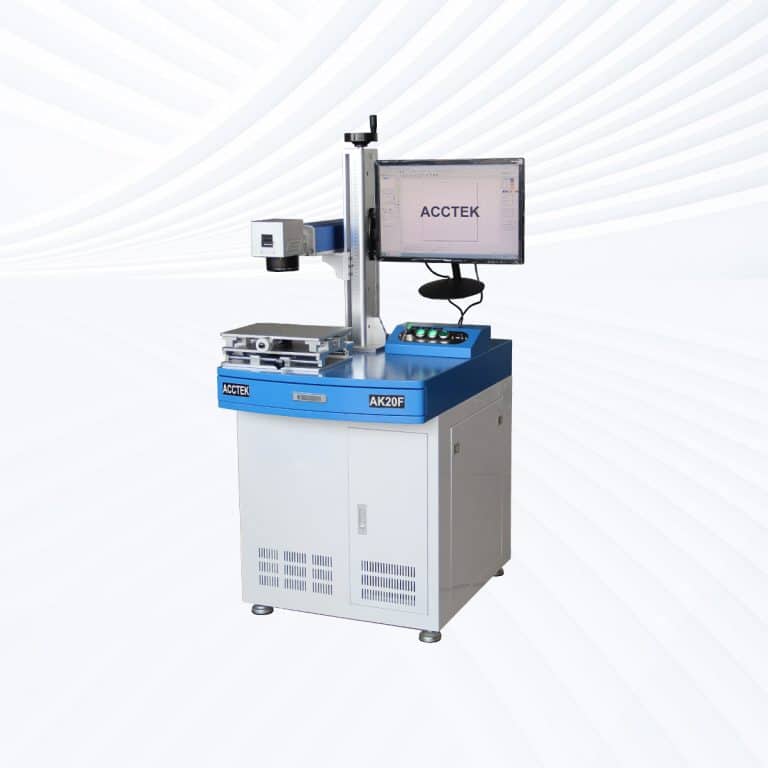
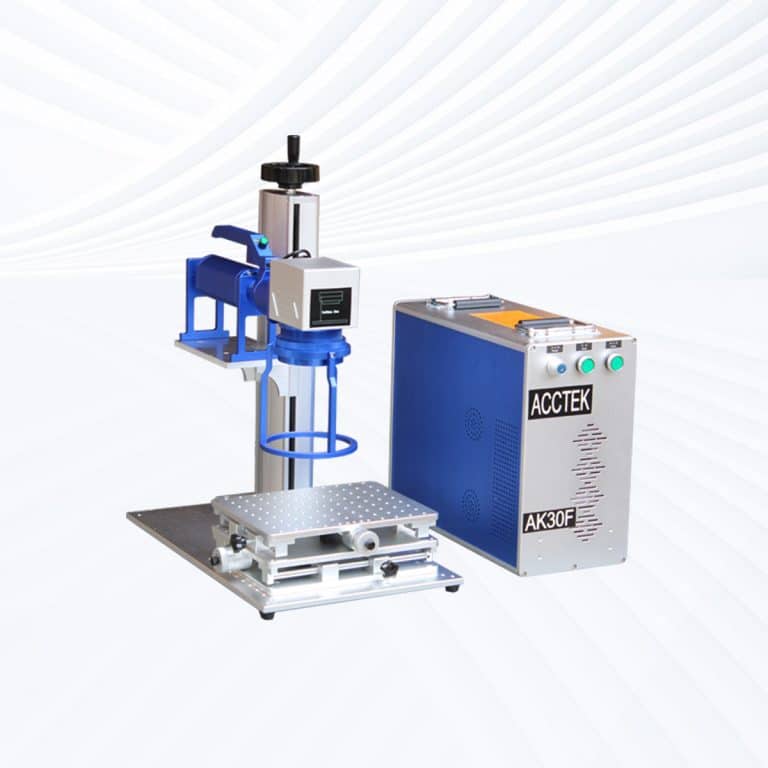
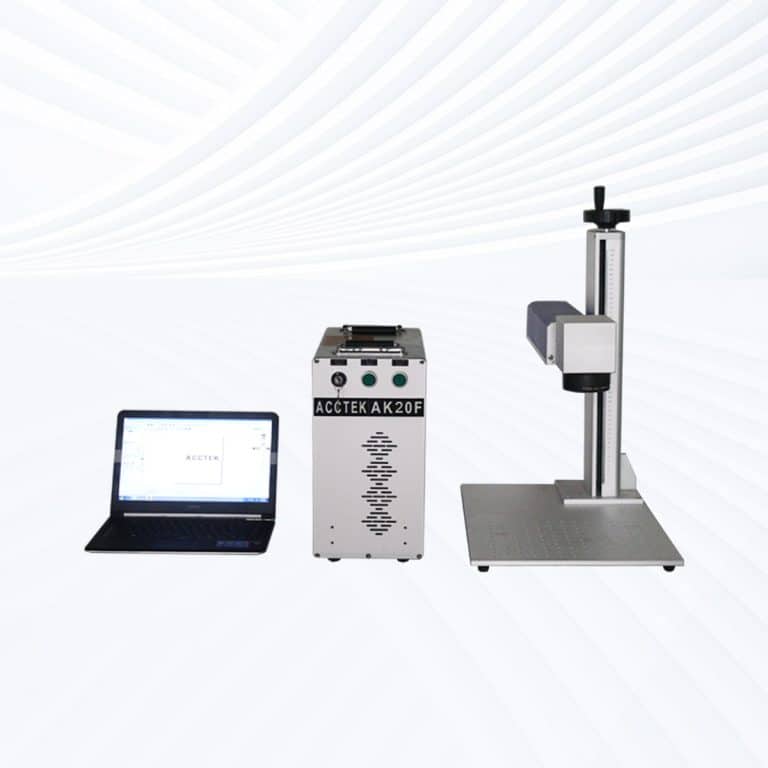
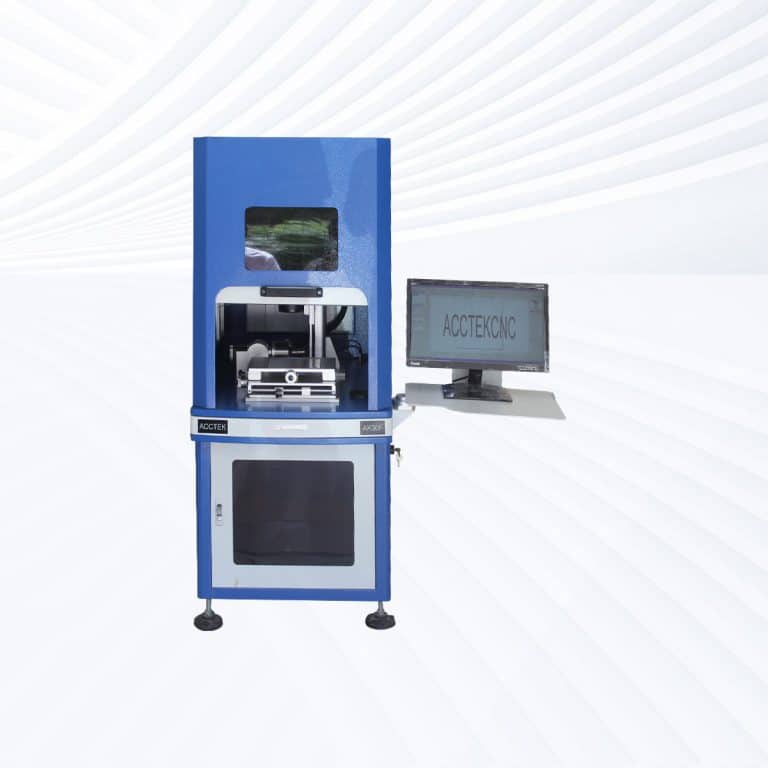
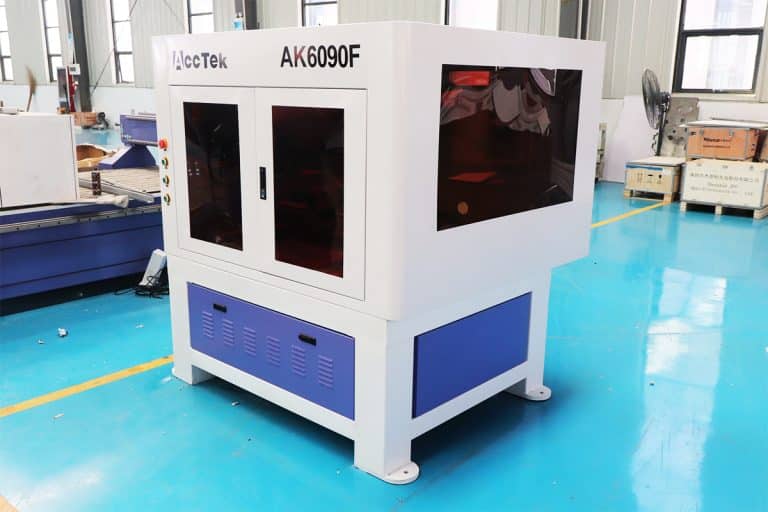
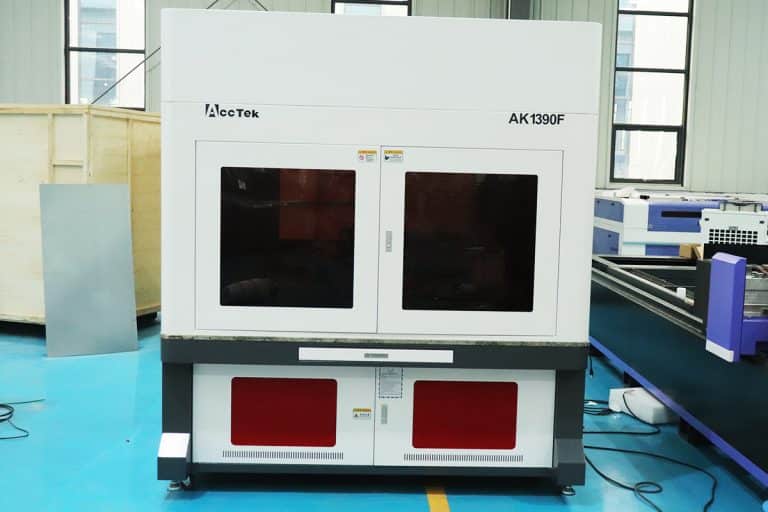
Product Introduction
Benefits of Laser Marking Metal
Permanent and Durable Marks
Laser marking creates high-contrast, wear-resistant marks that won't fade, chip, or peel over time. This permanence makes it ideal for parts requiring long-term identification in harsh environments such as heat, abrasion, or chemical exposure.
High Precision and Accuracy
Fiber laser marking systems deliver micron-level precision, allowing for clean, detailed marks on even the smallest components. This ensures consistency across large production runs and supports the intricate needs of industries like aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
No Contact, No Damage
Laser marking is a non-contact process, which means there's no mechanical pressure or risk of deforming the metal surface. It preserves the integrity of delicate or precision-engineered parts while ensuring consistent, high-quality results.
Low Operating Costs
With no need for inks, chemicals, or replacement tools, laser marking is a low-maintenance solution. The high efficiency and long lifespan of fiber lasers also contribute to lower overall operating costs over time, maximizing return on investment.
Fast Processing Speeds
Laser marking machines operate at high speeds without sacrificing quality. This boosts productivity and shortens turnaround times, making them well-suited for high-volume manufacturing and fast-paced production environments.
Environmentally Friendly
Unlike traditional marking methods, laser marking doesn't use toxic chemicals or generate waste. It's a clean, energy-efficient process that aligns with modern sustainability goals and helps manufacturers meet environmental compliance standards.
Compatible Metal Materials
- Stainless Steel
- Carbon Steel
- Mild Steel
- Tool Steel
- Galvanized Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Aluminum
- Anodized Aluminum
- Cast Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass
- Bronze
- Titanium
- Anodized Titanium
- Tungsten
- Nickel
- Nickel Alloys
- Inconel
- Monel
- Cobalt
- Cobalt-Chrome
- Chrome
- Zinc
- Zinc Alloys
- Magnesium
- Molybdenum
- Tantalum
- Niobium
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Gold
- Silver
- Rhodium
- Beryllium Copper
- Lead
- Pewter
- White Metal
- High-Speed Steel (HSS)
- Hardox Steel
- Maraging Steel
Application of Metal Laser Marking Machines







Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Marking Technologies
| Feature | Laser Marking | Screen Printing | Pad Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Quality | High precision, clean, permanent | Moderate; can blur over time | Good but limited detail | Good resolution, but not permanent |
| Durability | Excellent – wear, heat, and chemical-resistant | Poor – easily fades or wears off | Moderate – can wear over time | Low – not suited for harsh environments |
| Speed | Very fast, especially for large batches | Slow setup, moderate production speed | Moderate | Fast for short runs |
| Material Compatibility | Works on all metals | Limited to flat surfaces with coatings | Works on curved/small parts, limited to coatings | Limited by surface treatment |
| Setup Time | Minimal | High – screens must be prepared | High – pads must be custom-made | Moderate |
| Customization Flexibility | Extremely high, software-controlled | Low – new screens needed for changes | Low – limited by pad design | High |
| Tool Wear | None (non-contact) | Moderate | Moderate to high | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Low – no chemicals or inks | High – uses inks and solvents | High – uses pads, inks, waste | Medium – some ink use |
| Cost Per Mark (Long Term) | Low after initial investment | Medium to high | High due to consumables | Medium |
| Consumables | None required | Inks, screens | Inks, pads | Inks |
| Maintenance Needs | Very low | High – frequent cleaning and replacement | High – pad wear and ink handling | Moderate |
| Automation Integration | Easy to integrate into production lines | Difficult | Moderate | Moderate |
| Marking Depth | Adjustable (engraving or surface) | Surface only | Surface only | Surface only |
| Repeatability | Excellent – exact and consistent | Moderate – subject to manual variation | Moderate | Good |
| Traceability Capability | Ideal – supports barcodes, QR codes, UID | Poor – hard to scan printed marks | Moderate | Moderate |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

Can Lasers Be Used For Marking On Curved or Irregular Surfaces
This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of laser marking, including how it works, key technologies, applications, costs, and factors that determine when it is the right marking solution.

What Types of Laser Marking Machines Are There
This article explains the main types of laser marking machines, covering laser sources, marking methods, materials, applications, and how to choose the right system for production needs.
What Safety Precautions Are Required For Laser Marking
This article outlines essential safety precautions required for laser marking, including equipment safety, operator training, emergency protocols, and routine maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations.

How to Achieve High Contrast in Laser Marking
This article comprehensively covers the technologies, parameters, materials, and process controls required for consistent, high-contrast laser marking in industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Metal Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- Entry-Level Machines ($2,500–$6,000): These are compact, lower-power fiber laser markers (typically 20W–30W) designed for small-scale marking tasks on metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, or titanium. Ideal for hobbyists, startups, or light-duty industrial use. They often come with basic software and manual focus adjustment.
- Mid-Range Machines ($6,000–$15,000): These offer more power (30W–50W), better marking speed, and advanced features like auto-focus, rotary attachments for cylindrical objects, and improved heat dissipation systems. They’re built for small to medium manufacturing lines and can handle high-contrast marks, deeper engravings, and more complex patterns.
- High-End Industrial Systems ($15,000–$30,000): At this level, machines often include 60W+ fiber lasers, MOPA technology (for color marking on metals), large work areas, enclosed safety housings, and integration options for automation. These are designed for continuous, high-volume production environments and provide extremely fine resolution and durability for aerospace, automotive, or medical industries.
- Factors Affecting Price:
- Laser Type: Most metal marking machines use fiber lasers, but prices can vary depending on whether the system includes MOPA, CW, or pulsed technology.
- Power Output: Higher wattage increases marking depth and speed, but raises the cost.
- Cooling System: Air-cooled systems are cheaper and more compact, while water-cooled systems handle higher workloads.
- Software & Control Systems: More advanced software means greater precision, better graphics support, and easier automation.
- Build Quality and Brand Support: Machines from reputable manufacturers tend to cost more, but they also offer better customer support, training, and longer warranties.
Which Laser Marking Machine is Best for Marking Metal?
- High Absorption by Metals: Metals absorb the 1064nm wavelength of fiber lasers far better than the CO2 or UV spectrum, which makes fiber lasers both faster and more energy-efficient for metal marking tasks.
- No Need for Additives: Unlike some CO2 laser marking systems that require a marking spray or paste to work on metal, fiber lasers mark metal directly—no prep, no consumables.
- Minimal Maintenance, Long Life: Fiber laser sources often last 100,000 hours or more, require no mirror alignment, and utilize air cooling systems, thereby reducing maintenance.
- Marking Types: Fiber lasers can perform annealing (oxidation under the surface), engraving (material removal), deep engraving, foaming, and black marking depending on the material and laser settings.
- Speed and Automation: Fast marking speeds make fiber lasers an ideal choice for industrial settings, including mass production, where traceability and compliance are crucial.
What are The Disadvantages of Laser Marking Metal?
- High Initial Cost: Fiber laser marking systems, especially those with higher power or advanced features like MOPA technology, come with a significant upfront investment. Even entry-level models are more expensive than many other marking methods, such as inkjet or stamping.
- Material Sensitivity: While fiber lasers are effective on most metals, different alloys respond differently to laser energy. For example, anodized aluminum marks easily, but some stainless steel grades may require fine-tuning of parameters to avoid poor contrast or shallow markings.
- Surface Alteration Risk: Laser marking involves localized heating. If settings aren’t optimized, this can lead to unintended effects such as warping, micro-cracking, or weakening of thin or delicate metal parts, especially on fine instruments or precision components.
- Slower for Deep Engraving: For deep marking or engraving, multiple passes are needed, which slows down the process. Compared to mechanical engraving, this can result in lower throughput in high-volume operations where depth is required.
- Safety Concerns: Laser systems—especially high-powered ones—pose eye and skin hazards. Proper safety measures, such as enclosures, goggles, and ventilation systems, are essential. Failing to manage fumes from coated or treated metals can expose users to harmful particles.
- Limited Color Options: Most fiber laser marking systems produce high-contrast marks (black, gray, or white), but color marking is limited to specific machines (MOPA lasers) and only works on select metals like titanium and stainless steel. Even then, color durability may vary.
- Power Consumption and Maintenance: While generally efficient, fiber laser systems still require consistent cooling and may have sensitive optics that need periodic inspection or cleaning. Improper maintenance can reduce mark quality over time.
- Complex Setup for Variable Work: When marking different shapes, sizes, or materials, switching settings, adjusting focus, and calibrating the machine can slow production and require experienced operators.
What is the Lifespan of Metal Laser Marking Machines?
- Fiber Laser Source (Core Component): Most metal laser marking machines use a fiber laser source rated for 80,000 to 100,000 hours of operation. This translates to over a decade of use in standard industrial settings, assuming a few hours of daily operation. Some high-end sources can last even longer with consistent maintenance and controlled conditions.
- Scanning System (Galvo Head): The galvanometer head, which directs the laser beam, typically lasts 5–10 years, depending on workload and exposure to dust or vibration. Over time, mirror alignment and motor wear may affect marking precision, requiring adjustment or replacement.
- Optics and Lens: Marking lenses and protective windows can degrade with exposure to dust, fumes, or accidental contact. These components often last 3–5 years with regular cleaning and air filtration, but may need earlier replacement in harsh environments.
- Cooling and Electronics: Air-cooled systems (common in smaller units) have fewer maintenance needs but still require occasional fan or filter replacement. Water-cooled systems (in higher-power models) need routine flushing and coolant checks to extend component life. Electrical components like power supplies and control boards generally last 8–10 years if not exposed to voltage spikes or moisture.
- Mechanical Frame and Housing: The structural body and motion components (e.g., Z-axis lifts or enclosures) can last 15+ years, especially with minimal mechanical stress. However, frequent relocation or exposure to corrosive environments can shorten this.
- Software Compatibility: While not a physical lifespan issue, outdated software or driver support may limit functionality after 8–10 years unless the manufacturer provides long-term updates.
- Maintenance Matters: Proper usage, ventilation, scheduled cleaning, and avoiding overloading the system are key to reaching full lifespan. Machines that run in clean, temperature-controlled environments will always outlast those in dusty, hot, or unstable conditions.
How Should I Choose Metal Laser Marking Machines?
- Material Types and Marking Needs: Fiber lasers are the go-to choice for metal marking, capable of handling stainless steel, aluminum, brass, titanium, and more. For color marking on stainless steel or high-contrast black markings, a MOPA fiber laser is ideal. If you’re working with mixed materials, ensure the machine can adjust frequencies and pulse widths for clean, readable marks.
- Power Requirements: Entry-level machines start at 20W, good for basic engraving or serial codes. For faster marking speed or deeper etching, choose 30W to 60W units. Industrial applications that require marking on high-speed production lines or deeper engraving benefit from higher wattage (up to 100W).
- Work Area Size: Standard fiber laser markers have work areas from 100mm x 100mm to 300mm x 300mm. Choose a marking field that matches your part sizes. If you need to mark long or irregularly shaped items, consider a movable Z-axis or motorized platform for greater flexibility.
- Marking Type and Depth: Determine whether you need surface marking, deep engraving, annealing, or color marking. Surface marking is quick and low power, while deep engraving requires higher wattage and longer processing time. MOPA lasers excel in fine detailing and color control.
- Portability and Size: Benchtop units are compact and suitable for small workshops or offices. Larger enclosures offer better dust protection and safety for industrial environments. Some machines are designed for integration into automated lines, so consider your space and workflow.
- Software and Usability: Look for machines with intuitive, industry-standard software like EZCAD. Features like auto-focus, rotary attachments (for cylindrical parts), and pre-programmed templates reduce setup time and operator error. Check compatibility with file types like DXF, AI, PLT, or BMP.
- Cooling System and Durability: Most fiber lasers use air cooling, which is low-maintenance and compact. Water-cooled systems are reserved for high-power models that run continuously. Also consider build quality—steel casings, enclosed optics, and industrial-grade components last longer in tough environments.
- Support, Warranty, and Training: A machine is only as good as the support behind it. Reputable brands offer 1–3 year warranties, technical support, and training materials. Buying from a vendor that offers local service or spare parts can prevent downtime.
- Budget and ROI: Prices range from $2,500 to $30,000+. Factor in not just the machine cost, but also software licenses, accessories (like rotary tools), maintenance, and operator training. If production volume is high, a higher upfront investment may pay off in throughput and consistency.
What are the Risks of Laser Marking Metal?
- Laser Radiation Exposure: Metal laser marking machines, especially fiber lasers, operate in the near-infrared spectrum (usually around 1064 nm), which is invisible to the human eye but highly dangerous. Direct or reflected exposure can cause serious eye injury or permanent vision loss, even from scattered reflections off shiny surfaces. Proper laser safety goggles and enclosure systems are mandatory.
- Fume and Particle Emissions: Marking metals can release microscopic particles and metal oxide fumes, especially when dealing with coated, anodized, or alloyed materials. These emissions may contain toxic substances like chromium, nickel, or zinc, which are harmful when inhaled. Effective ventilation, fume extraction, and use of HEPA filtration are essential to protect operator health.
- Fire and Heat Hazards: Although laser marking does not usually cut deep into the metal, it does generate localized heat. This can ignite flammable coatings, dust, or packaging materials near the work area. Workspaces should be kept clear of combustibles, and fire suppression measures should be in place for industrial setups.
- Electrical and Mechanical Risks: Laser marking systems rely on high-voltage power supplies and precision galvanometers. Faulty wiring, poor grounding, or exposure to moisture can lead to electrical shock or equipment failure. Machines should be installed in dry, controlled environments with regular inspection of electrical connections.
- Damage to Parts or Surfaces: Incorrect settings—like overpowered beams, poor focus, or multiple passes—can cause burn marks, metal warping, or microcracks, especially on thin or precision parts. Overexposure may also alter the material’s structural integrity, impacting product performance in critical applications like aerospace or medical devices.
- Reflection Hazards: Some metals, like copper, brass, or polished aluminum, are highly reflective. They can bounce the laser beam back into the system, potentially damaging internal optics or posing a safety risk. Using matte finishes, marking pastes, or coatings can help minimize reflectivity issues.
- Software or Operational Errors: Operators must understand the software and machine interface thoroughly. Incorrect file imports, alignment errors, or focus settings can ruin components, waste material, or even cause laser head collisions if not programmed correctly.
- Long-Term Operator Exposure: Prolonged daily exposure to laser systems without proper safeguards can lead to chronic respiratory issues, eye strain, or repetitive strain injuries. Proper ergonomics, scheduled breaks, and personal protective equipment (PPE) reduce these long-term risks.
How Should I Maintain Metal Laser Marking Machines?
- Optics and Marking Lens: The marking lens and protective window can collect dust, smoke residue, or metal particles over time. Clean these components with lens-safe cleaning fluid and lint-free cloths on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, depending on usage. Dirty optics can distort the beam and reduce marking quality or power efficiency.
- Air and Fume Extraction Systems: Laser marking metal releases fine particles and vapors, especially from coated or treated surfaces. Filters in exhaust fans or fume extractors should be checked and replaced regularly (every 3–6 months) to ensure proper ventilation and operator safety. Clogged filters lead to poor air quality and potential damage to internal components.
- Cooling System: Most fiber laser marking systems are air-cooled, requiring occasional cleaning of intake vents and fans to prevent overheating. High-power or continuous-use systems may use water cooling, which involves checking coolant levels, inspecting for leaks, and replacing water or coolant every 6–12 months to avoid contamination or pump failure.
- Electrical Components and Wiring: Inspect the power cords, connections, and control boards periodically for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosened terminals. Ensure the machine is properly grounded, and avoid running the system in high-humidity or dusty environments that could damage electronics.
- Galvo Scanner Head: The galvanometer system directs the laser beam with precision. Keep this area free of dust and avoid physical shock to prevent misalignment. If markings become distorted or inconsistent, recalibration or professional servicing of the galvo head may be needed.
- Lubrication and Moving Parts: Machines with Z-axis lifts or motorized platforms benefit from periodic lubrication of rails, guides, or screw drives. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendation for oil or grease type and maintenance schedule. Dry or dirty rails can cause jerky movement or positioning errors.
- Software and Firmware Updates: Keep marking software (like EZCAD) and firmware up to date for improved functionality, bug fixes, and compatibility with newer operating systems. Back up your marking files and parameter settings regularly to avoid data loss during updates or system resets.
- Environmental Control: Place your machine in a dry, clean, and temperature-stable workspace. Avoid placing it near high-vibration equipment or in areas with high airborne dust. Stable conditions reduce the risk of contamination, condensation, and component fatigue.
- Routine Checks and Logs: Create a maintenance checklist or logbook to track cleaning, filter changes, alignment checks, and software updates. Performing quick daily visual inspections and more detailed monthly maintenance prevents small issues from becoming expensive repairs.
What is the Durability of Laser-Marking Metal?
- Material Bonding and Surface Penetration: Laser marking doesn’t apply ink or coating—it uses a focused beam to etch, oxidize, or anneal the surface of the metal. This creates a mark that’s integrated into the material itself. Whether it’s black annealing on stainless steel or deep engraving on aluminum, the result is resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and chemical exposure.
- Wear and Tear Resistance: Laser-marked metal parts can withstand friction, heat, and frequent handling without degrading. Deep engravings, in particular, can survive heavy-duty environments such as machinery, tools, and automotive parts. Surface markings like oxidation or annealing are less deep but still permanent unless the surface is physically ground down.
- Chemical and Solvent Resistance: Unlike printed labels or inkjet marks, laser marks won’t smear, fade, or dissolve under exposure to oil, fuel, acids, or cleaning solvents. This is especially valuable in medical, aerospace, and marine applications where harsh conditions are common.
- Temperature and UV Stability: Laser marks hold up under extreme temperatures—both hot and cold—without distortion or discoloration. They are also UV-stable, meaning sunlight and outdoor exposure won’t bleach or fade them, unlike some chemical coatings or paints.
- Traceability Longevity: Serial numbers, barcodes, and QR codes produced by laser marking remain readable for the entire life cycle of a product, which is crucial for industries that rely on long-term part tracking and traceability.
- Limitations in Surface Treatments: One exception is when laser marking is applied to plated, anodized, or coated metals. The durability then depends on the layer itself. If the coating wears off, so does the mark unless it was engraved into the base metal.
- Resistance to Tampering: Deep laser engraving provides anti-counterfeit and anti-tampering protection, as it’s extremely difficult to alter a mark without visibly damaging the metal part.







