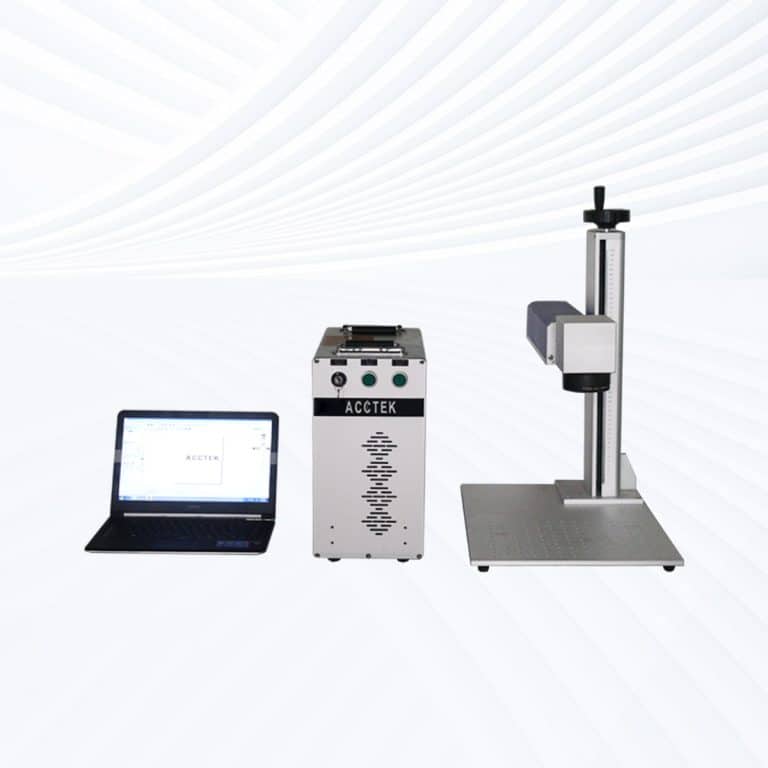
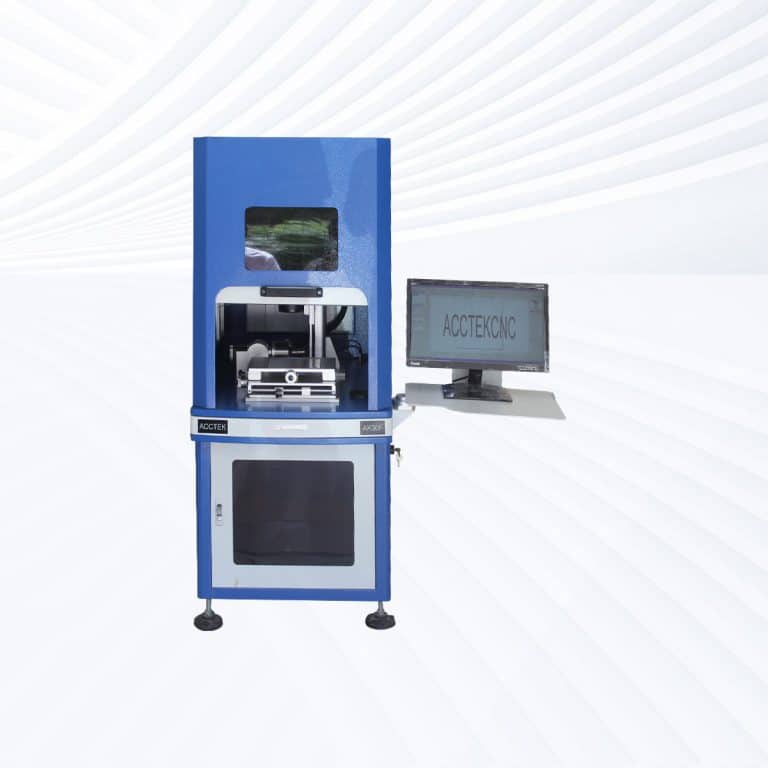
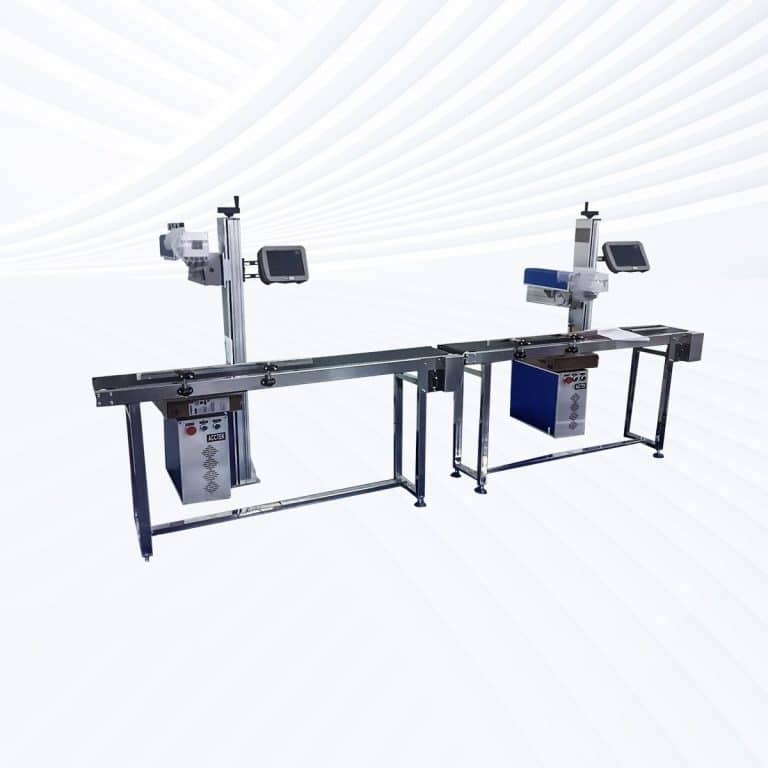
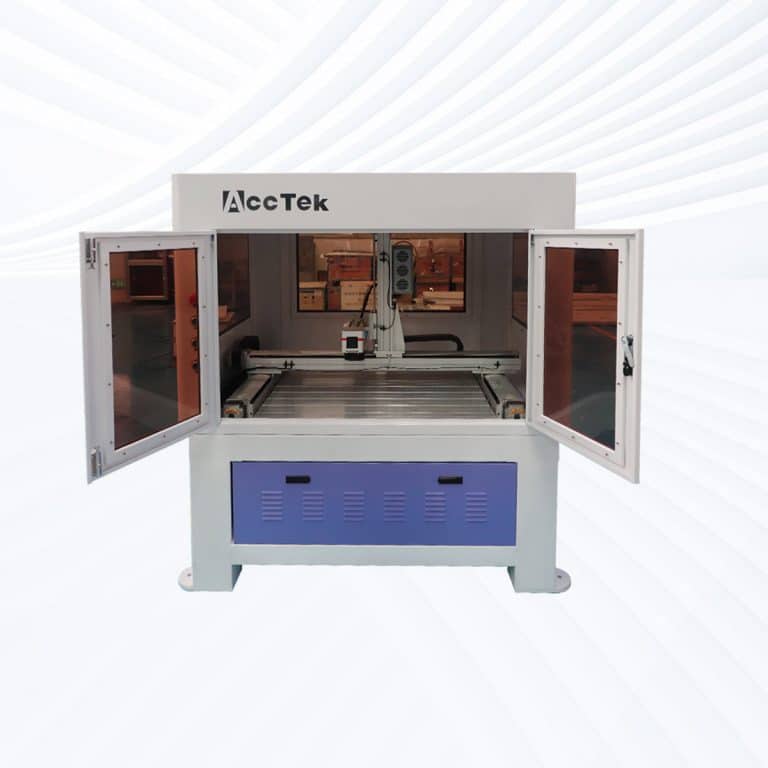
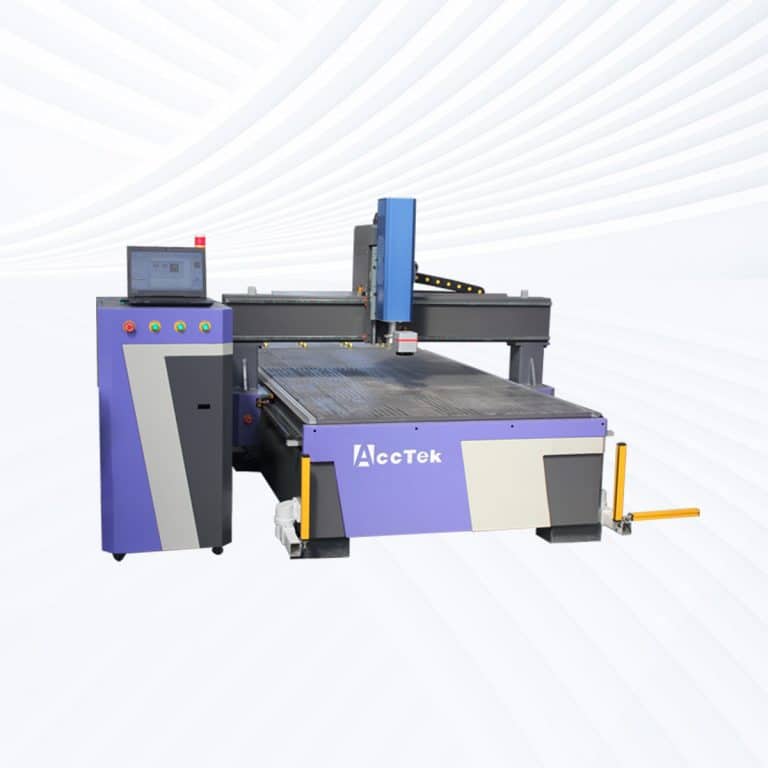
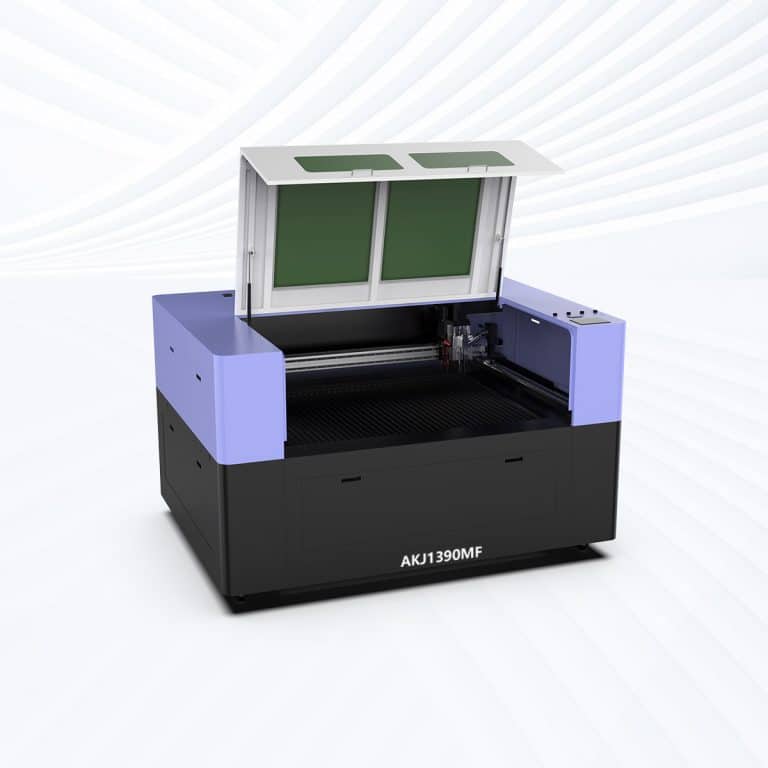
Product Introduction
Benefits of Laser Marking Plastic
Non-Contact, Damage-Free Marking
Laser marking is a non-contact process that applies no pressure to the plastic surface. This eliminates the risk of deformation, cracking, or wear, making it ideal for delicate or thin plastic components requiring precise, clean, and safe identification.
Permanent and Legible Results
Laser marks are highly durable, resistant to fading, abrasion, and chemicals. Whether exposed to UV light, moisture, or frequent handling, the mark remains sharp and readable, perfect for long-term traceability and compliance in demanding industries.
No Consumables Required
Unlike ink-based methods, laser marking doesn't use inks, chemicals, or labels. This reduces ongoing costs, simplifies maintenance, and eliminates waste, making the process both environmentally friendly and economically efficient over the lifetime of the equipment.
High-Speed, High-Volume Production
Plastic laser marking machines operate at high speeds with excellent repeatability, supporting fast production cycles without sacrificing quality. Ideal for automated manufacturing, they increase throughput while maintaining precise marking on every item.
Wide Material Compatibility
These machines can mark a broad range of plastics, including ABS, PE, PVC, PC, PP, and more. With the right laser type (fiber, CO2, or UV), you can achieve high-contrast marks on virtually any plastic surface or color.
Easy Integration and Automation
Modern systems are designed for seamless integration into existing production lines. With software-driven controls and support for automation, laser marking machines can be customized to match specific workflows, reducing labor and ensuring consistent results.
Compatible Plastic Materials
- ABS
- PC
- PVC
- PET
- PE
- PP
- PS
- PA
- POM
- PMMA
- PTFE
- PBT
- PPS
- SAN
- TPU
- TPE
- LCP
- EVA
- PI
- PES
- PPO
- CPVC
- UHMW
- LDPE
- HDPE
- FEP
- PVDF
- PFA
- PEEK
- PSU
- TPO
- ETFE
- Polyetherimide
- Polycarbonate-ABS Blends
- Thermoset Plastics
- BOPP
- HIPS
- Acrylic-Modified Plastics
- Bioplastics
- Ion-Doped Plastics
Application of Plastic Laser Marking Machines








Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Marking Technologies
| Feature | Laser Marking | Screen Printing | Pad Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Quality | High precision, sharp detail, no smudging | Good, but may blur on curved surfaces | Good for small, uneven areas | High resolution, but less durable |
| Durability | Permanent and wear-resistant | Fades with abrasion or chemicals | Moderate durability | Susceptible to wear and chemicals |
| Speed | High-speed marking for mass production | Slower setup, moderate production speed | Moderate | Fast for short runs |
| Setup Time | Minimal, software-based | High – requires screens | High – requires pad tooling | Moderate setup time |
| Customization | Extremely flexible with quick design changes | Limited – needs new screens per design | Limited – pad changes required | Flexible for design updates |
| Contact with Surface | Non-contact process | Direct contact | Direct contact | Minimal contact |
| Tool Wear | None – no physical contact | Screens degrade over time | Pads wear out regularly | Low tool wear |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no inks or solvents | Uses inks, solvents, and screens | High – uses inks, pads, solvents | Moderate – ink use involved |
| Cost per Mark (Long-Term) | Low – no consumables needed | Higher due to consumables and maintenance | High – frequent pad and ink replacement | Moderate cost, depends on ink use |
| Maintenance Needs | Very low | Frequent cleaning and screen replacement | Pad replacement and cleanup required | Moderate maintenance |
| Surface Compatibility | Works on flat, curved, or textured surfaces | Best on flat surfaces | Good for irregular shapes | Best on flat or slightly curved surfaces |
| Material Compatibility | Wide plastic compatibility (ABS, PP, PET, etc.) | Limited to ink-adherent plastics | Moderate – depends on ink adhesion | Moderate – needs specific surface prep |
| Automation Potential | Easy to automate and integrate into production | Harder to automate | Limited automation potential | Moderate automation compatibility |
| Marking Depth | Adjustable (engraving, surface effects) | Surface ink only | Surface ink only | Surface ink only |
| Repeatability | Excellent – consistent every time | Varies depending on screen condition | Consistent but depends on pad condition | Good repeatability |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

Can Lasers Be Used For Marking On Curved or Irregular Surfaces
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of laser marking, including how it works, key technologies, applications, costs, and factors that determine when it is the right marking solution.

What Types of Laser Marking Machines Are There
This article explains the main types of laser marking machines, covering laser sources, marking methods, materials, applications, and how to choose the right system for production needs.
What Safety Precautions Are Required For Laser Marking
This article outlines essential safety precautions required for laser marking, including equipment safety, operator training, emergency protocols, and routine maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations.

How to Achieve High Contrast in Laser Marking
This article comprehensively covers the technologies, parameters, materials, and process controls required for consistent, high-contrast laser marking in industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Plastic Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines ($2,500 to $30,000): Fiber lasers are typically used to mark engineered plastics or composite materials with high contrast. They excel in high-speed marking and offer long lifespans, making them suitable for industrial settings. However, fiber lasers can cause burning or melting on softer or light-colored plastics. Entry-level systems are great for basic logos and serial numbers, while high-end models support automation, deep engraving, and integration with production lines.
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines ($3,500 to $28,000): CO2 lasers are highly effective on organic and non-metallic plastics such as ABS, polyethylene, polypropylene, acrylic (PMMA), and polystyrene. They are ideal for packaging, signage, and labeling applications. Basic desktop units are available at the lower end, while high-speed, enclosed systems with conveyor integration or galvo heads fall on the higher end. These lasers offer non-contact, permanent marking, but may have limited effect on highly reflective or transparent plastics.
- UV Laser Marking Machines ($4,500 to $20,000): UV lasers are the most versatile for plastics, especially when dealing with heat-sensitive materials or fine-detail marking. Their low heat output means they can mark plastics without burning or deformation. They’re widely used in medical devices, electronics, and consumer packaging where clean, precise, and permanent marks are essential. UV machines cost more per watt, but they excel in delicate, high-contrast, and microtext marking.
- Factors That Influence Pricing:
- Power and Speed: Higher wattage enables faster marking or deeper engraving, but increases price.
- Build and Enclosure: Fully enclosed systems offer better safety and dust protection, but cost more.
- Software and Automation: Machines with touchscreen controls, rotary attachments, barcode reading, or integration into production systems will command a higher price.
- Cooling and Optics: Air-cooled systems are standard, but high-power machines may require water cooling and more expensive optics for precision.
Which Laser Marking Machine is Best for Marking Plastic?
- Fiber Laser Marking Machine: Fiber lasers are commonly used in metal marking, but they can mark some high-performance engineering plastics, such as PEEK, polycarbonate, and Delrin (acetal). They offer fast marking speed and high contrast, especially on dark or filled plastics. However, they tend to generate more heat, which can lead to melting, bubbling, or charring on softer plastics. Fiber lasers are suitable for:
- Industrial parts made of technical plastics
- High-speed production lines with filled plastics
- Applications where deep marking is acceptable
- CO2 Laser Marking Machine: CO2 lasers are better suited for organic and softer plastics, including ABS, acrylic, polyethylene, and polycarbonate. They work by heating and vaporizing the surface of the material, leaving a clean, legible mark. CO2 lasers are non-contact, cost-effective, and offer wide compatibility with packaging, signage, and consumer products. However, they can struggle with very reflective or clear plastics. Best for:
- Consumer goods and product packaging
- Acrylic signage and ID tags
- Marking large batches of standard thermoplastics
- UV Laser Marking Machine: UV lasers are the most versatile and precise option for marking plastic. They use a shorter wavelength (typically 355 nm), allowing for “cold marking” that minimizes heat buildup. This makes UV lasers ideal for heat-sensitive, thin, or light-colored plastics and applications requiring fine detail. The marks are clear, high-contrast, and permanent without surface damage. UV lasers excel in:
- Medical devices and electronics with strict precision requirements
- Light or translucent plastics, where other lasers cause discoloration
- High-resolution logos, codes, or microtext on delicate components
How Do I Remove Laser Markings from Plastic?
- Mechanical Abrasion: Light laser markings, such as surface charring or discoloration, can often be removed by gentle sanding or polishing. Use fine-grit sandpaper (e.g., 600–1200 grit) or a micro-abrasive pad to smooth the surface. This method is more effective on thicker, opaque plastics like ABS or polycarbonate, but it may leave visible scuff marks or uneven surfaces if not done carefully.
- Solvent or Chemical Cleaning: Some plastics—particularly those marked with UV lasers—undergo a surface chemical reaction rather than deep engraving. For these, mild solvents like isopropyl alcohol or acetone (on acetone-safe plastics) may help lighten or dissolve superficial marks. Always test a small area first, as harsh solvents can warp, cloud, or discolor the plastic.
- Thermal Reflow (for Thermoplastics): On certain thermoplastics, gently heating the surface with a heat gun can cause the polymer to soften and reflow, partially reducing the appearance of shallow marks. Use low heat and monitor carefully to avoid distortion or bubbling. This technique is not suitable for heat-sensitive plastics or precision parts.
- Surface Recoating: If removal is not feasible without damaging the plastic, applying a coating or finish may help conceal the mark. Options include paint, vinyl wraps, plastic fillers, or texturing sprays designed for plastic surfaces. This is often used in product refurbishing or aesthetic restoration.
- Laser Reprocessing (Advanced): In controlled environments, some manufacturers use a second laser pass to “erase” marks by blending them into the surrounding surface, either by annealing or retexturing. This requires high-precision laser control and may not be effective on deep engravings or certain plastics.
- Limitations and Considerations:
- Engraved or deep marks are difficult or impossible to fully remove without reshaping or damaging the part.
- Transparent or glossy plastics often show removal attempts more clearly than textured or matte surfaces.
- Always verify plastic compatibility before applying heat or solvents, as some materials like PVC can release harmful fumes or degrade rapidly.
Is Laser Marking Plastic Safe?
- Laser Emissions and Eye Safety: All laser marking systems emit high-intensity beams that pose serious risks to eyes and skin. Fiber, CO2, and UV lasers can cause permanent eye damage from direct or reflected beams. To ensure operator safety:
- Use fully enclosed machines or protective housings
- Wear appropriate laser safety goggles rated for the machine’s wavelength
- Follow Class 1 laser system standards where possible for risk-free use
- Plastic Composition and Fume Hazards: Some plastics, when marked with lasers, release toxic fumes or particulate matter. This is especially true for plastics that contain halogens, flame retardants, or fillers. Common hazards include:
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride): Emits chlorine gas, which is corrosive and toxic. Never laser mark PVC.
- ABS and polycarbonate: Can release styrene or bisphenol-A (BPA), both of which are harmful in enclosed spaces.
- Treated or dyed plastics: May produce unknown or harmful byproducts depending on their chemical additives.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: To mitigate air quality risks, proper fume extraction systems with HEPA and activated carbon filters should be used. These systems capture harmful particulates and neutralize toxic gases before they circulate in the workspace. Ventilation is especially important in high-volume or enclosed operations.
- Thermal Damage and Fire Risk: Laser energy generates heat, and plastics are flammable. Improper focus, too much power, or lack of supervision can cause melting, ignition, or uncontrolled smoke. Use:
- Air assist to blow away debris and reduce heat buildup
- Flame-retardant work surfaces
- Fire suppression systems or extinguishers should be nearby in industrial environments
- Residual Mark Safety (Post-Marking): Once properly marked and ventilated, the finished plastic part is typically safe for use, even in sensitive applications like medical or food-contact components, provided the material itself meets regulatory standards. UV laser marking is often preferred in these cases due to its minimal heat impact and precision.
How Should I Choose Plastic Laser Marking Machines?
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines: CO2 lasers are commonly used for marking plastics such as ABS, acrylic, polystyrene, and polyethylene. They produce marks by heating the surface, often resulting in a foamed or discolored area with good contrast. These machines are affordable and efficient for applications like consumer packaging, labels, and nameplates. However, they may cause melting or deformation of thin or heat-sensitive plastics.
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines: Fiber lasers are typically used for metal marking, but they can mark filled or engineered plastics like Delrin, PEEK, and certain polyamides. Their high power and deep penetration make them suitable for durable, high-contrast marks, though they generate more heat, which can damage softer or light-colored plastics. Fiber lasers are best for industrial components where speed and mark permanence are critical.
- UV Laser Marking Machines: UV lasers are the most versatile and safest option for marking plastics. They use a short wavelength (355 nm) that allows for cold marking, producing sharp, high-resolution marks without burning or melting the plastic surface. UV lasers are especially effective on sensitive materials, such as white plastics, clear polymers, and medical-grade components. They’re commonly used in electronics, medical devices, and fine-detail branding.
- Factors to Consider When Choosing:
- Plastic Type: CO2 is ideal for common thermoplastics, fiber lasers for industrial-grade polymers, and UV for delicate or specialty plastics.
- Marking Contrast and Detail: For clean, legible codes, logos, or serial numbers—especially on light or clear plastics—UV lasers offer the best precision and clarity.
- Heat Sensitivity: Choose a UV system for materials that deform easily under heat. Avoid fiber lasers for low-melting-point plastics unless testing proves compatibility.
- Production Speed and Volume: Fiber and CO2 lasers offer faster processing for high-volume lines. UV systems are slower but excel in precision and low-damage marking.
- Budget: CO2 lasers are generally the most cost-effective, with UV systems being more expensive due to their precision optics and cooling systems. Fiber lasers fall in the middle range but are less suitable for general plastic use.
- Work Environment: In enclosed or sensitive spaces, machines with built-in fume extraction, laser shielding, and low heat output (like UV systems) are safer and more operator-friendly.
What Are the Environmental Requirements for Using Plastic Laser Marking Machines?
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Plastic laser marking produces smoke, vapors, and potentially toxic gases depending on the type of plastic being marked. Materials like ABS and polycarbonate release harmful compounds when heated. For safety and air quality, a laser fume extractor equipped with HEPA and activated carbon filters is essential. Ducted exhaust systems should be used to remove fumes from the workspace entirely.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Plastic laser marking machines perform best in environments where the ambient temperature is kept between 18℃ and 25℃ (64℉ to 77℉). Operating in extreme temperatures can affect marking quality and internal electronics. Humidity should be maintained between 40% and 60% to prevent static discharge, which can damage sensitive electronics, and to avoid condensation on optics that could interfere with the laser beam.
- Dust-Free Environment: Dust and airborne particles can interfere with the optics and precision parts of the machine. Plastic particles or static-laden dust from other processes should be kept out of the marking area. Use the machine in a cleanroom or enclosed workspace if high-quality, high-precision marking is required.
- Stable Surface and Vibration-Free Setup: For accurate laser marking, the machine must be placed on a stable, vibration-free work surface. External vibrations can misalign the laser beam, affecting marking sharpness and consistency. Avoid locating the machine near heavy industrial equipment or high foot traffic areas.
- Electrical Requirements: Plastic laser marking machines require a stable power supply—typically 110V or 220V, depending on the model. Surge protectors or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) are recommended to protect the machine from voltage spikes and sudden outages, which can interrupt operation or damage internal components.
- Lighting and Accessibility: Good lighting is important for aligning parts, inspecting marks, and maintaining equipment. Ensure the work area is well-lit and easily accessible for cleaning and troubleshooting. Machines should also have easy access to emergency stop buttons and ventilation controls.
- Safety Measures: All laser marking systems must be operated in a designated laser-safe area. Use proper shielding or Class 1 laser enclosures to prevent exposure to stray beams. Operators should wear laser safety goggles rated for the wavelength of the system (e.g., 1064 nm for fiber, 10.6 μm for CO2, 355 nm for UV). Keep flammable materials away from the marking zone, and have fire extinguishers nearby for emergencies.
What is the Lifespan of Plastic Laser Marking Machines?
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines: CO2 lasers commonly use sealed glass or metal RF (radio frequency) tubes.
- Glass tube CO2 lasers typically last 2,000 to 10,000 hours, depending on quality and usage intensity. They are more affordable but require more frequent replacement or recharge.
- Metal RF CO2 tubes, used in industrial machines, can last 20,000 to 40,000 hours, making them more suitable for high-volume production.
- Regular maintenance of optics, ventilation systems, and alignment keeps these machines running smoothly for 8 to 10 years or more.
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines: Fiber lasers are known for their exceptional longevity, with lifespans often rated at 80,000 to 100,000 hours.
- These systems require minimal maintenance, as the fiber laser source is sealed and solid-state.
- With proper care, a fiber laser marking system can operate reliably for 10 to 15 years, even in demanding environments.
- UV Laser Marking Machines: UV lasers use diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) or frequency-tripled Nd:YVO4 or Nd:YAG lasers.
- These systems typically offer 10,000 to 25,000 hours of operating life.
- While not as long-lasting as fiber lasers, they offer precision and low-heat marking essential for sensitive plastic materials.
- With routine upkeep and use in clean, stable environments, UV systems generally last 6 to 10 years.
- Factors That Affect Lifespan:
- Usage Intensity: High-duty cycles, 24/7 operation, or marking dense materials can shorten component life.
- Environmental Conditions: Dust, heat, humidity, or poor ventilation accelerate wear on optics, electronics, and cooling systems.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning of lenses, filters, fans, and galvo motors ensures consistent performance and avoids premature failure.
- Component Replacement: Even long-lasting systems may require occasional replacement of scanners, lenses, power supplies, or control boards after 5–8 years.
How Should I Maintain Plastic Laser Marking Machines?
- Optics and Lenses: Over time, marking plastic produces vapors and fine particles that can settle on the lens or mirrors, reducing beam quality. Clean optics:
- Weekly or bi-weekly, using lens-safe wipes and alcohol-based optical cleaner
- Inspect for burn marks, cloudiness, or residue that could distort the laser path
- Avoid touching lenses with your bare hands, as oils can damage coatings
- Air Filters and Fume Extractors: Laser marking plastic generates fumes that can be corrosive or toxic, depending on the material.
- Check and clean intake filters monthly; replace HEPA or carbon filters every 3–6 months or as recommended by the manufacturer
- Make sure exhaust fans and ducts are clear of debris and functioning properly
- A clogged extractor reduces air quality and can allow contaminants to build up inside the machine
- Cooling System (if equipped): UV and high-powered CO2 laser marking systems may use water cooling; others are air-cooled.
- Air-cooled units: Clean fan inlets and ensure airflow is not blocked
- Water-cooled units: Check coolant level, inspect hoses for leaks, and flush the system every 6–12 months to prevent corrosion or biological growth
- Laser Tube or Source (CO2 and UV): Glass CO2 laser tubes degrade over time.
- Monitor output power and replace glass tubes every 2,000–10,000 hours
- Metal RF tubes (in higher-end models) and UV laser modules may need professional servicing or calibration after several years
- Galvo Scanner and Mechanical Parts: The galvo head (laser mirror system) must move freely and precisely.
- Avoid any physical shock or vibration to this assembly
- If precision drifts, realignment or recalibration by a technician may be needed
- Clean the marking area regularly to prevent dust buildup on moving components
- Software and Firmware: Keep the marking software (e.g., EZCAD or proprietary platforms) and firmware up to date.
- Back up custom marking files, templates, and settings
- Update firmware cautiously, following the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid system crashes
- Electrical Safety and Power Supply: Inspect cables, connectors, and grounding.
- Use a surge protector or UPS to shield against voltage spikes
- Watch for signs of overheating or electrical noise, especially in humid or dusty conditions
- Alignment Checks and Calibration: Over time, laser output or focus may drift slightly.
- Periodically check beam alignment, focus distance, and mark quality using test patterns
- Recalibrate when switching between different plastic types or marking depths
- Maintenance Logs and Schedules: Use a checklist or logbook to track cleaning, filter changes, and inspections.
- Set monthly, quarterly, and annual tasks to catch issues early
- A consistent schedule improves output quality and helps justify warranty or support claims






