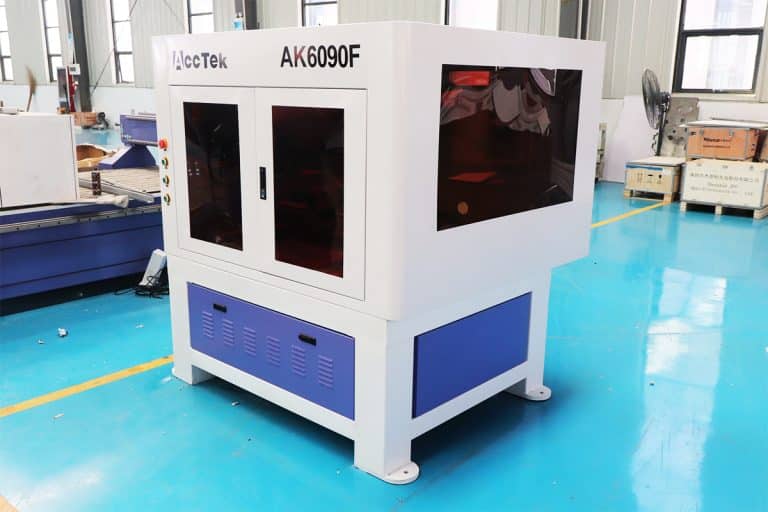
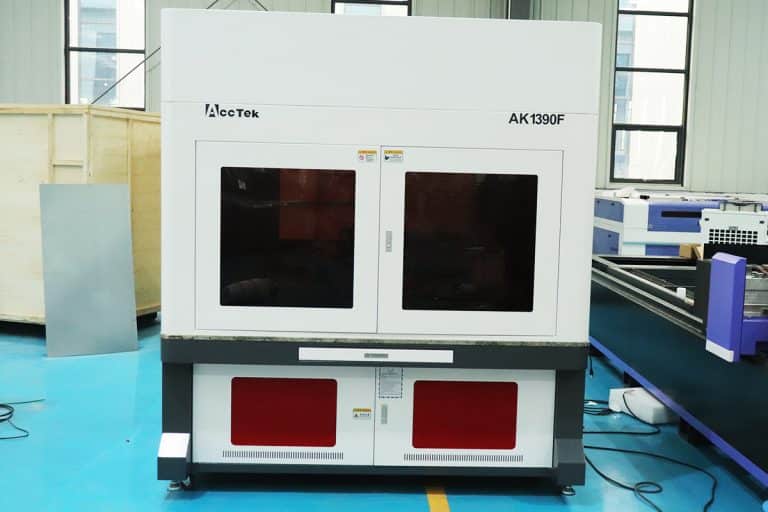
Product Introduction
Types of Rubber Laser Marking Machines
Benefits of Laser Marking Rubber
Permanent and Wear-Resistant Marking
Laser marking creates high-contrast, durable engravings that won't fade, rub off, or degrade under heat, abrasion, or chemical exposure—ideal for rubber parts used in demanding industrial, automotive, or outdoor environments.
Non-Contact, Damage-Free Process
The laser marking process is completely non-contact, meaning there's no physical stress or pressure on the rubber surface. This prevents distortion, tearing, or compression, maintaining the integrity of both soft and hard rubber components.
High Precision and Fine Detail
Laser technology enables sharp, precise markings even on small or irregularly shaped rubber parts. It's ideal for fine text, serial numbers, logos, and complex graphics with consistent quality across multiple production runs.
No Inks or Chemicals Needed
Laser marking uses only focused light—no inks, solvents, or stencils. This reduces waste, eliminates consumable costs, and creates a cleaner, more environmentally friendly process with minimal maintenance and no drying or curing time.
Compatible with Various Rubber Types
Whether you're working with silicone, EPDM, NBR, SBR, natural rubber, or TPE, laser machines can be adjusted to suit different material properties and surface textures with consistently excellent results.
Ideal for High-Speed Production
Laser marking supports fast cycle times and automation, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. It ensures repeatable, high-throughput performance without sacrificing quality, even on complex rubber parts or curved surfaces.
Compatible Rubber Materials
- Natural Rubber
- Silicone Rubber
- EPDM
- NBR
- NBR
- Neoprene
- Neoprene
- FKM
- PU
- TPE
- TPV
- TPO
- HNBR
- ACM
- ECO
- AEM
- FFKM
- Latex Rubber
- Isoprene Rubber
- Synthetic Rubber
- Fluorosilicone Rubber
- Butadiene Rubber
- Chloroprene Rubber
- Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene
- Ethylene-Propylene Rubber
- Liquid Silicone Rubber
- High Consistency Rubber
- Conductive Rubber
- Foam Rubber
- Sponge Rubber
- Hard Rubber
- Soft Rubber Blends
- Soft Rubber Blends
- Heat-Resistant Rubber
- Abrasion-Resistant Rubber
- UV-Resistant Rubber
- Colored Rubber Compounds
- Anti-Static Rubber
- FDA-Grade Rubber
- Recycled Rubber Materials
Application of Rubber Laser Marking Machines








Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Marking Technologies
| Feature | Laser Marking | Screen Printing | Pad Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Quality | High precision, clean, and permanent | Good, but may smudge on flexible surfaces | Decent, limited detail on textured rubber | High resolution, not always durable |
| Durability | Permanent, abrasion- and chemical-resistant | Prone to cracking and fading | Wears off under friction or stretch | Moderate, fades with use |
| Material Compatibility | Works on all rubber types (natural, synthetic) | Limited to flat, treated surfaces | Moderate-best on small, curved parts | Limited-best on smooth, coated surfaces |
| Surface Contact | Non-contact, no distortion | Requires contact and pressure | Requires contact | Minimal contact |
| Risk of Damage | None-no stretching, denting, or residue | Risk of smudging or surface deformation | May deform soft or thin rubber | Low risk on treated surfaces |
| Setup Time | Very low-file-based | High-screen preparation needed | High-pads and fixtures required | Moderate setup via software |
| Customization Speed | Instant digital updates | Slow-new screen for every design | Moderate-tooling swap needed | Quick digital design changes |
| Environmental Impact | No ink, chemicals, or waste | High-uses ink, solvents, and screens | High-uses pads, solvents, and chemicals | Moderate-uses ink and generates some waste |
| Cost per Mark (Long-Term) | Low-no consumables | Higher-requires screens and inks | High-pads, inks, and cleanup | Medium-ongoing ink cost |
| Maintenance Needs | Minimal-simple cleaning | Frequent-ink handling and screen washing | High-pad replacement and cleaning | Moderate-printhead maintenance |
| Marking Depth | Surface-level or lightly engraved | Ink sits on surface only | Surface ink only | Surface ink only |
| Automation Potential | Easily integrated into production lines | Difficult to automate | Limited automation potential | Moderate automation compatibility |
| Repeatability | Excellent-uniform output across batches | Varies with screen and manual input | Can vary depending on pad wear | Consistent if settings are maintained |
| Production Speed | High-speed, ideal for batch or inline marking | Slower due to manual prep and cleanup | Moderate-requires cycle time per item | Fast for short runs, slower at high volumes |
| Best Use Cases | Logos, serials, barcodes, graphics on all rubbers | Flat, simple designs on smooth rubber | Small curved rubber parts | Color images or logos on treated rubber |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

Can Lasers Be Used For Marking On Curved or Irregular Surfaces
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of laser marking, including how it works, key technologies, applications, costs, and factors that determine when it is the right marking solution.

What Types of Laser Marking Machines Are There
This article explains the main types of laser marking machines, covering laser sources, marking methods, materials, applications, and how to choose the right system for production needs.
What Safety Precautions Are Required For Laser Marking
This article outlines essential safety precautions required for laser marking, including equipment safety, operator training, emergency protocols, and routine maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations.

How to Achieve High Contrast in Laser Marking
This article comprehensively covers the technologies, parameters, materials, and process controls required for consistent, high-contrast laser marking in industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Rubber Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines ($2,500 to $30,000)
- Lower-end models ($2,500 – $8,000): These machines typically have lower power output (around 20W to 30W) and are suited for smaller production runs or simpler marking tasks on rubber.
- Mid-range models ($8,000 – $15,000): These machines offer higher power outputs (40W to 60W) and greater precision, suitable for more detailed work and higher production volumes.
- High-end models ($15,000 – $30,000): High-power fiber lasers (80W to 100W) with faster processing speeds, larger marking areas, and additional features like automation, advanced cooling systems, and high-efficiency capabilities for heavy-duty, high-volume applications.
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines ($3,500 to $25,000)
- Lower-end models ($3,500 – $8,000): These machines typically have power outputs in the range of 30W to 50W and are ideal for marking softer rubber types and small batches.
- Mid-range models ($8,000 – $15,000): These machines offer better precision, faster speeds, and slightly higher power outputs (60W to 80W), making them suitable for more detailed work and medium-scale production.
- High-end models ($15,000 – $25,000): These machines feature powerful lasers (up to 100W), larger work areas, faster processing speeds, and the ability to handle larger and more complex rubber marking tasks.
Which Laser Marking Machine is Best for Marking Rubber?
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines for Rubber
- Best for Non-Metallic Materials: CO2 lasers are highly effective for organic materials, including various types of rubber. They are often used for engraving and marking rubber products, such as gaskets, seals, and rubber stamps.
- Material Compatibility: CO2 lasers work well with rubber materials that do not contain chlorine. They can mark or engrave rubber by vaporizing the top layer, creating a visible contrast. However, when working with rubber that contains chlorine (like PVC-based rubber), there are risks due to the toxic fumes released during the process.
- Considerations: When using a CO2 laser on rubber, it’s essential to ensure proper ventilation to handle fumes, especially if working with synthetic rubbers or any material containing harmful substances like PVC. Also, the engraving depth can be controlled for fine details, making it ideal for logos, text, and patterns.
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines for Rubber
- Better for Certain Rubber Types: Fiber lasers are generally better suited for marking harder rubbers or rubber products that have metal components, such as rubber parts embedded with metal. They offer high precision and durability for engraving metal-rubber composites.
- Limited to Certain Applications: Fiber lasers are less effective for pure rubber, especially softer rubber types, because the laser beam may not efficiently interact with the non-metallic surface. They also tend to work better for industrial applications where higher contrast marking is needed.
How Should I Choose Rubber Laser Marking Machines?
- Type of Laser Source
- CO2 Lasers: These are the most commonly used lasers for rubber marking due to their high precision and ability to produce clean marks on non-metallic materials like rubber. They are especially effective for marking rubber with high contrast and detail.
- Fiber Lasers: Fiber lasers are typically used for metals, but they can be adapted for rubber marking as well. However, they may not offer the same contrast and depth as CO2 lasers for rubber materials.
- Laser Power
- Lower Power (10W–50W): Ideal for smaller, less detailed marks and fine engraving on rubber. This power range is usually sufficient for most rubber products.
- Higher Power (50W–100W): Needed for deeper engravings or faster marking on thicker or denser rubber. High power allows for faster processing but requires more precise control.
- Marking Speed
- Depending on your production volume, choose a machine with an appropriate marking speed. Higher power machines often mark faster, but it’s essential to balance speed with the required precision and material type.
- Accuracy and Precision
- Rubber marking requires high accuracy for detailed designs and text. Ensure that the machine has a high-resolution marking head, capable of precise positioning and small focal points for detailed markings.
- Cooling System
- Rubber materials are sensitive to excessive heat. Look for a machine with an efficient cooling system (water or air-cooled) to prevent damage to the rubber due to heat buildup during the marking process.
- Material Compatibility
- Ensure that the laser marking machine is compatible with the specific type of rubber you are working with. Rubber materials like natural rubber, silicone, or synthetic rubber may react differently to lasers, so testing the machine on your materials is crucial.
- Software and Control System
- User-Friendly Software: Choose a machine with software that supports common file formats (e.g., DXF, AI) and provides advanced features for engraving, text, logos, and more.
- Control System: The control system should allow for precise adjustments to laser settings such as power, speed, and focus to achieve the best marking results.
- Maintenance and Durability
- Look for a machine that requires minimal maintenance and has a long operational lifespan. Rubber laser marking machines should have robust components that can withstand high-volume usage.
- Cost and ROI
- Consider both the initial cost of the machine and the long-term operating expenses. While high-quality machines can be costly, they may offer a better ROI through higher efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and faster production times.
- Safety Features
- Rubber marking can produce fumes and small particles, so ensure the machine has appropriate ventilation or an exhaust system. Also, check for built-in safety features such as automatic shut-off, protective covers, and laser safety goggles for operators.
- After-Sales Support
- Ensure that the manufacturer or supplier provides reliable after-sales support, including training, installation, and troubleshooting assistance. Having access to spare parts and customer support can save time and money in the long run.
- Customization and Additional Features
- Some machines offer customization options like different lens sizes for various marking depths, rotary attachments for cylindrical items, or larger marking areas. Choose a machine that fits the specific requirements of your products.
What are the Risks of Laser Marking Rubber?
- Fume and Smoke Emissions
- Risk: The laser marking process can release fumes and smoke, especially when working with synthetic rubbers, which may contain harmful chemicals or volatile compounds.
- Consequence: Prolonged exposure to these fumes can be hazardous to health, causing respiratory issues, eye irritation, or other health problems for operators.
- Mitigation: Ensure the use of proper ventilation systems, such as fume extraction units, to capture and filter harmful emissions. Always work in a well-ventilated area and provide proper protective equipment.
- Surface Damage
- Risk: If the laser settings (power, speed, focus) are not correctly adjusted, there is a risk of excessive heat being applied to the rubber surface, leading to surface damage.
- Consequence: Overheating can cause the rubber to burn, discolor, or degrade, resulting in poor quality marks, visible damage, or material wastage.
- Mitigation: Carefully adjust laser parameters to suit the rubber type and thickness. Use lower power and slower speeds for more delicate rubbers to avoid overheating.
- Inconsistent Marking Quality
- Risk: Rubber is a heterogeneous material, meaning it can have variations in density, composition, or texture, leading to inconsistent marking quality.
- Consequence: This can result in uneven or blurry marks, reduced clarity of text or graphics, and ultimately lower-quality final products.
- Mitigation: Conduct tests on various rubber samples before starting the marking process. Regularly inspect the material for consistency and adjust the laser settings accordingly.
- Fire Hazard
- Risk: Some types of rubber, especially those with higher carbon content or certain additives, can be flammable.
- Consequence: If not properly controlled, the heat generated by the laser could ignite the rubber, potentially leading to fires.
- Mitigation: Always ensure that the laser has proper safety mechanisms in place, such as flame detectors or automatic shutdown systems. Employ a fire extinguisher nearby and avoid leaving the machine unattended during operation.
- Laser Eye Safety
- Risk: The powerful laser beams used for marking can pose a risk to the eyes if proper safety precautions are not taken.
- Consequence: Exposure to laser light, even at lower levels, can cause severe eye injuries, including permanent blindness.
- Mitigation: Operators must wear laser safety goggles that are appropriate for the laser wavelength. The machine should also have protective covers and interlock systems to prevent accidental exposure.
- Damage to Sensitive Materials
- Risk: In some cases, rubber products may be sensitive to heat, chemicals, or environmental conditions.
- Consequence: Laser marking could alter the physical properties of sensitive rubber items, affecting their elasticity, flexibility, or other characteristics.
- Mitigation: Ensure you select the appropriate laser type and settings for the specific rubber material being used. Perform tests on small batches to check for any undesirable changes.
- Cost of Maintenance and Consumables
- Risk: Laser marking machines require regular maintenance, and consumables like laser tubes and lenses may wear out over time.
- Consequence: If maintenance is neglected, the machine may perform poorly or fail, leading to downtime and increased operational costs.
- Mitigation: Follow a regular maintenance schedule, clean the lenses and mirrors frequently, and replace consumables as needed to keep the machine running smoothly.
- Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
- Risk: The laser generates localized heat that can affect the area around the marked spot, potentially causing unwanted changes in the surrounding rubber material.
- Consequence: The HAZ can lead to material degradation or distortion, especially in rubber with a low melting point.
- Mitigation: Minimize the HAZ by carefully adjusting the laser power, speed, and focus. Ensure that the rubber is held firmly in place during marking to avoid shifting.
- Toxic Chemical Reactions
- Risk: Some rubber materials, particularly those with certain additives or coatings, may react with the laser’s heat, releasing toxic chemicals.
- Consequence: The release of harmful substances, such as toxic gases or fumes, could pose serious health risks to operators or damage the environment.
- Mitigation: Conduct a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) review of the rubber material and its additives. Choose rubber types that are less likely to emit harmful substances when exposed to laser energy.
How Should I Maintain Rubber Laser Marking Machines?
- Clean the Laser Optics Regularly
- Focus Lens: Rubber marking produces a significant amount of smoke and residue. Regularly clean the focus lens to prevent buildup, which could affect the laser’s precision. Use a soft cloth or lens cleaning wipes specifically designed for optical components. Make sure to handle the lens carefully to avoid scratches.
- Mirror Cleaning: The mirrors that direct the laser beam should be cleaned at regular intervals, especially if you’re marking rubber frequently. Use appropriate optical cleaning solutions and a lint-free cloth to remove debris.
- Air Assist: Many laser systems come with an air assist feature to blow away smoke and particles during marking. Ensure the air assist nozzle and hose are free of obstructions and that the air pressure is consistent. Clean the nozzle periodically to prevent any clogging or inefficiency.
- Maintain the Cooling System
- Check Water Chillers or Coolant Levels: Most laser systems, especially CO2 lasers, require cooling to prevent overheating. Regularly check the water or coolant levels in the chiller. Ensure the system is running at the proper temperature to avoid damage to the laser tube.
- Clean the Cooling Fans: Dust accumulation in cooling fans can reduce their efficiency. Clean the fans and ensure air can circulate properly through the system.
- Inspect Hoses and Connections: Over time, rubber hoses used in cooling systems may crack or become damaged. Inspect all hoses for leaks or wear and replace them as necessary.
- Ensure Proper Laser Tube Maintenance
- Laser Tube Inspections: Laser tubes can degrade over time, especially when used frequently. Check for signs of wear, such as reduced power output or inconsistent marking quality. It’s essential to replace the tube before it fails, which can cause more significant damage to the machine.
- Cooling of the Laser Tube: Ensure that the cooling system is always functioning correctly, as the laser tube can overheat if not properly cooled, leading to reduced lifespan and performance.
- Check the Exhaust System
- Airflow and Filters: Marking rubber generates smoke and fumes that need to be extracted effectively. Regularly check the exhaust system and clean or replace filters. An inefficient exhaust system can lead to poor air quality, which could affect both the marking quality and machine performance.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure that the workspace has adequate ventilation to avoid the buildup of toxic fumes, especially when marking certain types of rubber that could release harmful gases.
- Inspect and Maintain the Motion System
- Rails and Bearings: The motion system, including rails and bearings, should be lubricated to reduce wear and ensure smooth operation. Clean and inspect the rails regularly for dirt or debris.
- Drive Belt: Check the drive belt for any signs of wear or slippage. If needed, replace the belt to avoid interruptions in machine operation or inconsistency in marking quality.
- Software and Control System Updates
- Laser Control Software: Ensure that the machine’s software is updated and configured to handle the specific types of rubber marking you’re doing. Software updates can provide new features, improve laser control, and enhance compatibility with various rubber materials.
- Calibrate the Laser: Regular calibration ensures optimal focus and marking quality. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for calibrating the laser to ensure consistent results.
- Maintain the Power Supply
- Power Supply Check: Laser marking machines require a stable power supply for proper functioning. Ensure that the power supply is within the recommended range and that there are no fluctuations. Power surges or drops can cause damage to the laser system over time.
- Inspect Cables and Connectors: Over time, cables and connectors can wear out. Regularly inspect all electrical connections for any signs of wear, fraying, or loose connections. Replace or tighten any loose connections to avoid electrical issues.
- General Machine Care
- Protect the Machine from Dust and Debris: Keep the machine’s exterior clean by wiping down surfaces regularly to prevent dust from entering the internal components. Cover the machine when not in use to protect it from environmental contaminants.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Lubricating moving parts, such as the linear rails and motors, can reduce friction and prevent wear. Use the recommended lubricant for your specific machine.
- Record Regular Maintenance: Keep a maintenance log to track cleaning schedules, part replacements, and any issues encountered with the machine. This will help identify patterns that could indicate a problem early.
- Safety Considerations
- Safety Glasses: Always use appropriate laser safety glasses when operating the machine to protect your eyes from harmful laser radiation.
- Fume Management: Ensure that the workspace is equipped with proper fume extraction systems to prevent inhalation of harmful gases released from the rubber during marking.
What is the Durability of Laser-Marking Rubber?
- Rubber Type: The composition of the rubber plays a significant role in how well it holds a laser mark. Natural rubber typically shows good results with CO2 lasers, while synthetic rubbers (like silicone or neoprene) might require special settings to achieve the best results.
- Laser Power and Speed: The laser power and speed settings directly impact how deep or shallow the engraving or marking will be. Higher power settings can create deeper, more durable marks, while lower settings may result in lighter marks that may wear out over time.
- Surface Treatment: The treatment of the rubber surface before marking can also influence the longevity of the marking. A smooth, clean surface will yield better results compared to a rough or contaminated one.
- Exposure Conditions: While laser markings on rubber can be highly resistant, their durability is also determined by the specific environmental conditions the rubber is exposed to. For example, rubber exposed to high temperatures, ozone, or harsh chemicals may cause the laser marking to degrade over time. Some laser marks are resistant to fading due to UV exposure, but extended exposure to sunlight could eventually lead to wear.
- Type of Laser: While CO2 lasers are commonly used for marking rubber, fiber lasers are sometimes employed for certain types of rubber. Fiber lasers can produce finer markings but are generally more effective on harder materials.
What Training is Required to Operate Rubber Laser Marking Machines?
- Basic Laser Safety Training
- Understanding Laser Safety Standards: Laser marking machines, including CO2 and fiber lasers, emit powerful beams that can be hazardous if not handled properly. Training must include knowledge of safety protocols, such as the use of protective eyewear, understanding beam hazards, and implementing laser safety zones.
- Proper Ventilation: Laser marking on rubber can produce fumes and particles. Training will include proper ventilation systems, fume extraction, and how to use the machine’s air assist features to maintain a safe working environment.
- Emergency Procedures: Operators must be trained on how to handle emergencies like fire, electrical failures, or laser malfunctions. They should know the location of safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers, emergency shutoff buttons, and first-aid kits.
- Machine Operation Training
- Basic Functionality of Laser Marking Machines: Operators need to learn the basic functionality of the laser marking machine, including powering it on and off, adjusting laser power, speed, frequency, and focus.
- Loading and Positioning Materials: Correctly positioning rubber material on the laser machine bed and ensuring proper alignment is crucial for accurate marking. Training includes material handling, proper setup, and fixture usage.
- Software Training: Most laser marking machines come with specialized software that controls the design, positioning, and laser settings. Operators must be trained to use this software to upload designs, adjust parameters, and troubleshoot issues.
- Laser Settings Adjustments: Rubber is a material that requires specific settings (power, speed, frequency) to achieve optimal results. Training will involve understanding how to adjust these settings to mark rubber effectively without damaging it.
- Understanding Material-Specific Requirements
- Rubber Types and Variants: Different types of rubber (natural rubber, silicone, neoprene, etc.) may require different laser parameters to achieve the desired result. Operators need to be familiar with these material differences and how they impact the marking process.
- Testing and Adjustments: Operators should be trained to conduct test runs to check the marking quality, depth, and durability on different rubber types. This includes modifying laser settings based on the rubber’s hardness and thickness.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Routine Maintenance: Regular maintenance ensures the longevity of the machine and prevents malfunctions. Operators should be trained in cleaning lenses, mirrors, and other parts of the machine, replacing parts as needed, and calibrating the laser.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Training will cover how to identify and address common issues such as poor marking quality, inconsistent engraving depth, or machine misalignment. Operators should be able to perform basic troubleshooting steps or know when to call for technical support.
- Quality Control and Production Management
- Inspecting Markings: Operators need to be trained to check the quality of laser markings, including legibility, contrast, and uniformity. They should also understand how to inspect the durability of markings under stress or environmental exposure.
- Optimizing Production Workflow: As laser marking is often part of larger production lines, operators may need training on how to optimize workflow, reduce downtime, and improve production efficiency. This could include scheduling, load balancing, and managing job queues.
- Environmental Considerations
- Fume Extraction Systems: Training on the proper use of fume extraction systems is essential because rubber can emit potentially harmful gases and particulates when laser-marked. Operators must know how to use these systems to ensure safe working conditions.
- Waste Management: Training on how to handle and dispose of waste materials generated during the laser marking process is critical to maintain a safe and clean environment.
- Certification and Continuing Education
- Certification Programs: Some laser equipment manufacturers or training organizations offer certification programs that validate an operator’s proficiency with laser systems. These certifications can ensure operators are up to date with the latest safety standards and technological advances.
- Ongoing Education: Since technology and rubber material innovations evolve, operators may need to take refresher courses or attend training sessions to keep their skills current.
What is the Lifespan of Rubber Laser Marking Machines?
- Quality of the Laser Source
- CO2 Lasers: The lifespan of a CO2 laser source (the heart of most rubber laser marking machines) is typically around 8,000 to 15,000 hours of operation, depending on the quality and power of the laser tube. Lower-power laser tubes generally last longer, while high-power tubes may degrade faster.
- Fiber Lasers: If the machine uses a fiber laser (less common for rubber marking but used for specific tasks), the lifespan can be longer, around 25,000 to 30,000 hours, since fiber lasers don’t use consumable parts like CO2 lasers do.
- Usage Intensity
- Heavy Use: Machines used in high-volume environments or for prolonged hours daily (such as in industrial settings) may experience more wear and tear, shortening their lifespan. Frequent heavy use can also lead to faster degradation of critical components like the laser source, cooling systems, and mechanical parts.
- Light Use: Machines that are used intermittently or for light-duty applications will typically last longer since the components undergo less stress.
- Maintenance Practices
- Routine Maintenance: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of a rubber laser marking machine. This includes cleaning the laser lenses, mirrors, and cooling systems, checking for alignment, and replacing worn-out components like belts or fans. A well-maintained machine can last significantly longer than one that is neglected.
- Preventative Maintenance: Scheduling regular checks to replace consumables, such as the laser tube or air filters, is essential to keep the machine running efficiently and prevent more serious damage.
- Environmental Conditions
- Dust and Debris: A clean operating environment can prolong the life of the machine. Dust and debris in the air can damage optical components like lenses and mirrors, which may require frequent cleaning and replacement.
- Temperature and Humidity: Laser machines are sensitive to temperature extremes and humidity. Ensuring the machine operates in a stable, controlled environment will minimize the risk of premature breakdowns.
- Technological Obsolescence
- Advancements in Technology: While the physical lifespan of a laser machine might be 10-20 years, the technological advancements in laser technology could make older machines seem obsolete. Newer models may feature improved efficiency, faster processing speeds, and more advanced features that older machines may lack. This could prompt businesses to upgrade or replace their machines even if the old ones are still functioning.
- Component Lifespan
- Laser Tube and Power Supply: These components are often the first to wear out, especially in CO2 laser systems. Laser tubes typically need replacement every 2,000 to 4,000 operating hours (depending on power and usage), which can significantly affect the machine’s overall lifespan.
- Cooling System: Over time, the cooling system (often water or air-cooled) may become less efficient, which can lead to overheating and reduced machine life if not properly maintained.
- Mechanical Parts: The mechanical components, such as motors, rails, and belts, also have a finite lifespan. Regular lubrication and periodic replacement can prevent mechanical breakdowns.
- Software and Control Systems
- While the software itself may not directly impact the lifespan of the machine, older software may become incompatible with newer operating systems or may not receive updates. In such cases, the control system might require upgrades or complete replacement after several years.








