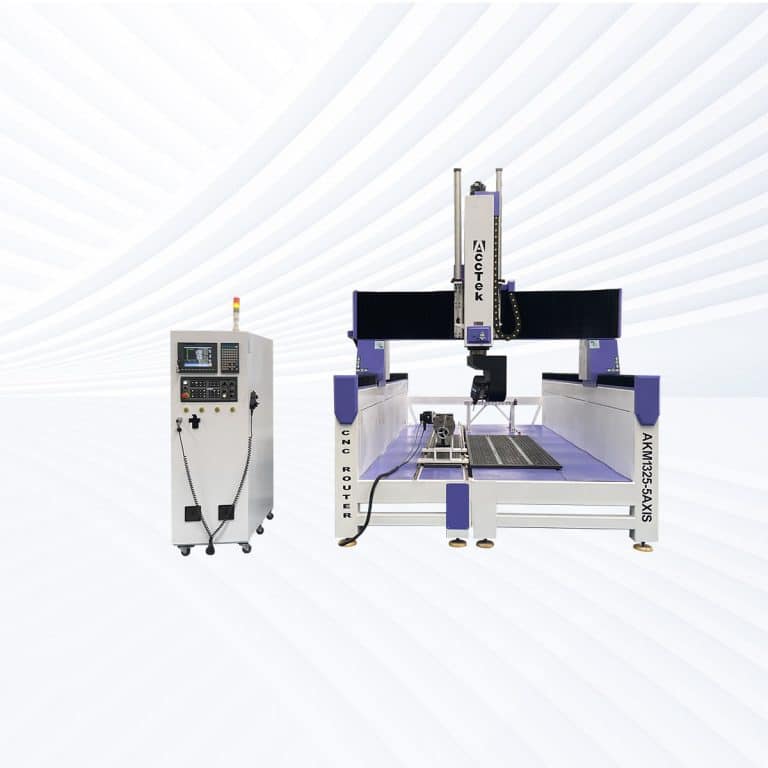
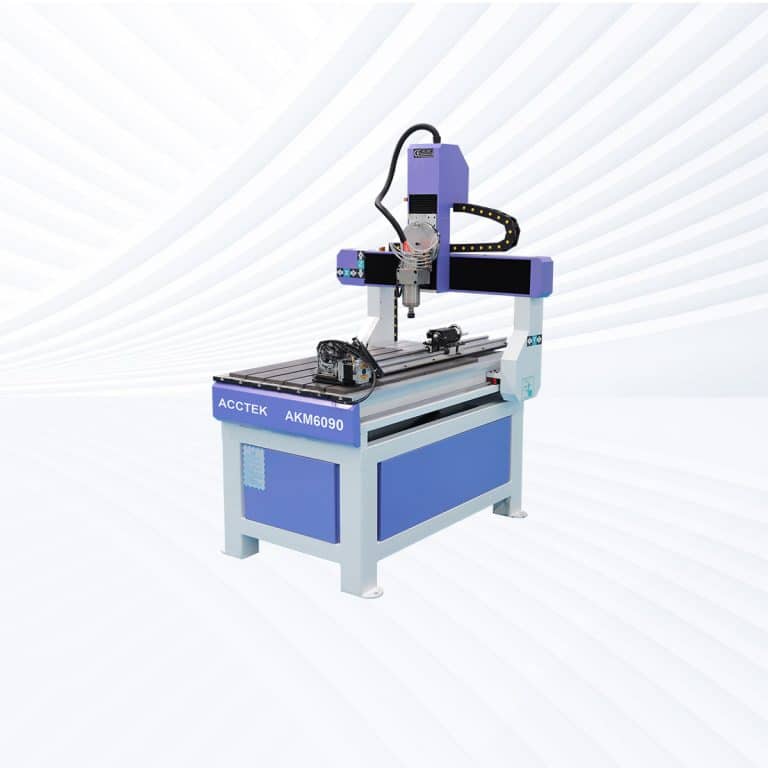
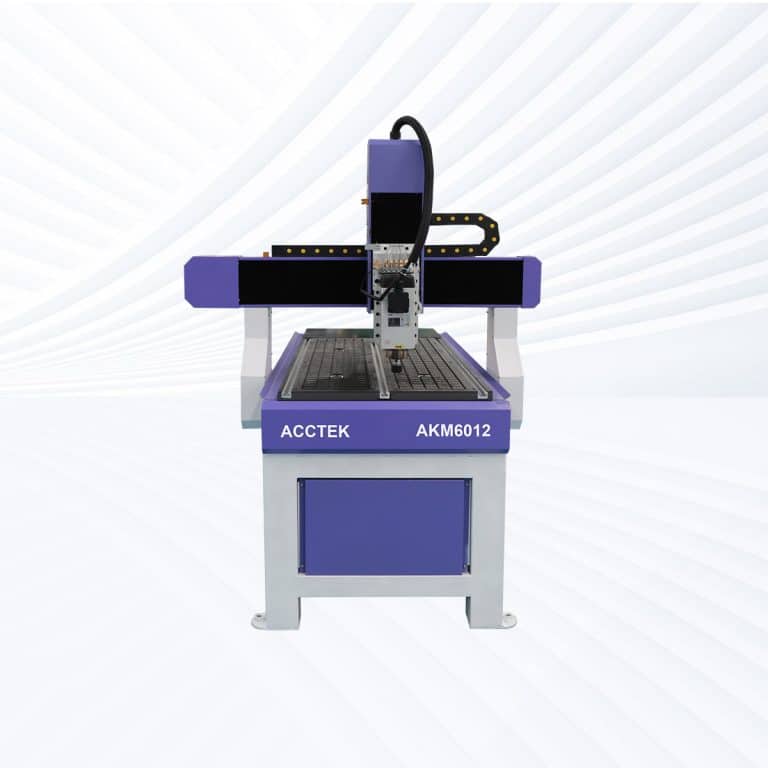
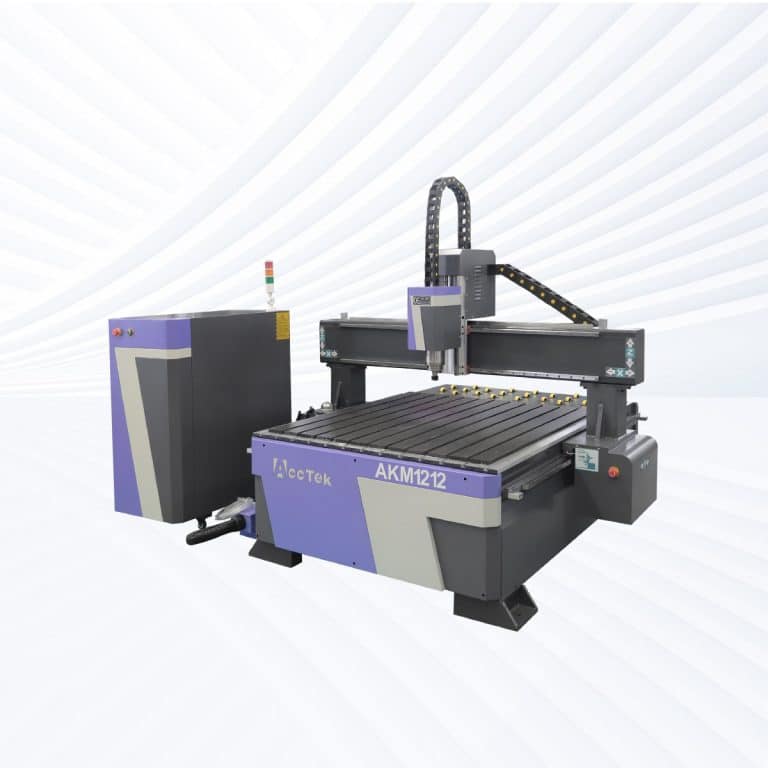
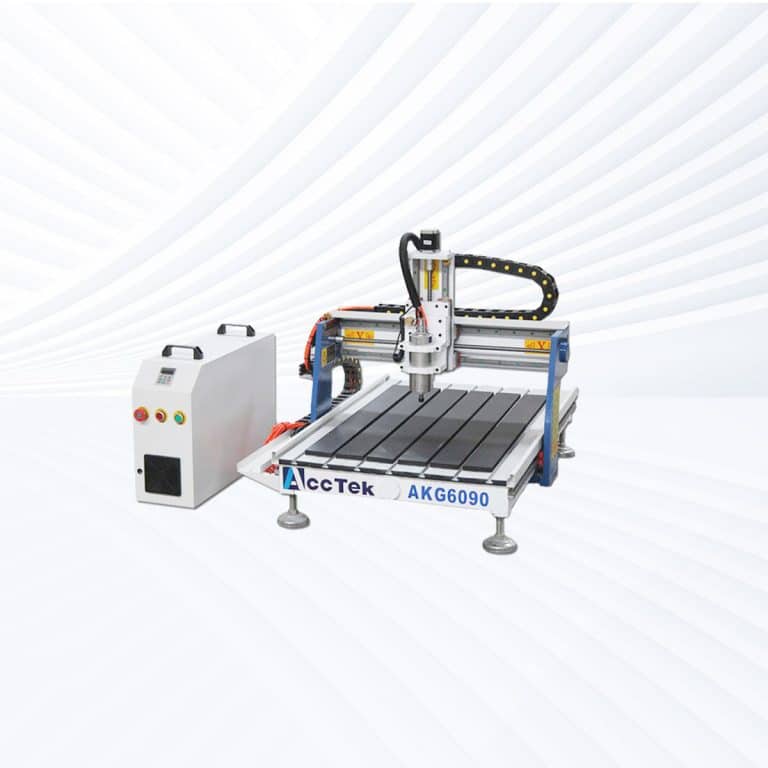
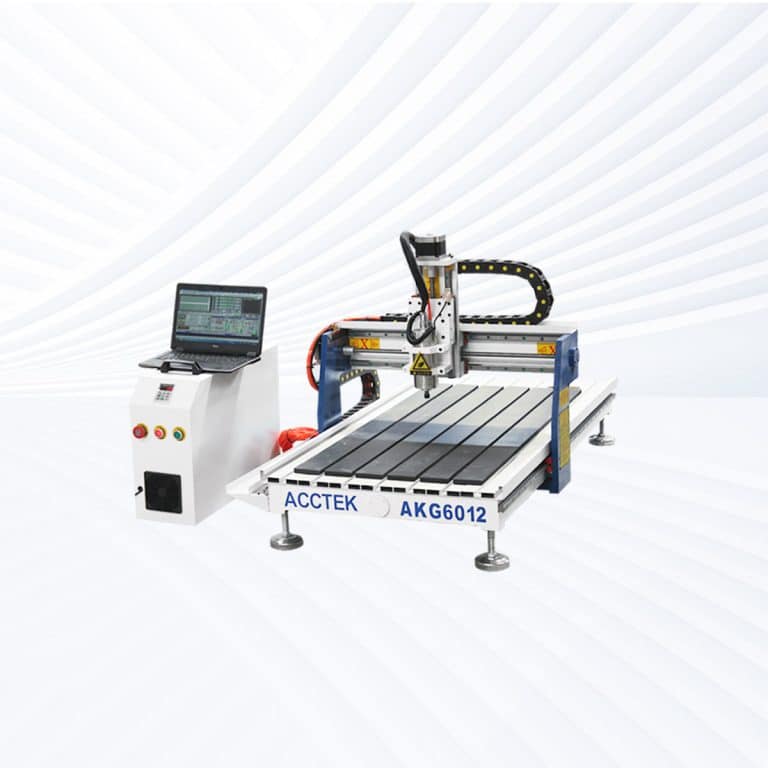
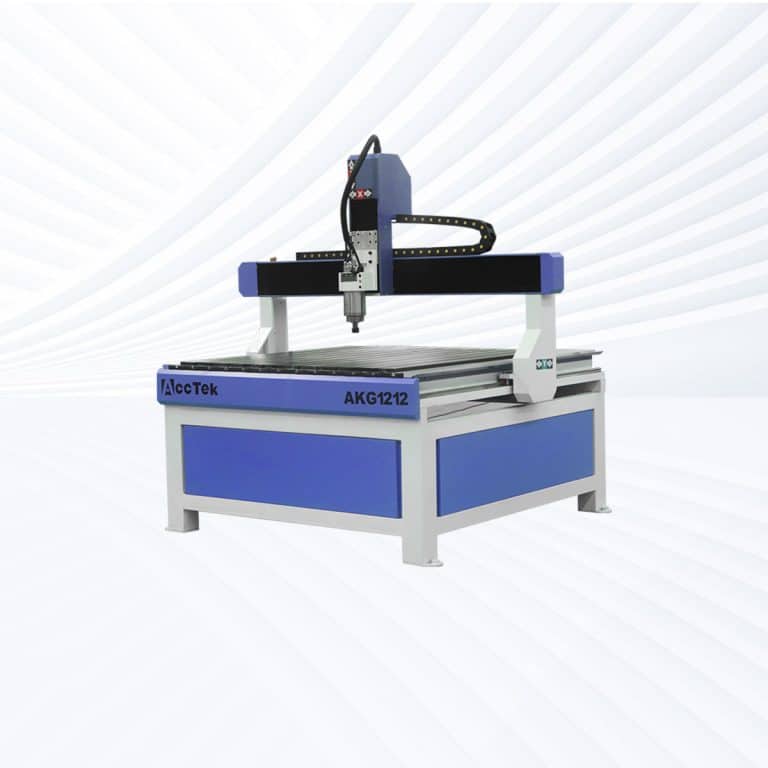
Product Introduction
Material Routing Capability
| Material Type | 1.5 kW | 2.2 kW | 3.0 kW | 3.2 kW | 3.5 kW | 4.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 6.0 kW | 7.5 kW | 9.0 kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood | Light Cutting | Standard Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Speed Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Hardwood | Light Duty | Standard Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Plywood/MDF | Basic Cutting | Smooth Cutting | Fast, Clean Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Smooth Cuts | High-Volume Cutting | High-Volume Cutting |
| HDF/Particle Board/Melamine | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Clean Cuts | Clean Cuts | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Acrylic(PMMA) | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Fast, Clean Edges | High Clarity | High Clarity | Smooth Finishing | Smooth Finishing | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity |
| Polycarbonate/PETG | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | Precision Cutting | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ABS/PVC Foam Board | Light Duty | Standard | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High Stability | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| HDPE/LDPE/PP/Nylon | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Stable Cuts | Stable Cuts | Deep Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque | Industrial | Industrial |
| Delrin/UHMW | Light Duty | Standard | Accurate Routing | Accurate Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Solid Surface (Corian) | Very Light | Standard | Strong Cutting | Clean Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Fiberglass/Carbon Fiber Sheet | Light Trimming | Standard | Precise Routing | Precise Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Phenolic/Bakelite | Limited | Standard | Clean Routing | Clean Routing | Precision Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Foam(EVA, XPS, EPS, PU) | Very Easy | Very Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | High-Speed | High-Speed | High-Speed |
| Rubber/Leather/Cork | Light Duty | Standard | Clean Edges | Clean Edges | Faster Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Cardboard/Paperboard | Easy | Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ACP/ACM (Surface Routing Only) | Very Light | Standard | Clean Grooves | Clean Grooves | High Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
Compatible Materials
- Cast Acrylic
- Extruded Acrylic
- Clear Acrylic
- Frosted Acrylic
- Colored Acrylic
- Translucent Acrylic
- Opaque Acrylic
- Tinted Acrylic
- Mirror Acrylic (One-Side)
- Mirror Acrylic (Two-Side)
- Fluorescent Acrylic
- LED Light-Guide Acrylic
- Matte Acrylic
- Glossy Acrylic
- Textured Acrylic
- Anti-Glare Acrylic
- UV-Resistant Acrylic
- Outdoor-Grade Acrylic
- Impact-Modified Acrylic
- High-Temperature Acrylic
- Acrylic Sheets with Protective Film
- Acrylic Diffusion Panels
- Acrylic Lightbox Panels
- Acrylic Signage Sheets
- Acrylic Lettering Sheets
- Acrylic Rods
- Acrylic Tubes
- Acrylic Blocks
- Thick Acrylic Sheets (20–50 mm)
- Thin Acrylic Sheets (1–3 mm)
- Acrylic Composite Sheets
- Acrylic–ABS Composite
- Acrylic–PVC Composite
- Acrylic Display Board
- Acrylic Furniture Panels
- Acrylic Decorative Sheets
- Glitter Acrylic
- Marbled Acrylic
- Patterned Acrylic
- Acrylic with Embedded Textures
Application of Acrylic CNC Routers







Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Engraving Technologies
| Comparison Item | Acrylic CNC Routing | Laser Engraving | Chemical Etching | EDM Engraving |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Mechanical cutting with rotating tools | Vaporizes or melts acrylic surface | Chemicals dissolve surface layers | Electrical discharge removes material |
| Material Suitability | Acrylic, PMMA, plastics | Acrylic, plastics, coated materials | Metals and glass (not acrylic) | Conductive materials only |
| Cutting Ability | Full-depth cutting, profiling | Limited cutting on thin acrylic | Cannot cut acrylic | Cannot cut acrylic |
| Edge Quality | Smooth edges with polishing tools | Flame-polished edges | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Engraving Depth | Deep, 2.5D and 3D engraving | Shallow, surface-level | Very shallow | Moderate depending on spark energy |
| Detail Resolution | High with correct tooling | Extremely high | Good for fine metal patterns | High but not ideal for plastics |
| Heat Influence | Low heat if feeds are correct | High heat; risk of melting burns | No heat | Heat from sparks damages plastics |
| Production Speed | Fast for cutting and shaping | Fast for engraving, slow for deep work | Medium | Slow |
| Design Complexity | Excellent for 3D relief and full cuts | Excellent for 2D engraving | Good for repetitive surface patterns | High precision but limited use cases |
| Setup Requirements | Medium: fixturing + tooling | Low: software only | High: chemicals, masks | Medium: fixtures + electrodes |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Easy to moderate | Moderate to high | High |
| Operating Cost | Low: bits + electricity | Low-medium: laser tube wear | Medium: chemicals + disposal | High: electrodes + energy |
| Maintenance | Routine lubrication and tool changes | Optics cleaning + tube replacement | Chemical handling, tank cleaning | Electrode wear + dielectric maintenance |
| Safety Concerns | Debris, noise | Laser radiation + fumes | Chemical burns + fumes | Sparks + dielectric fumes |
| Best Applications | Signage, displays, acrylic panels, 3D carving | Fine text, logos, detailed surface engraving | Metal nameplates, serial marking | Precision metal engraving (not acrylic) |
Why Choose Us
High Precision & Efficiency
AccTek CNC routers deliver fast, accurate results with minimal errors, supporting intricate designs and mass production across the woodworking, plastic, and metal industries.
Robust and Durable Design
Our machines are built with high-quality frames and components, ensuring long service life, high load-bearing capacity, and stability during high-speed operations.
Intelligent Control Systems
Equipped with user-friendly interfaces and smart controllers, our routers offer smooth motion control, automatic toolpath optimization, and easy integration with various CAD/CAM software.
Flexible Customization
From machine size to spindle power and motor type, we offer flexible configurations to suit different production needs, budgets, and material requirements.
Related Resources
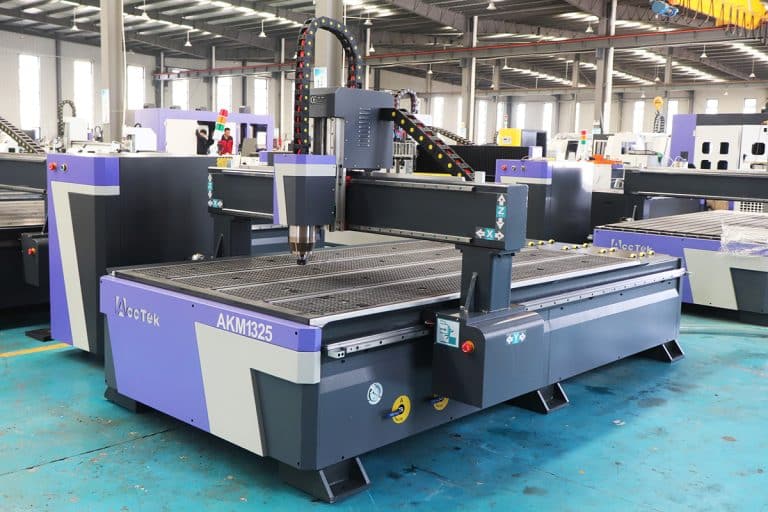

How Do CNC Routers Work
This article explains the working principle of CNC routers, from the motion system and cutting tools to the software workflow, materials, precision, and actual machining principles.
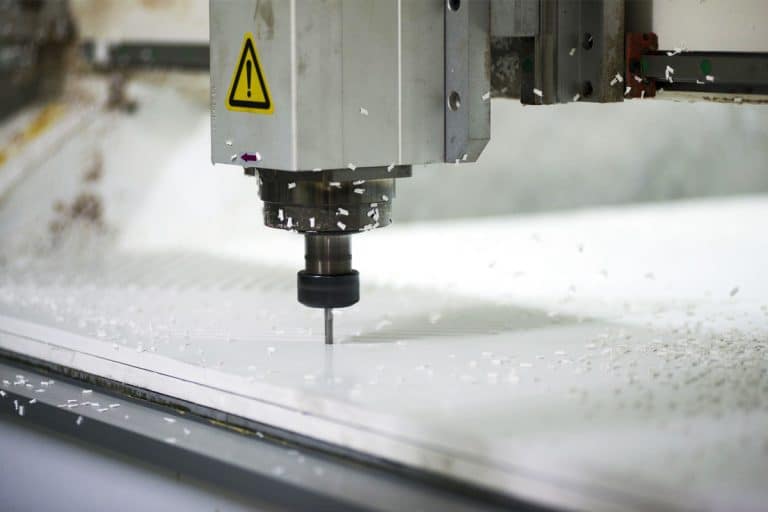

How To Maintain CNC Routers
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to maintain CNC routers, covering essential tasks, troubleshooting tips, upgrades, and best practices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
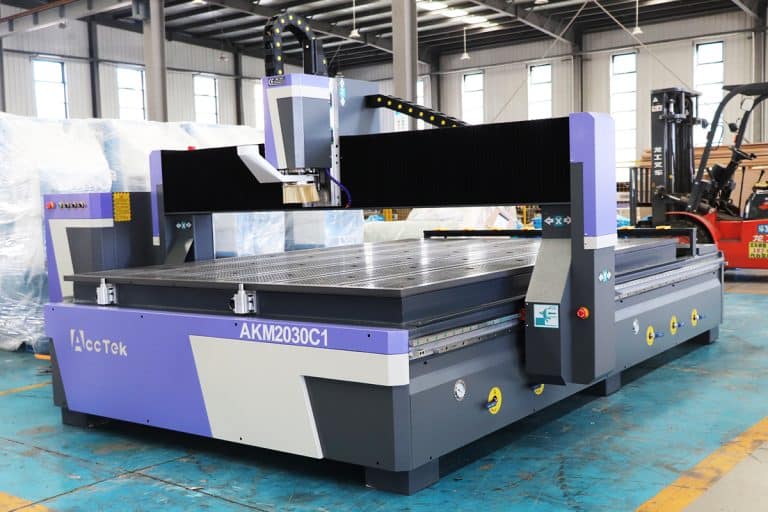

What Is The Accuracy Of CNC Routers
This article is a comprehensive guide that explains the precision of CNC routers, the key factors affecting precision, expected performance, and how to improve machining results.
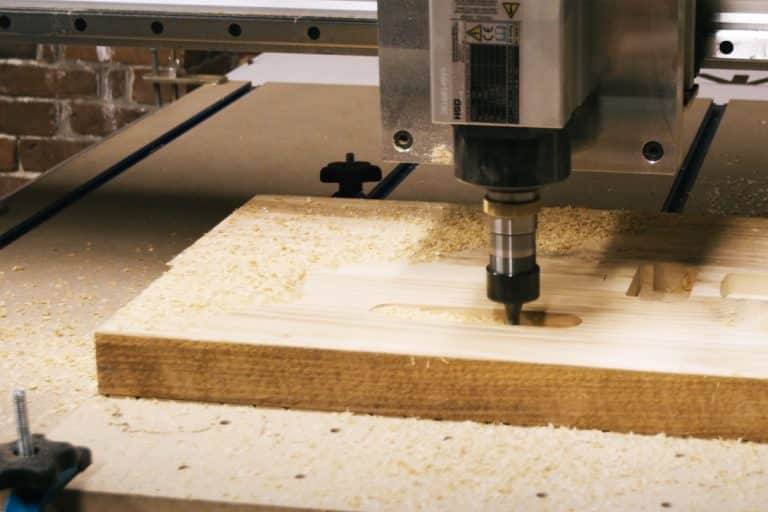

How to Choose the Right Router Bits for CNC Routers
This article explains how to select the right router bit for your CNC router, including cutter type, material, coating, and tip, to achieve precise, efficient, and durable cutting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Price Of Acrylic CNC Routers?
What Is The Working Range Of Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Standard Working Sizes
- 600mm×900mm: This is a compact size, ideal for small-scale projects such as engraving or cutting small acrylic components, signs, or displays. It’s perfect for hobbyists, craft makers, and small businesses that don’t require large-scale production.
- 600mm×1200mm: This size accommodates slightly larger projects, such as custom cutouts, signage, and small panel fabrication. It’s commonly used in workshops where precision is key, but where larger working areas are not needed.
- 1200mm×1200mm: This size is popular for standard applications like medium-sized signage, displays, and prototypes. It provides a good balance between work area and machine footprint, making it suitable for various small to medium-scale businesses.
- 1200mm×2400mm: Used for larger projects, this size is ideal for cutting full-size sheets of acrylic into various shapes. It’s often used in commercial settings where high-volume production is required, such as for larger signage, panels, or displays.
- 1300mm×2500mm: This size accommodates large-scale projects, such as industrial signage, larger prototypes, and parts. It’s commonly used in more industrial settings or by companies that need to cut multiple sheets or large acrylic components at once.
- 1500mm×3000mm: Often found in larger businesses or industries that deal with bulk cutting, this size allows for machining large sheets of acrylic used in interior design, furniture manufacturing, and large displays. It’s also used in mass production settings.
- Larger Industrial Formats
- 2000mm×3000mm: This size is used for heavy-duty industrial applications where large acrylic components are needed, such as for automotive, construction, or aerospace industries.
- 2000mm×4000mm: Used in very large production settings, this size accommodates even larger panels and heavy-duty machining.
- 2000mm×6000mm: This is one of the largest available standard sizes and is ideal for extremely large projects, including full-sized partitions, furniture panels, and large-scale signage.
- 3000mm×6000mm: This size is suitable for large-scale industrial projects, providing a substantial working area for cutting multiple sheets of acrylic at once, making it ideal for bulk production.
- Custom Sizes
- Many manufacturers offer customized CNC routers with working areas tailored to specific requirements. Custom sizes can be requested depending on the specific needs of the business or project, ensuring flexibility and maximizing productivity for specialized applications.
What Problems Might Occur When Using Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Cracking and Chipping: Acrylic is a brittle material, and improper cutting techniques can lead to cracks or chips along the edges. This is especially common when using a feed rate that is too fast or a tool that is not sharp enough. The router bit may cause stress along the cut, leading to unwanted fractures. To avoid this, it’s crucial to use a sharp, high-quality tool and to adjust the feed rate and spindle speed based on the thickness and type of acrylic being cut.
- Rough Edges and Poor Finish: Acrylic is prized for its smooth, polished finish, but poor cutting conditions can result in rough, uneven edges. This is usually due to incorrect spindle speed, an inappropriate feed rate, or dull cutting tools. If the material isn’t properly held in place during cutting, vibrations can also create imperfections. To prevent this, it’s important to use a properly calibrated router, optimize cutting settings, and ensure tight clamping of the acrylic.
- Melting or Burning: Acrylic is sensitive to heat, and prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause it to melt or burn. This happens if the spindle speed is too slow or the feed rate is too fast, generating excessive friction and heat. Additionally, a lack of cooling or air assistance can exacerbate this issue. To prevent burning or melting, it’s essential to optimize cooling systems (like air or mist cooling) and choose the right spindle speed and feed rate.
- Dust Accumulation: CNC routers cutting acrylic generate significant amounts of fine dust and particles. If not properly extracted, this dust can interfere with the machining process, obstruct cutting tools, and even pose a health risk. Poor dust collection or a clogged dust system can lead to machine inefficiency and safety hazards. A proper dust extraction system should be in place to ensure a clean work environment and maintain machine performance.
- Tool Wear and Tear: CNC routers cutting acrylic at high speeds can experience rapid tool wear. The accumulation of heat, friction, and pressure during prolonged cutting can dull router bits quickly, leading to poor-quality cuts and increased downtime for tool changes. Regular tool maintenance and monitoring are necessary to prevent this issue.
- Material Warping: Acrylic can warp under heat or improper handling. If the material is not properly supported during cutting, or if the CNC router’s bed is uneven, it can lead to distorted cuts. To avoid warping, make sure the acrylic sheet is securely clamped and evenly supported throughout the cutting process.
What Factors Affect The Price Of Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Machine Size and Working Area: The size of the CNC router’s working area is a significant factor in its price. Smaller machines with a working range of 600mm×900mm or 600mm×1200mm are typically less expensive, as they are designed for smaller projects such as detailed engravings or small-scale cutting. Larger machines with working areas of 1200mm×2400mm, 1300mm×2500mm, or even larger custom sizes are more expensive because they provide more versatility and can handle larger acrylic sheets or larger production volumes. The increased size requires stronger motors, larger frames, and more powerful spindles, all of which add to the cost.
- Spindle Power and Quality: The spindle power is a critical factor affecting both cutting ability and price. Higher-powered spindles (e.g., 2.2 kW or 3.2 kW) allow for faster and more efficient cutting of thicker acrylic sheets. Spindles with water-cooling systems also tend to be more expensive but are necessary for maintaining consistent cutting performance, especially during long, continuous operations. The quality of the spindle can also affect the CNC router’s precision and longevity.
- Precision and Accuracy: CNC routers designed for high precision and fine details will typically cost more than lower-precision models. Acrylic machining often requires a high degree of accuracy, especially when cutting intricate shapes or producing smooth finishes. Machines with high-quality linear guides, ball screws, and servo motors offer better movement accuracy and repeatability, ensuring smoother cuts and reduced errors. This level of precision often comes at a premium.
- Additional Features and Capabilities: The inclusion of advanced features such as automatic tool changers (ATC), dust collection systems, vacuum tables, and laser sensors can significantly increase the price. These features improve efficiency, reduce manual intervention, and enhance safety during operations. A dust collection system is particularly important when working with acrylic, as it helps manage the fine particles produced during cutting and ensures a clean workspace. Vacuum tables provide better clamping, ensuring that the acrylic sheets stay firmly in place during cutting.
- Brand and Build Quality: Renowned brands and machines with high build quality are generally priced higher. Machines from established manufacturers often come with better customer support, more reliable parts, and longer warranties, which justifies the higher price tag. These CNC routers tend to have better structural integrity, longer tool life, and more consistent performance.
- Customization and Automation: Customized or highly automated CNC routers are more expensive due to their ability to handle specific materials, tasks, or large-scale production runs. Automation features, like robotic arms for material handling, can increase efficiency but also add to the cost of the machine.
What Is The Accuracy Of Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Machine Quality and Build: The build quality of the CNC router has a direct impact on its accuracy. Machines with rigid frames, high-quality linear guides, and precision ball screws are designed to minimize vibration and maintain stability during operation. This structural rigidity ensures that the CNC router maintains precise movement along all axes, which is crucial when working with materials like acrylic that require clean, smooth cuts.
- Spindle Power and Stability: Spindle power and stability also contribute to the accuracy of acrylic CNC routers. A high-quality spindle, such as a 2.2 kW or 3.2 kW water-cooled spindle, provides consistent speed and torque during the cutting process. This consistency helps reduce fluctuations in cutting force, ensuring more precise cuts and a better overall finish. When the spindle is stable and operating at the correct speed, it improves both cutting accuracy and edge quality.
- Tool Selection and Maintenance: The type of tool used in the CNC router significantly influences the final results. Sharp, high-quality carbide tools are ideal for acrylic, as they maintain their cutting edge longer and minimize the risk of rough edges or poor finishes. Dull tools can lead to inaccurate cuts, increased friction, and the potential for overheating. Regular tool maintenance and sharpness checks are essential to maintain consistent accuracy over time.
- Calibration and Setup: Proper machine calibration ensures that the CNC router operates within its specified accuracy range. Misalignment or mechanical issues, such as loose bearings or worn components, can lead to deviations from the desired cut path. Routine calibration and maintenance are necessary to maintain precision and reduce the likelihood of dimensional errors.
- Cutting Parameters (Speed and Feed Rate): The speed and feed rate settings directly impact the accuracy of the cuts. If the feed rate is too high or the spindle speed is incorrect, it can lead to poor cuts, tool wear, or even burning and melting of acrylic. By adjusting these parameters based on the material’s thickness and properties, operators can achieve smoother, more precise cuts.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Material Fragility: Acrylic is relatively brittle and prone to cracking, chipping, and breaking, especially when subjected to excessive force or improper handling. During machining, if the CNC router’s settings (e.g., feed rate, spindle speed) are not optimized, acrylic sheets may crack along the cut line or at corners. Additionally, any vibration or instability in the machine or material clamping can exacerbate this issue, requiring extra care to ensure a clean, accurate cut.
- Tool Wear and Maintenance: Although acrylic is softer than metals, it still causes wear and tear on cutting tools. Over time, repeated use of CNC routers on acrylic material can dull bits, leading to poor cut quality, increased heat generation, and possible damage to both the acrylic and the CNC router itself. To maintain optimal performance, tools need regular inspection and replacement, which adds to maintenance costs and downtime.
- Heat Generation: CNC routers, when cutting acrylic, can generate significant amounts of heat due to friction between the cutting tool and the material. This heat can lead to the material melting at the edges, causing poor finishes, rough edges, or even warping. Proper cooling methods, such as misting or air-assisted cooling, are essential but can add to the complexity and cost of the operation.
- Dust and Debris: Cutting acrylic produces a large amount of fine dust and particles, which can interfere with the CNC router’s mechanics and the quality of the cuts. If not properly extracted, this dust can clog the CNC router, leading to malfunctions or a reduction in cutting accuracy. Inadequate dust control systems can also pose health risks to operators. Ensuring that a high-quality dust collection system is in place is crucial; it can increase both upfront costs and ongoing maintenance.
- Limited Material Compatibility: Acrylic CNC routers are designed specifically for cutting materials like acrylic sheets, but they are not as versatile when working with other materials like metals or composites. If an operator needs to frequently switch between materials, they may need to adjust the CNC router or use separate machines, adding complexity and operational costs.
- Operational Costs: While CNC routers provide high precision, their operational costs can add up. Maintenance of the machine, tool replacements, cooling systems, and dust extraction systems all require ongoing investment. Additionally, training is required to properly operate the CNC router, further adding to the overall cost of ownership.
Is It Safe To Use Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Dust and Fume Hazards: One of the biggest safety concerns when using CNC routers to cut acrylic is the generation of fine dust. Acrylic dust can be harmful if inhaled, and long-term exposure can lead to respiratory issues. Additionally, cutting acrylic can create toxic fumes, especially if the material is not adequately cooled or ventilated. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to have a high-efficiency dust collection system in place. The workspace should also be well-ventilated, with extraction systems designed to remove dust and fumes from the air. Operators should also wear proper PPE, such as respirators with HEPA filters and safety glasses.
- Proper Machine Setup and Maintenance: When CNC routers are set up improperly or not maintained well, they can pose safety risks such as vibrations, tool breakage, and machine malfunctions. To ensure safety, the CNC router should be calibrated regularly, and all moving parts, such as the spindle and linear guides, should be properly maintained to prevent any unexpected failures during cutting. Routine inspections for wear and tear on cutting tools are essential to ensure that the CNC router operates at optimal conditions, preventing accidents from tool malfunctions.
- Fire Hazards: While acrylic itself is not highly flammable, friction-generated heat during cutting can cause ignition of acrylic dust if it accumulates in the machine. Additionally, improper feed rates or spindle speeds can result in excess heat buildup, leading to potential melting or burning of the acrylic. Proper cooling systems, such as air assist or mist cooling, should be used to manage the heat during cutting and keep the material from overheating. Operators should ensure that the CNC router’s cooling system is functioning properly at all times.
- Handling and Clamping Risks: Acrylic can be brittle, and improper handling or clamping can cause it to crack or shatter. This can be dangerous if the material is not securely fixed during cutting. Using appropriate clamping systems, such as vacuum tables or T-slot clamps, helps ensure the material stays in place during machining. Operators should also be cautious when handling acrylic sheets to avoid personal injury from sharp edges.
- Electrical Safety: As with any machinery, there is a risk of electrical hazards if the CNC router is not properly grounded or if the wiring becomes damaged. Ensuring that the machine is installed with proper electrical grounding and that all connections are regularly inspected will reduce the risk of electrical accidents.
What PPE Is Required To Operate Acrylic CNC Routers?
- Respiratory Protection (Dust Masks or Respirators): Acrylic cutting generates fine dust and particles that can pose a respiratory hazard. Inhalation of acrylic dust can lead to respiratory issues over time, so wearing a dust mask or a P100 respirator (which filters 99.97% of airborne particles) is essential. For prolonged exposure, a half-face or full-face respirator with a HEPA filter is recommended to prevent inhalation of the fine particles created during cutting or engraving.
- Safety Glasses or Face Shield: When working with acrylic, small debris and particles can be ejected at high speeds during the cutting process. Safety glasses with side shields are necessary to protect the eyes from flying debris. For additional protection, especially during more intense operations, a face shield is recommended. It provides full face coverage, ensuring that any particles or debris are blocked from contacting the face, reducing the risk of injury.
- Hearing Protection: CNC routers can generate significant noise, especially when cutting hard materials like acrylic at high speeds. Prolonged exposure to loud noises can lead to hearing damage. Operators should wear earplugs or over-the-ear earmuffs to protect their hearing. Hearing protection is essential when working in a factory or shop setting where multiple machines may be running simultaneously.
- Protective Gloves: While acrylic is not a sharp material in itself, handling large sheets or components can lead to cuts from sharp edges or router bits. Cut-resistant gloves should be worn when handling acrylic sheets to protect hands from accidental cuts or abrasions. Gloves also help maintain a secure grip when moving or installing acrylic sheets, reducing the risk of slippage.
- Protective Clothing: To further reduce the risk of injury, operators should wear protective clothing such as long-sleeve shirts and long pants to protect against flying debris or contact with the CNC machine’s moving parts. Wearing clothing that fits snugly prevents it from getting caught in the machine and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Foot Protection: Since CNC routers are often used in industrial environments with heavy machinery, steel-toed boots or safety shoes are essential to protect the feet from accidental drops of heavy acrylic sheets or tools.
- Ventilation Systems: While not technically a form of PPE, proper ventilation or dust extraction systems are necessary to complement personal protective equipment. These systems ensure that the work area is free from airborne dust and fumes, further safeguarding the health of the operator.







