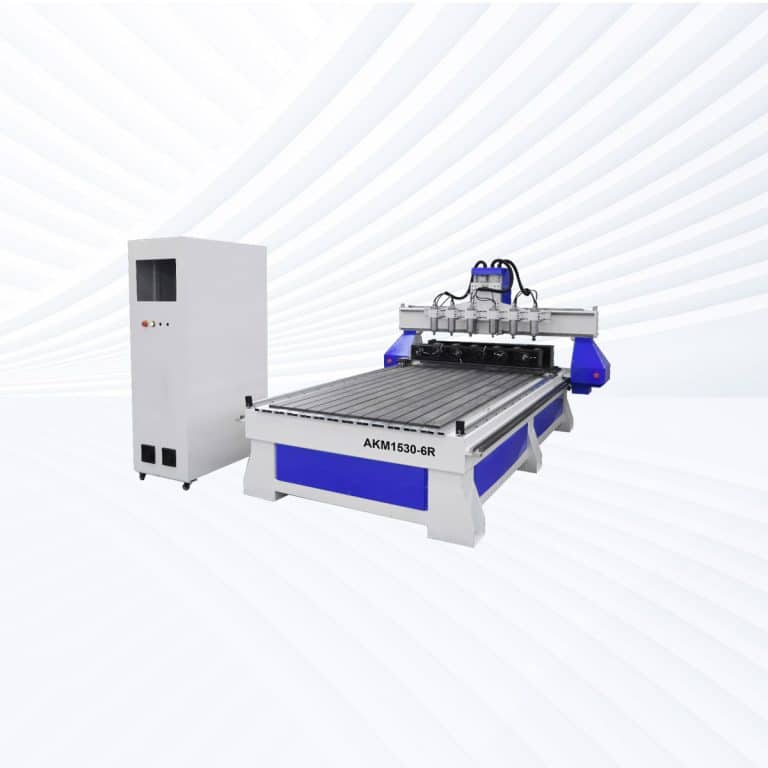
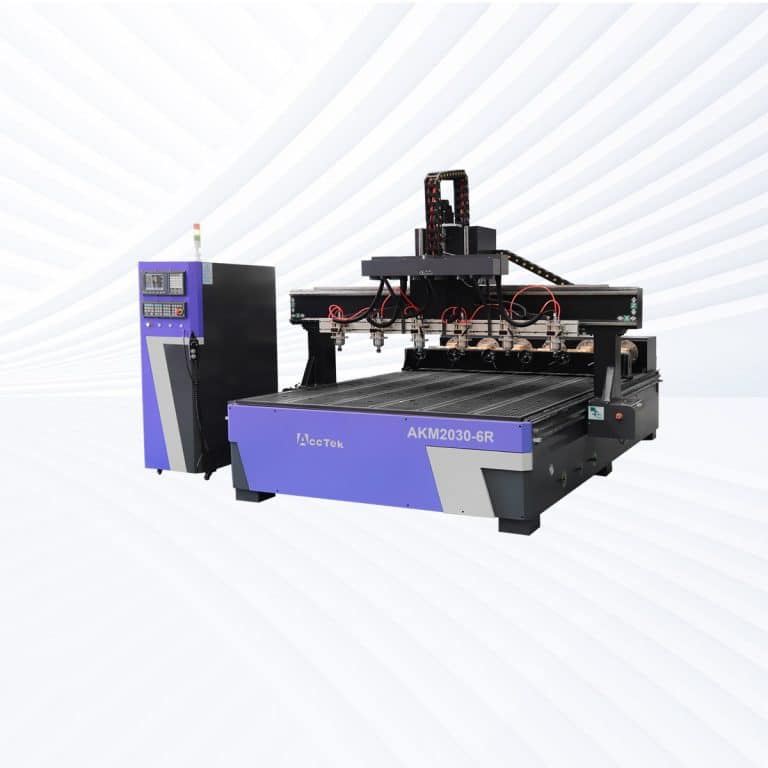
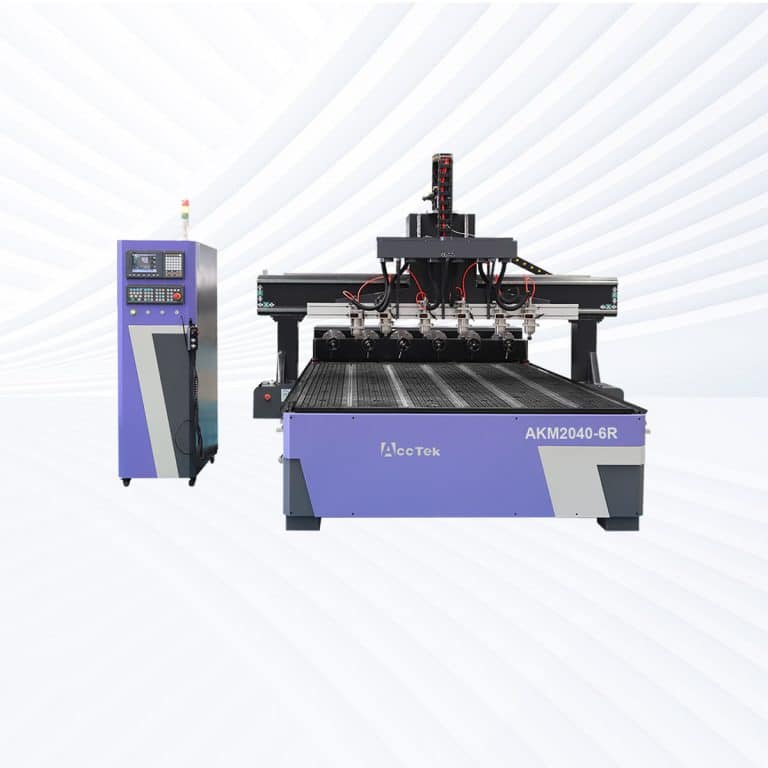
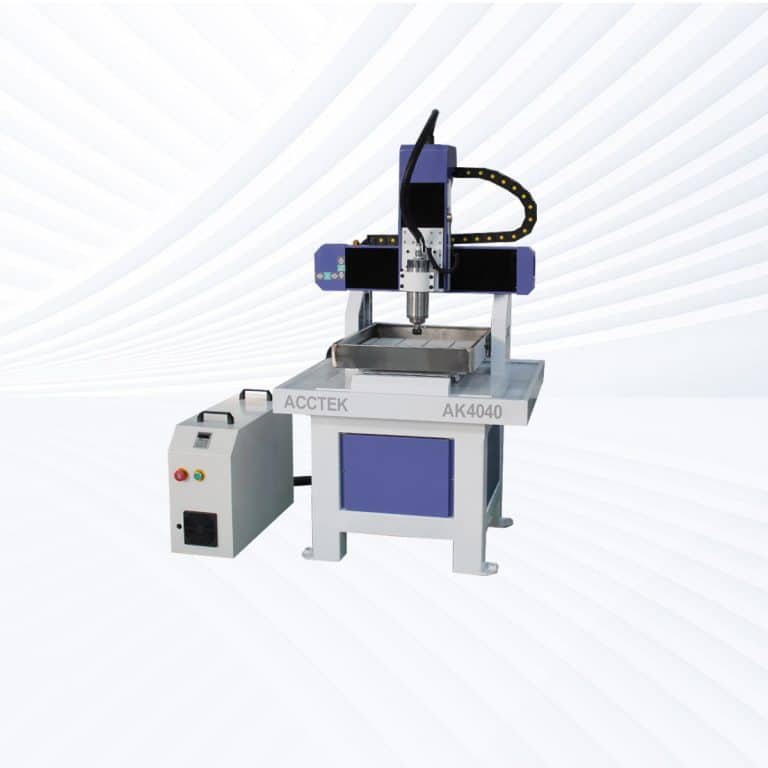
Product Introduction
Material Routing Capability
| Material Type | 1.5 kW | 2.2 kW | 3.0 kW | 3.2 kW | 3.5 kW | 4.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 6.0 kW | 7.5 kW | 9.0 kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood | Light Cutting | Standard Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Speed Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Hardwood | Light Duty | Standard Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Plywood/MDF | Basic Cutting | Smooth Cutting | Fast, Clean Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Smooth Cuts | High-Volume Cutting | High-Volume Cutting |
| HDF/Particle Board/Melamine | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Clean Cuts | Clean Cuts | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Acrylic(PMMA) | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Fast, Clean Edges | High Clarity | High Clarity | Smooth Finishing | Smooth Finishing | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity |
| Polycarbonate/PETG | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | Precision Cutting | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ABS/PVC Foam Board | Light Duty | Standard | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High Stability | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| HDPE/LDPE/PP/Nylon | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Stable Cuts | Stable Cuts | Deep Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque | Industrial | Industrial |
| Delrin/UHMW | Light Duty | Standard | Accurate Routing | Accurate Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Solid Surface (Corian) | Very Light | Standard | Strong Cutting | Clean Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Fiberglass/Carbon Fiber Sheet | Light Trimming | Standard | Precise Routing | Precise Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Phenolic/Bakelite | Limited | Standard | Clean Routing | Clean Routing | Precision Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Foam(EVA, XPS, EPS, PU) | Very Easy | Very Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | High-Speed | High-Speed | High-Speed |
| Rubber/Leather/Cork | Light Duty | Standard | Clean Edges | Clean Edges | Faster Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Cardboard/Paperboard | Easy | Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ACP/ACM (Surface Routing Only) | Very Light | Standard | Clean Grooves | Clean Grooves | High Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
Compatible Materials
- Virgin HDPE Sheet
- Recycled HDPE Sheet
- HDPE Block (Thick Plate)
- HDPE Cutting Board Grade
- HDPE Industrial Grade
- HDPE Food-Grade Sheet
- HDPE UV-Stabilized Sheet
- HDPE Marine-Grade Sheet
- HDPE High-Density Sheet
- HDPE Low-Density Sheet
- HDPE High Molecular Weight
- HDPE Ultra High Molecular Weight
- HDPE Smooth Sheet
- HDPE Textured Sheet
- HDPE Matte Sheet
- HDPE Color-Core Sheet
- HDPE Drainage Board
- HDPE Geomembrane Sheet
- HDPE Pipe Grade
- HDPE Rod Stock
- HDPE Welding Rod
- HDPE Foam Board
- HDPE Anti-Slip Sheet
- HDPE Chemical-Resistant Grade
- HDPE Electrical-Insulation Grade
- HDPE Impact-Resistant Grade
- HDPE High-Stiffness Grade
- HDPE High-Temperature Grade
- HDPE Whiteboard/Signboard Sheet
- HDPE Playground/Outdoor Panel Sheet
- HDPE Black UV Sheet
- HDPE Color Sheet
- HDPE Composite Sheet
- HDPE Glass-Filled Grade
- HDPE Mineral-Filled Grade
- HDPE Flame-Retardant (FR) Grade
- HDPE Anti-Static Grade
- HDPE Medical-Grade Sheet
- HDPE Packaging-Grade Sheet
- HDPE Machining Grade
Application of HDPE CNC Routers







Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Engraving Technologies
| Comparison Item | HDPE CNC Routing | Laser Engraving | Chemical Etching | EDM Engraving |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Mechanical cutting with rotating tools | Heat melts/vaporizes surface | Chemical reaction removes material | Electrical discharge erodes material |
| Material Compatibility | Excellent for HDPE, plastics, composites | Poor on HDPE (melts easily) | Not suitable for HDPE | Not suitable for HDPE |
| Cutting Ability | Full-depth cutting & shaping | Limited shallow engraving | No cutting capability | No cutting on plastics |
| Edge Quality | Clean edges with correct tools | Melted or charred edges | Chemical swelling, poor finish | Not applicable |
| Precision Level | High accuracy for plastics | High precision on rigid materials | Moderate | Extremely high (metals only) |
| Detail Resolution | Good for small features | Limited due to HDPE melting | Poor for plastics | Cannot engrave HDPE |
| Production Speed | Fast for routing HDPE | Slow due to melting behavior | Slow, multi-step | Very slow |
| Heat Impact | Low heat machining | High heat, melts HDPE | Chemical heat effect possible | Significant heat; incompatible |
| Surface Finish | Smooth with proper feed rates | Burn/melt marks | Chemical residue | Not applicable |
| Setup Requirements | Simple fixturing and tooling | Low setup | Requires chemical masking | Requires conductive material |
| Learning Curve | Moderate and practical | Easy to moderate | Moderate | High technical skill |
| Operating Cost | Low (bits + power) | Moderate (laser tube wear) | Medium–high (chemicals) | Very high (tool wear + power) |
| Safety Risks | Chips, noise | Fumes, laser radiation | Hazardous chemicals | High voltage, fire risk |
| Best Applications | HDPE sheets, plastic parts, signs, fixtures | Engraving on rigid non-melting materials | Metal patterns | Precision metal dies |
| Ideal Use Case | High-speed cutting and shaping of HDPE | Fine detail on acrylic/wood | Chemical marking on metals | Micro-precision metal machining |
Why Choose Us
High Precision & Efficiency
AccTek CNC routers deliver fast, accurate results with minimal errors, supporting intricate designs and mass production across the woodworking, plastic, and metal industries.
Robust and Durable Design
Our machines are built with high-quality frames and components, ensuring long service life, high load-bearing capacity, and stability during high-speed operations.
Intelligent Control Systems
Equipped with user-friendly interfaces and smart controllers, our routers offer smooth motion control, automatic toolpath optimization, and easy integration with various CAD/CAM software.
Flexible Customization
From machine size to spindle power and motor type, we offer flexible configurations to suit different production needs, budgets, and material requirements.
Related Resources

How Do CNC Routers Work
This article explains the working principle of CNC routers, from the motion system and cutting tools to the software workflow, materials, precision, and actual machining principles.

How To Maintain CNC Routers
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to maintain CNC routers, covering essential tasks, troubleshooting tips, upgrades, and best practices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

What Is The Accuracy Of CNC Routers
This article is a comprehensive guide that explains the precision of CNC routers, the key factors affecting precision, expected performance, and how to improve machining results.

How to Choose the Right Router Bits for CNC Routers
This article explains how to select the right router bit for your CNC router, including cutter type, material, coating, and tip, to achieve precise, efficient, and durable cutting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Price Of HDPE CNC Routers?
What Is The Working Range Of HDPE CNC Routers?
- Small to Medium Format Sizes (600mm×900mm, 600mm×1200mm): These smaller sizes are commonly used for detailed cutting and engraving of HDPE parts, ideal for prototype work or small-scale production. These machines are often found in small workshops or by hobbyists and custom manufacturers who need to create precise components from smaller HDPE sheets.
- Medium to Large Format Sizes (1200mm×1200mm, 1200mm×2400mm, 1300mm×2500mm): These sizes are suitable for a wider range of applications, including larger industrial components, signs, or packaging elements. The 1200mm×2400mm size is often chosen for cutting larger sheets of HDPE used in the construction, automotive, and packaging industries. It is a versatile format for both custom projects and small-scale industrial production.
- Large Industrial Sizes (1500mm×3000mm, 2000mm×3000mm, 2000mm×4000mm): These sizes are more common in industrial settings, designed for high-volume production and the cutting of large HDPE panels used in applications like storage tanks, industrial containers, or construction materials. The larger working area allows for more efficient cutting of large sheets and reduces the need for repositioning during long production runs.
- Extra-Large Format Sizes (2000mm×6000mm, 3000mm×6000mm): For large-scale industrial operations, these extra-large working ranges are used to accommodate mass production of large HDPE components. Industries such as water treatment, piping, and automotive manufacturing frequently require large sheet sizes, and these CNC routers can handle large cutting jobs without the need for multiple setups.
- Custom Sizes: In addition to the standard sizes, many manufacturers offer custom CNC routers that can be tailored to specific working range requirements. Custom sizes can be requested for unique applications, ensuring that the CNC router fits the exact needs of the business or project.
Are The Routing Edges Of HDPE CNC Routers Clean?
- Cutting Speed and Feed Rate: The feed rate and spindle speed directly impact the edge finish. If the feed rate is too high or the spindle speed is too low, it can cause rough edges, melted surfaces, or uneven cuts. On the other hand, using the correct cutting parameters for HDPE—such as optimizing the feed rate and speed—helps ensure smooth, clean edges without excess heat or material deformation.
- Tool Selection and Condition: The sharpness and type of tool used for cutting HDPE are critical for producing clean edges. High-quality router bits, such as carbide tools, are ideal for cutting HDPE because they maintain sharpness for longer and reduce friction during the cut. Dull or inappropriate tools can create fuzzy edges or cause the material to melt, leaving behind a rough surface. Regular tool maintenance is necessary to maintain edge quality.
- Cooling and Lubrication: HDPE is sensitive to heat, and excessive heat can cause the material to melt at the cutting edge. Proper cooling systems, such as air-assist or misting, are essential to reduce friction and keep the material cool during cutting. If the material heats up too much, it can lead to rough edges and undesirable finishes. Cooling ensures the edges stay smooth and free from melted residue.
- Material Clamping: If the HDPE sheet is not securely clamped, it can shift during cutting, which leads to vibration and inaccurate cuts. A properly clamped material ensures a stable cutting environment, reducing the likelihood of edge irregularities and improving the quality of the cut. Using vacuum tables or T-slot fixtures can help ensure that the material remains firmly in place during the machining process.
- Machine Calibration and Maintenance: CNC routers must be properly calibrated to ensure that the axes move smoothly and accurately. Any misalignment or mechanical issues, such as worn-out bearings or loose components, can result in inconsistent cutting and rough edges. Regular machine maintenance and calibration are crucial to achieving clean cuts and optimal edge quality.
What Problems Might Occur When Using HDPE CNC Routers?
- Material Melting or Burning: HDPE is a thermoplastic, which means it can melt if too much heat is generated during the cutting process. If the spindle speed is too slow or the feed rate is too fast, friction can cause the material to soften, leading to melted edges or smearing. To prevent this, it is crucial to use appropriate cutting speeds and cooling methods, such as air-assisted cooling or misting, to keep the material cool and prevent it from melting during the cut.
- Rough Edges and Inconsistent Cuts: Inaccurate cuts and rough edges can occur if the cutting tools are dull or the machine is not properly calibrated. Worn-out router bits can create a rough surface finish on HDPE, especially when making intricate cuts or fine details. Regular tool inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure sharpness. In addition, vibrations caused by improper clamping or loose machine components can also lead to poor-quality cuts. Proper calibration and tool selection are essential to achieve clean, smooth edges.
- Dust and Debris Accumulation: CNC routers cutting HDPE generate a large amount of dust and debris, which can clog up the machine, interfere with its operation, and create an unsafe work environment. Without effective dust extraction systems, the fine particles can accumulate on the machine’s components, leading to inefficient operation or even mechanical failure. Ensuring the machine is equipped with a high-efficiency dust collection system is essential to keep the work area clean and prevent buildup that could hinder machine performance.
- Material Warping: HDPE is prone to warping or flexing during the cutting process, especially when working with large sheets. Without proper clamping or support, the material can shift or distort, leading to misalignment and inaccurate cuts. To prevent this, the material should be securely held in place using vacuum tables, T-slot clamps, or other material-holding systems. In some cases, a multi-zone vacuum table may be necessary for larger pieces to ensure that the material remains flat and stable during the machining process.
- Tool Wear and Tear: While HDPE is relatively soft compared to metals, it still causes tool wear over time. Repeated use can dull cutting bits, leading to poor-quality cuts and increased friction. If the tool is not regularly inspected or replaced, it may also cause excessive heat, which can damage the HDPE material or reduce the overall cutting efficiency. Regular tool changes and maintenance are necessary to ensure that the CNC router is running optimally and producing high-quality cuts.
- Noise and Vibration: CNC routers can produce significant noise and vibration during operation, especially when cutting dense materials like HDPE. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to hearing damage for operators, and excessive vibrations can negatively affect cutting accuracy. Hearing protection and machine damping systems are essential for ensuring a safe and comfortable working environment.
What Control System Do HDPE CNC Routers Use?
- Mach3 Control System: Mach3 is a popular CNC control system known for its compatibility with a wide range of CNC routers, including HDPE machines. It is particularly favored for its user-friendly interface and flexibility in controlling stepper and servo motors, which are often used in HDPE routing. Mach3 supports both 3-axis and multi-axis movements, making it suitable for intricate cuts and engravings in HDPE. Users can customize Mach3’s settings, including speed, acceleration, and feed rates, to optimize the cutting process for different thicknesses and properties of HDPE. Additionally, Mach3 is compatible with a variety of hardware components and offers extensive community support, making it a reliable choice for many manufacturers.
- Syntec Control Systems: Syntec control systems, such as the Syntec 60W-E and Syntec 610MA-E5, are advanced controllers commonly used in high-performance CNC machines. The Syntec 60W-E is known for its precision and high-speed processing, making it ideal for detailed and high-quality cuts in HDPE materials. It offers advanced features like dynamic adjustment of cutting parameters, real-time feedback, and high-frequency control, which ensure accurate and smooth operations. The Syntec 610MA-E5 is another advanced controller, providing greater capabilities for multi-axis movements, ensuring enhanced precision and control when cutting through HDPE sheets or performing complex operations like engraving or 3D routing.
- Choosing the Right Control System: The selection between Mach3 and Syntec control systems typically depends on the complexity of the operations and the specific needs of the machine owner. While Mach3 is a more cost-effective and versatile option, Syntec control systems offer superior precision, especially for high-end and more complex tasks. The Syntec 610MA-E5, in particular, offers advanced functionalities like optimized cut paths and better control over tool compensation, making it an excellent choice for high-volume production or highly detailed projects.
What Type Of Worktable Do HDPE CNC Routers Use?
- Vacuum Worktable
- A vacuum worktable is one of the most popular choices for HDPE CNC routers, particularly for handling large sheets of material. The table uses a vacuum system to hold the HDPE securely in place during the routing process. This system works by creating suction through a series of holes or channels on the worktable’s surface, effectively preventing material movement. It is ideal for thin or flexible HDPE sheets, where material shifting could lead to inaccuracies.
- The primary benefit of a vacuum worktable is its ability to handle a variety of sizes without the need for manual clamping, which can save time and reduce setup costs. It ensures even pressure distribution across the material, providing a stable environment for precise cuts. Additionally, vacuum tables can be adapted for different thicknesses of HDPE and other materials, offering high versatility. However, the vacuum system requires regular maintenance, and it might not be ideal for extremely small workpieces or those with irregular shapes.
- T-Slot Worktable
- A T-slot worktable is another commonly used option, particularly for HDPE CNC routers requiring more secure, adjustable holding systems. This type of table features a series of T-shaped grooves along the surface, into which clamps or other holding fixtures can be inserted. The T-slot worktable is more suited to larger or thicker HDPE materials that need additional support and stability during routing.
- Unlike the vacuum worktable, which relies on suction, the T-slot worktable offers more flexibility in terms of material clamping and is ideal for materials with varying shapes or when there is a need for frequent reconfiguration of the workpieces. It is also more durable and less prone to wear over time, making it a good choice for high-volume operations or heavy-duty applications.
- Choosing the Right Worktable
- The choice between a vacuum and a T-slot worktable for HDPE CNC routing depends on the material type, project size, and production requirements. Vacuum worktables are perfect for quickly and efficiently processing flat, flexible materials, while T-slot tables provide more robust, adjustable clamping for materials that require more rigid support.
What Are The Environmental Requirements For HDPE CNC Routers?
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels in the workspace is essential for both the machine’s operation and the material being processed. CNC routers, including those used for HDPE, should ideally operate in environments with a temperature range of 18℃ to 25℃ (64℉ to 77℉). Extreme temperatures can cause mechanical issues or affect the dimensional stability of HDPE, leading to warping or irregular cuts. Similarly, humidity levels should be kept moderate (around 40-60%) as excessive moisture in the air can cause corrosion on machine components, particularly metal parts, while very low humidity can lead to static buildup and affect the precision of the CNC router.
- Ventilation: HDPE CNC routers generate dust and particulate matter during the routing process, which can accumulate in the air and pose a health risk to operators. Proper ventilation is crucial to maintaining a safe working environment. It’s important to have a dust extraction system installed to capture airborne particles. This system should be connected to the CNC router’s dust collection port, ensuring that debris does not clog the machine’s components or interfere with its functionality. Effective ventilation also prevents the buildup of fumes, especially when cutting or routing HDPE at higher speeds or under heavy loads.
- Clean and Dry Environment: The workspace should be kept clean and free from excessive dust, oil, or grease that could affect the machine’s performance. Moisture or spills on the floor can also create slippery surfaces, increasing the risk of accidents. Regular cleaning of the CNC router and its worktable is important to ensure optimal operation, especially since HDPE can generate static or cling to surfaces. It’s also advisable to store materials like HDPE sheets in a dry area, away from direct sunlight or humidity, which could alter their physical properties.
- Electrical Power Supply: A stable electrical power supply is essential to ensure that the CNC router functions without interruption. Voltage fluctuations or unstable power sources can damage sensitive components like motors, controllers, and electronic parts. A voltage regulator or UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is recommended to prevent power surges or outages that could disrupt operations or lead to data loss during a job.
- Safety Considerations: As with any industrial machine, it is important to provide safety barriers or guards around the CNC router to protect operators from potential hazards. Operators should wear appropriate PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) such as safety goggles, dust masks, and ear protection to reduce exposure to airborne particles and noise.
What PPE Is Required To Operate HDPE CNC Routers?
- Safety Glasses or Face Shield: Safety glasses with side shields or a face shield are critical to protect the eyes from flying debris and particles, which can be generated during the routing process. While HDPE is not inherently hazardous, the machining process can result in sharp fragments or dust particles that could injure the eyes. A face shield is recommended for additional protection, particularly when working with larger pieces or heavier cuts.
- Dust Mask or Respirator: During the cutting or routing of HDPE, fine plastic dust can become airborne, which can be harmful if inhaled. A dust mask is the minimum PPE required, but for better protection, a respirator (with a P100 or N95 rating) is advisable, particularly if working in a poorly ventilated area or during heavy routing operations. The respirator will filter out particulate matter and help reduce the risk of respiratory irritation or long-term health issues associated with inhaling plastic dust.
- Hearing Protection: HDPE CNC routers can generate significant noise levels, especially when cutting at high speeds or with larger machines. Earplugs or earmuffs are essential to protect against hearing damage. Prolonged exposure to noise levels above 85 decibels can lead to hearing loss, so it’s critical to wear hearing protection when operating the CNC router, particularly for extended periods.
- Protective Gloves: Cut-resistant gloves are recommended to protect the hands from sharp edges on the HDPE material or during machine setup. These gloves also help to maintain a firm grip when handling the workpieces, minimizing the risk of slippage or injury. While HDPE itself is not particularly hazardous, sharp edges from cut parts or tools can cause injury if not handled carefully.
- Protective Clothing: Long-sleeve shirts and long pants made from durable materials are important to protect the skin from accidental contact with moving parts or sharp objects. High-visibility clothing is also recommended in busy work environments to ensure the operator is easily seen by others, especially in larger production areas.
- Foot Protection: Steel-toed boots are recommended to protect the feet from heavy objects or tools that might fall. CNC routers often involve the movement of large materials and equipment, and protective footwear helps reduce the risk of foot injuries from dropped items or mishaps.
- Hair and Jewelry Protection: If the operator has long hair, it should be tied back to prevent it from getting caught in the machine. Additionally, loose jewelry such as rings or bracelets should be avoided to prevent accidental entanglement in moving parts.








