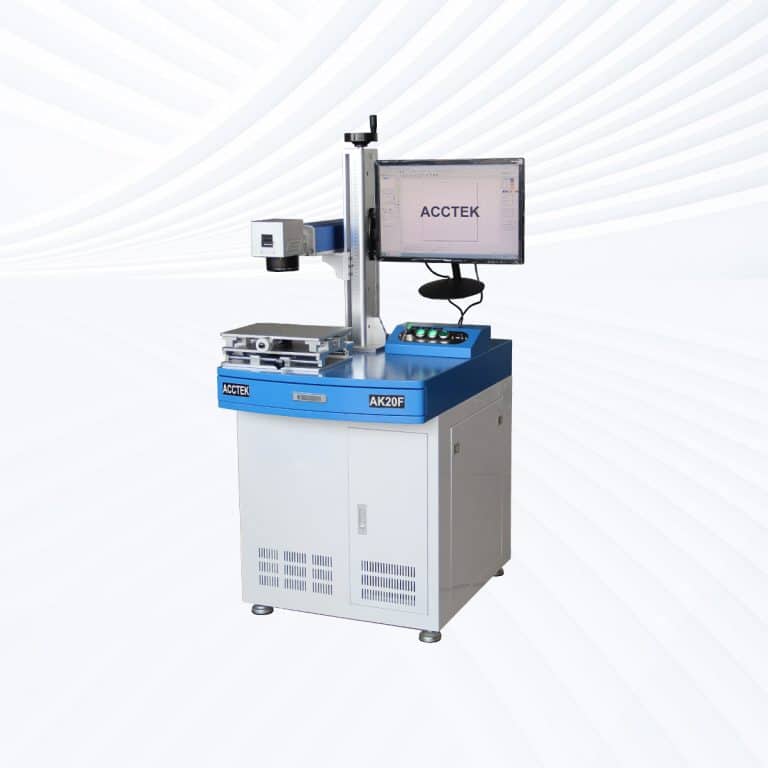
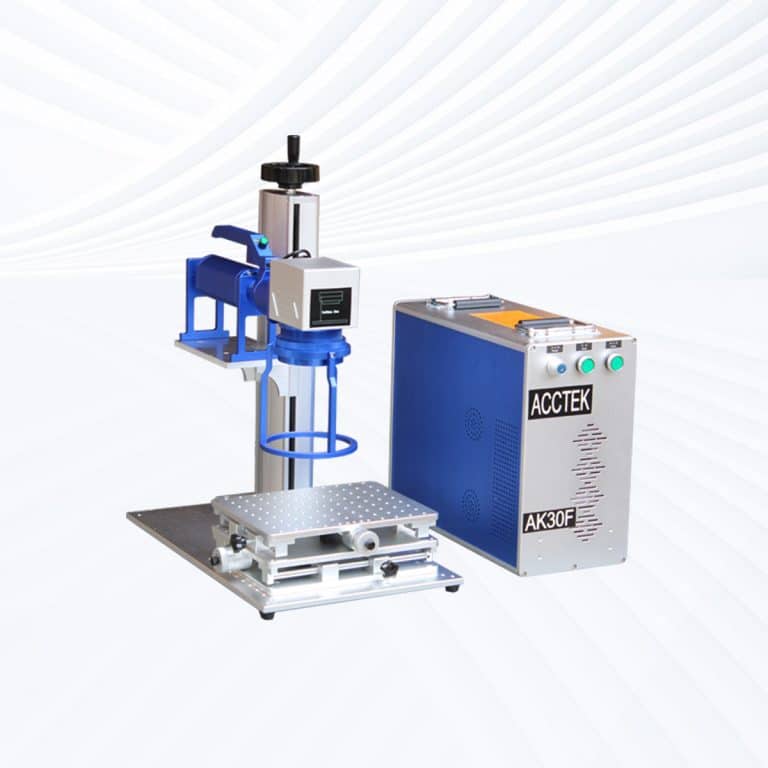
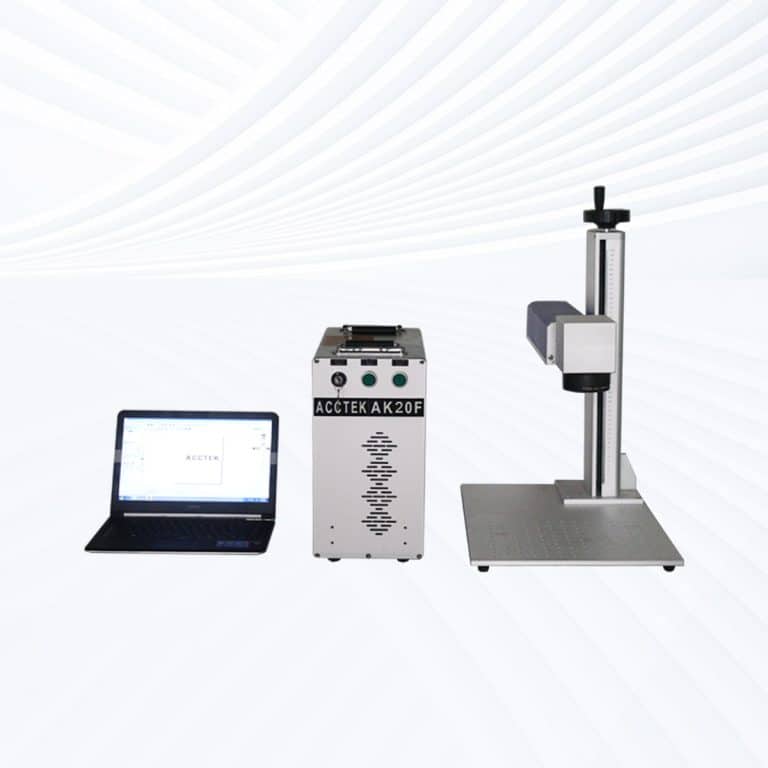
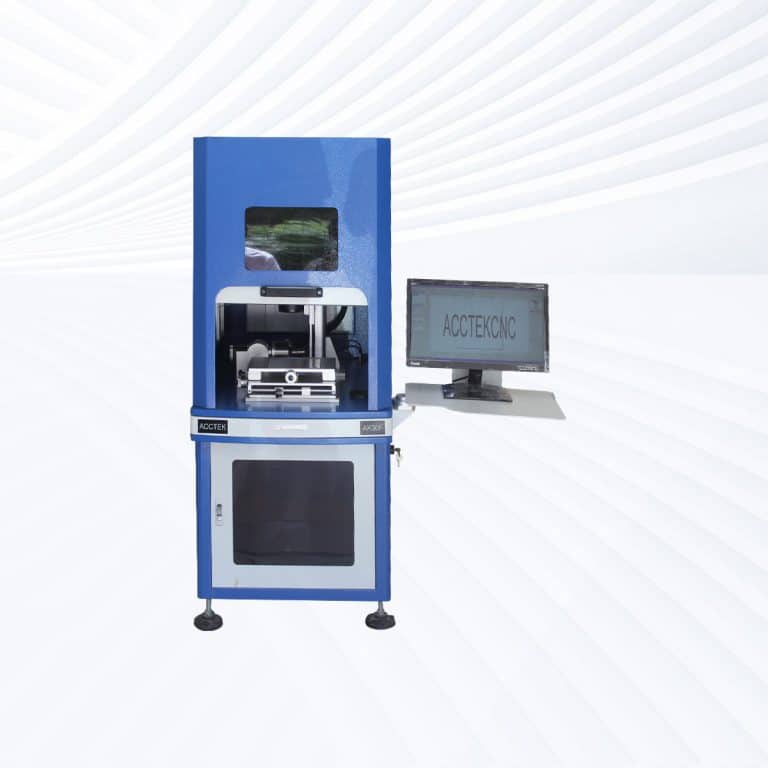
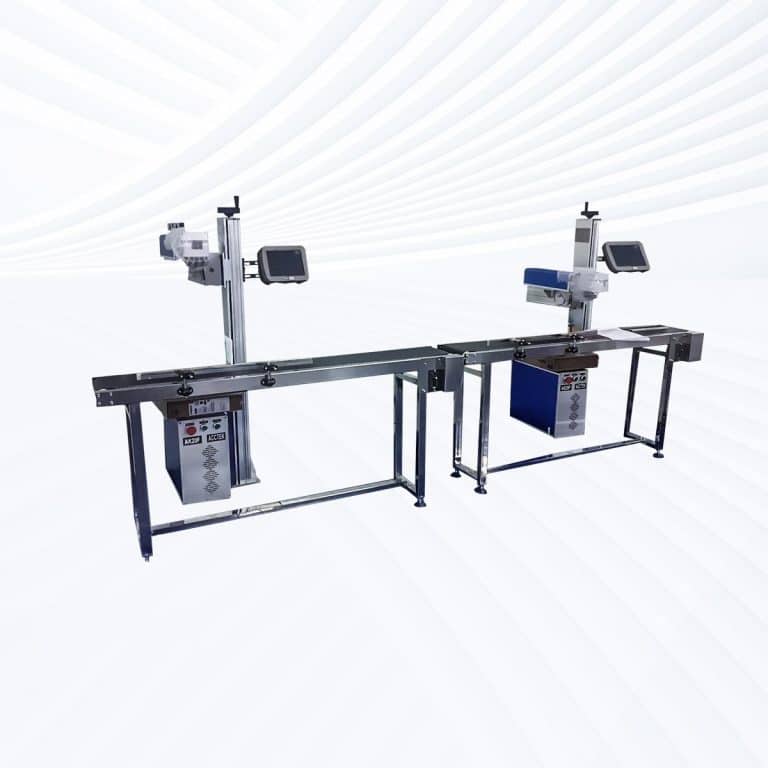
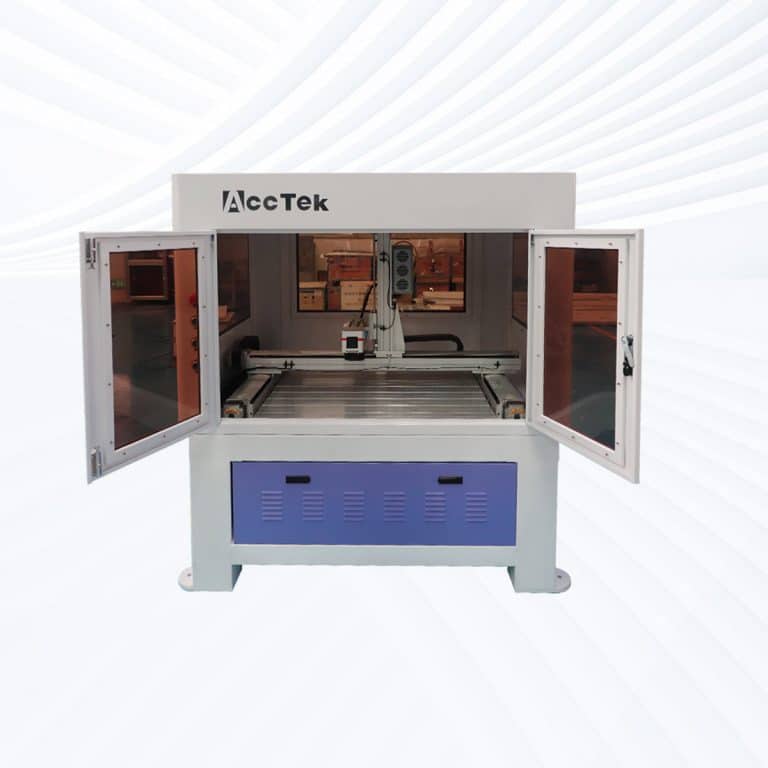
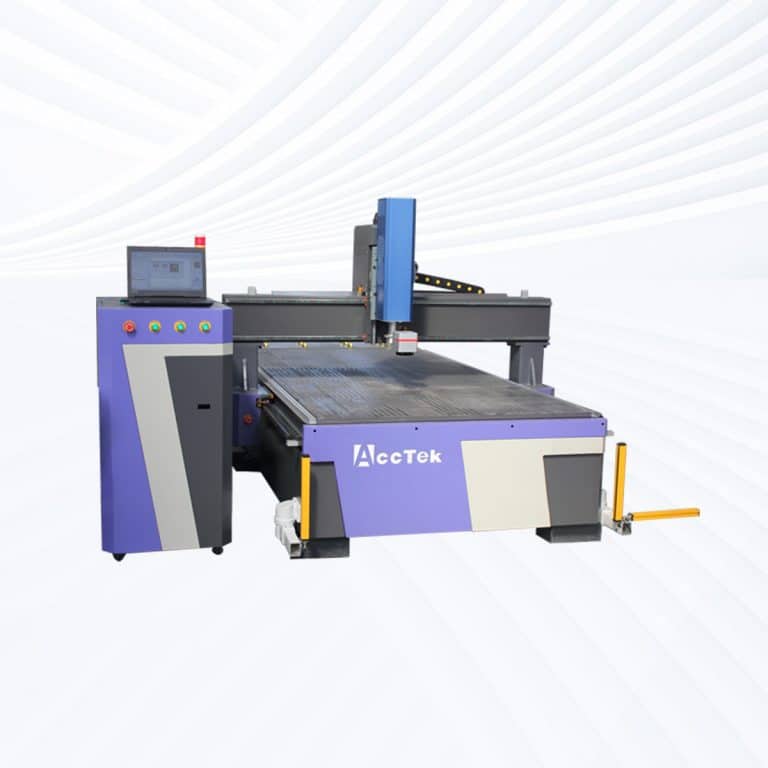
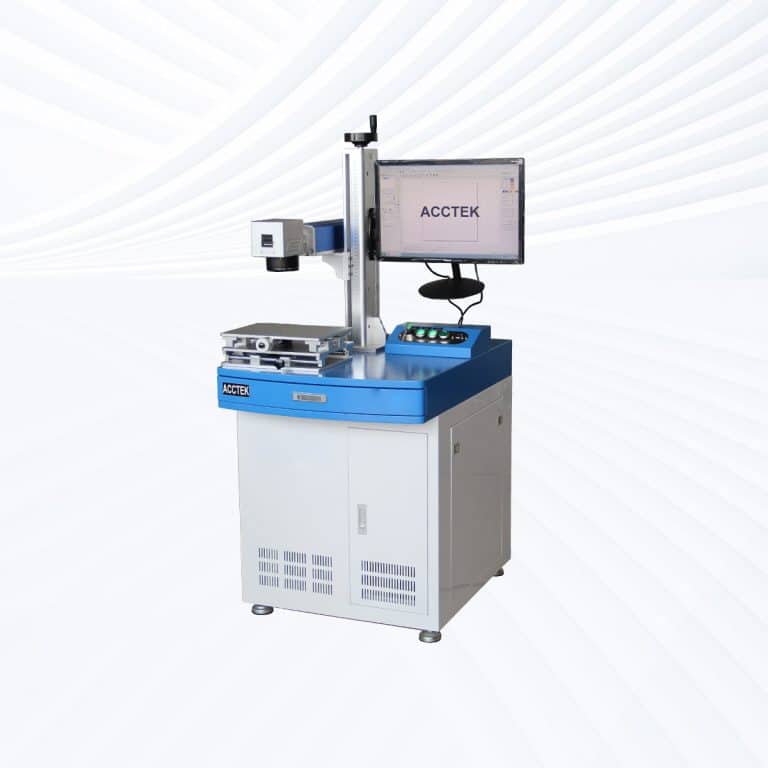
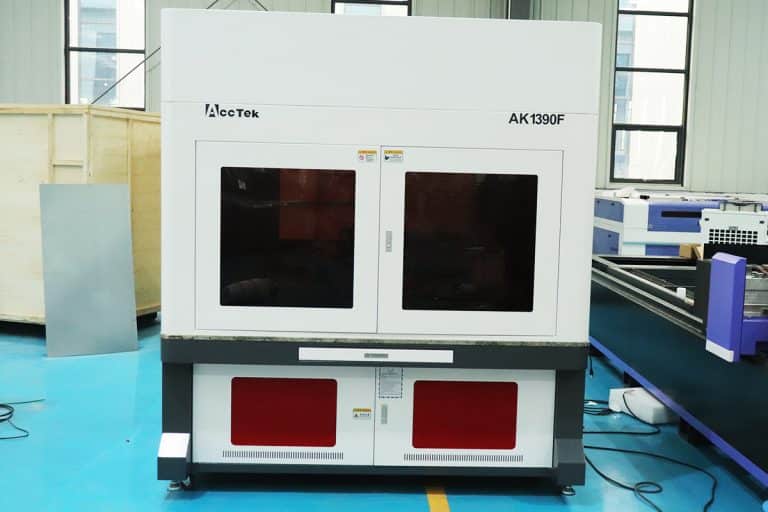
Product Introduction
Types of Stone Laser Marking Machines
Benefits of Laser Marking Stone
Permanent and Weatherproof Marks
Laser marking on stone produces highly durable marks that withstand extreme weather, abrasion, and time. Ideal for memorials, signage, and outdoor installations, these marks remain sharp and visible for years with no fading or erosion.
High Precision and Fine Detail
Laser marking delivers crisp, detailed results—even for intricate patterns, small text, and complex images. This level of precision makes it ideal for both industrial labeling and decorative applications such as personalized gifts or artistic designs.
Non-Contact, Damage-Free Process
Laser marking is a non-contact method, meaning no physical pressure is applied to the stone surface. This eliminates the risk of cracking or chipping, preserving the structural integrity of delicate or thin stone materials.
Works with Many Stone Types
Compatible with granite, marble, slate, limestone, quartz, sandstone, and more, laser marking machines adapt easily to different textures and hardness levels, ensuring consistent results across natural and engineered stone surfaces.
Fast and Scalable for Production
Laser marking supports both one-off customization and high-volume production. With fast processing speeds and repeatable accuracy, it's ideal for businesses that require efficiency without sacrificing detail or quality.
No Inks or Consumables Required
Because it uses only focused light, laser marking eliminates the need for paints, inks, or chemical treatments. This makes it a clean, eco-friendly solution with low operating costs and minimal maintenance requirements.
Compatible Stone Materials
- Granite
- Marble
- Slate
- Limestone
- Sandstone
- Basalt
- Quartz
- Travertine
- Onyx
- Soapstone
- Bluestone
- Dolomite
- Serpentine
- Schist
- Gabbro
- Andesite
- Tuff
- Jasper
- Alabaster
- Flint
- Obsidian
- Gneiss
- Feldspar-Rich Stone
- Conglomerate Stone
- Engineered Quartz
- Reconstituted Stone
- Terrazzo
- Ceramic Stone
- Artificial Marble
- Cultured Stone
- Concrete Pavers
- Cement-Based Composites
- Porcelain Tiles
- Lava Stone
- Quartzite
- Sintered Stone
- Crystallized Glass Stone
- Mosaic Stone Tiles
- Brick Stone
- River Rock
Application of Stone Laser Marking Machines








Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Marking Technologies
| Feature | Laser Marking | Screen Printing | Pad Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Quality | High precision, sharp detail, permanent | Decent on flat surfaces, limited resolution | Limited resolution on rough surfaces | High detail, but not deeply engraved |
| Durability | Permanent and weather-resistant | Can fade, chip, or wear with time | Prone to wear, especially outdoors | Vulnerable to scratching and UV degradation |
| Material Compatibility | Works on nearly all stone types | Limited to flat and smooth surfaces | Difficult on hard, uneven stone | Requires treated or coated surfaces |
| Contact with Surface | Non-contact, safe for delicate or textured stone | Direct contact, risk of smearing | Requires physical pressure | Minimal contact |
| Surface Adaptability | Excellent-works on flat, curved, or textured stone | Poor-best on flat surfaces only | Moderate-only slightly curved surfaces | Best on flat, coated surfaces |
| Setup Time | Minimal-file-based, no tooling | High-screens must be prepared per design | High-pad tooling setup required | Moderate-software setup only |
| Customization Flexibility | High-easy digital updates for unique designs | Low-new screens for every design | Moderate-requires pad changes | High-digital files easily updated |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly-no inks or chemicals | Uses inks, solvents, and screens | Uses inks and disposable pads | Uses ink-moderate waste |
| Cost per Mark (Long-Term) | Low-no consumables or recurring costs | Higher-ongoing cost for inks and screens | High-pad, ink, and cleaning supply costs | Medium-ink and maintenance costs |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low-simple lens and fume extraction care | High-screen cleaning and ink handling | High-pad wear and ink management | Moderate-printhead maintenance |
| Marking Depth | Surface etching to deep engraving | Surface-level ink only | Surface ink only | Surface-level coloration |
| Repeatability | Excellent-consistent results over long runs | Can vary with screen wear or ink application | Moderate-depends on pad condition | Good-consistent with stable calibration |
| Production Speed | Fast-ideal for custom and bulk work | Slower-prep and cleanup time required | Moderate-cycle time needed for each item | Fast for small runs, slower for textured stone |
| Automation Potential | High-easily integrated into production workflows | Difficult-manual process | Limited-some semi-automation possible | Moderate automation with flat media |
| Best Use Cases | Engraving stone tiles, monuments, gifts, signage | Simple logos or fills on flat stone panels | Small flat decorative items with simple art | Color images on flat coated stones |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

What Types of Laser Marking Machines Are There
This article explains the main types of laser marking machines, covering laser sources, marking methods, materials, applications, and how to choose the right system for production needs.
What Safety Precautions Are Required For Laser Marking
This article outlines essential safety precautions required for laser marking, including equipment safety, operator training, emergency protocols, and routine maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations.

How to Achieve High Contrast in Laser Marking
This article comprehensively covers the technologies, parameters, materials, and process controls required for consistent, high-contrast laser marking in industrial applications.

How Accurate Is Laser Marking
This article explores how laser marking achieves superior precision, the factors that influence this precision, and how various industries ensure consistent, high-quality, and permanent markings.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Stone Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- CO2 Laser Marking Machines for Stone ($3,500 to $25,000): CO2 laser marking machines, which are commonly used for engraving and marking on non-metals, are often used for stone, ceramics, and similar materials. They are widely available in various price ranges:
- Entry-Level Models: These machines typically fall at the lower end of the price range, offering basic features and smaller marking areas. They are suitable for small to medium-scale stone engraving tasks and are ideal for hobbyists or small businesses.
- Mid-Range Models: These offer better precision, larger working areas, and higher power for more efficient and faster engraving on stone. They are suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that need more consistent performance and higher-quality engraving.
- High-End Models: High-end CO2 lasers come with advanced features such as larger marking areas, higher laser power, faster processing speeds, and more precise control. These machines are often used in industrial applications, where high volume and high precision are required for engraving on stone.
- Fiber Laser Marking Machines for Stone ($2,500 to $30,000): While fiber lasers are typically more common for metal engraving, they can also be used for stone marking, especially when precise detail and high efficiency are required. They offer faster marking speeds and better precision compared to CO2 lasers, but may require additional adjustments or settings for stone materials.
- Entry-Level Fiber Lasers: Lower-end fiber laser machines are priced more affordably and are suitable for lighter marking tasks on stone. They are used for small businesses or personal projects that require high-quality detail but don’t need industrial-strength power.
- Mid-Range Fiber Lasers: These machines offer improved laser quality, higher engraving speeds, and greater precision, making them ideal for professional users working with a variety of materials, including stone. They are suitable for medium-scale production environments.
- High-End Fiber Lasers: High-power, advanced fiber laser systems are designed for high-efficiency, industrial-scale operations. These models feature larger marking areas, higher laser powers, and faster speeds, ideal for heavy-duty use on stones in large volumes.
Which Laser Marking Machine is Best for Marking Stone?
- CO2 Laser Marking Machine: Best for soft stones like marble and sandstone. It offers high precision, detailed engravings, and deeper marking. However, it operates more slowly and requires more maintenance.
- Fiber Laser Marking Machine: Best for hard stones like granite and quartz. It provides faster marking speeds, a longer lifespan, and minimal thermal damage. However, it’s less effective on soft stones and creates shallower marks.
How Do I Remove Laser Markings from Stone?
- Mechanical Abrasion
- Sanding or Polishing: For surface-level laser markings, mechanical abrasion such as sanding or polishing with a diamond grinding pad or stone polishing tools can effectively remove the marks. This method works well for smoother stones and can restore the surface finish.
- Wire Brushes or Abrasive Blasting: For more textured stones, abrasive blasting or wire brushing may be necessary. Using media like aluminum oxide or silicon carbide in sandblasting can effectively remove laser marks, especially on rough or porous stone surfaces.
- Chemical Methods
- Acid Treatment: Some stones, like marble or granite, can be treated with mild acids (e.g., hydrochloric acid diluted with water). This can help remove the marks but requires careful handling and testing on a small area first to ensure that the stone is not damaged. Always wear protective gear and ensure good ventilation.
- Stone Polishing Chemicals: Specialized stone polish products that contain mild abrasives can sometimes help to remove surface markings. These are typically used for natural stones like marble, granite, or limestone.
- Laser Ablation (Reverse Process)
- Laser Cleaning: In some cases, a different laser system can be used to perform a reverse cleaning process. This technique uses a laser of a different wavelength to focus on the laser-marked area, effectively removing or reducing the visibility of the marking by vaporizing it. However, this process requires precision and specialized equipment and may not be cost-effective for all scenarios.
- Surface Restoration
- If the marking is deep or has caused surface damage, a more advanced restoration process may be required. This can involve reshaping or resurfacing the stone entirely to remove any visible signs of the marking, which can be costly but may be necessary for high-value stonework.
- Polishing the Surface
- After removing the laser markings, it is often necessary to polish the stone again to restore its original shine and appearance. This can be done with a polishing compound and a mechanical buffer designed for stone.
How Should I Choose Stone Laser Marking Machines?
- Laser Type
- CO2 Lasers: The most common laser type for stone marking, especially for non-metallic materials like stone, marble, and granite. CO2 lasers can create high-contrast marks and are ideal for engraving or cutting on stones. They work well for applications requiring detailed markings and designs.
- Fiber Lasers: Although fiber lasers are more commonly used for metals, they can also mark stone surfaces, especially for tasks that require high precision. Fiber lasers tend to offer faster engraving speeds but might not be as effective for all types of stones as CO2 lasers.
- Power Requirements
- The power of the laser determines the depth and speed of the marking. For stone marking, a machine with a power range of 30W to 150W is usually sufficient, depending on the type and hardness of the stone.
- Lower power (30W to 50W) is suitable for surface marking or engraving delicate designs.
- Higher power (100W to 150W) is needed for deeper engraving or cutting harder stones like granite.
- Marking Speed and Precision
- Speed: If you need to mark large quantities of stone, the speed of the machine becomes essential. Some laser marking machines are optimized for speed but may sacrifice precision. Consider whether speed or precision is more important based on your project’s volume and complexity.
- Precision: For intricate designs or fine text, a high-precision machine is necessary. Look for machines that offer high resolution (e.g., 1,000 DPI or higher) to ensure sharp and detailed markings.
- Stone Compatibility
- Material Support: Not all stone types react the same way to lasers. CO2 lasers, for example, work well with most stones, including marble, granite, and slate. However, certain stones might require specific wavelengths to achieve optimal results.
- Stone Thickness: Make sure that the machine is compatible with the thickness of the stone you are marking. Some lasers are optimized for thin materials, while others can handle thicker stones. Check the machine’s max engraving depth to ensure it meets your needs.
- Cooling System
- Water Cooling: Stone marking generates significant heat, especially when working with higher-powered lasers. Look for a machine with an efficient water-cooling system to ensure the laser operates continuously without overheating.
- Air Assist: Some laser machines are equipped with air assist systems that blow air over the engraving area to keep the stone cool, reduce smoke, and improve the quality of the marking.
- Software and Control System
- User-Friendly Software: The laser machine should come with software that is easy to use for designing, importing files, and controlling the laser. Look for compatibility with popular file types like AI, DXF, and PDF.
- Control Interface: The machine should allow for easy adjustment of parameters like laser power, speed, and focal distance. A digital control system or touchscreen interface will make it easier to fine-tune settings for different stone materials.
- Maintenance and Service
- Ease of Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial to keeping a laser marking machine running efficiently. Look for machines with easy-to-replace parts, such as the lens and mirrors, and a user-friendly design for cleaning.
- Technical Support: Ensure that the manufacturer provides good customer service and support, especially if you encounter issues with the machine. A warranty, training, and ongoing assistance are essential for smooth operation.
- Machine Size and Footprint
- Consider the space available in your workshop or production area. The machine should fit comfortably within your available workspace without compromising its ability to process larger stone pieces.
- Check whether the working area (the size of the stone you can mark) is large enough for your typical projects.
- Budget
- Initial Investment: Stone laser marking machines can vary widely in price, ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. The machine’s power, features, and capabilities will all influence the price. Be sure to balance your budget with the features you need.
- Operating Costs: Consider not only the upfront cost but also the operating costs, including energy consumption, replacement parts, and maintenance.
- Safety Features
- Enclosures and Safety Locks: Laser marking machines can be dangerous if used improperly. Look for machines that come with built-in safety enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and safety interlocks to protect operators from accidental exposure to the laser.
- Fume Extraction: Stone marking can produce fumes, especially when engraving certain materials. A built-in fume extraction system is vital for maintaining a safe and clean working environment.
Is Laser Marking Stone Safe?
- Laser Safety
- Eye Protection: One of the most significant risks with laser systems is the potential harm to the eyes. Lasers can cause permanent eye damage if the beam is directly or indirectly reflected into the eyes. Laser safety goggles specific to the wavelength of the laser being used (e.g., CO2 or fiber) should always be worn by operators and anyone near the machine.
- Enclosures and Safety Guards: Most modern laser marking machines are equipped with enclosures or safety barriers to prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam. Ensure that the laser machine has a fully enclosed system to minimize the risk of accidental exposure.
- Fume and Dust Hazards
- Fume Generation: Laser marking stone materials, especially harder stones like granite or marble, can release fine dust and fumes. Some stone types may produce harmful compounds when heated by the laser. For instance, marble can emit silica dust, which can be harmful when inhaled.
- Fume Extraction Systems: A fume extraction system should always be in place to remove the harmful fumes and particulates from the air. These systems draw fumes away from the work area and filter out harmful substances, preventing them from being inhaled by operators.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace to reduce the buildup of fumes and dust, especially in smaller or poorly ventilated areas.
- Fire Hazards
- Ignition of Flammable Materials: While stone itself is generally not flammable, materials like wood or plastic (used in combination with stone) may catch fire if exposed to the high heat generated by the laser. It’s crucial to clear the work area of any combustible materials and use air assist to reduce the likelihood of ignition.
- Proper Fire Extinguishing Equipment: Always have fire extinguishers nearby and ensure staff are trained on how to use them in case of an emergency.
- Heat Management
- Laser Heat Generation: Laser marking can generate significant heat, especially when engraving hard stones or using high-powered lasers. The stone can also become hot to the touch, which could cause burns or injuries.
- Cooling Systems: Ensure the machine is equipped with an efficient cooling system (typically water-cooling for the laser and air assist for the engraving surface). Cooling systems help manage the heat generated during the marking process, protecting both the equipment and the operator.
- Machine Safety Features
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Many laser machines come with emergency stop buttons that can immediately halt the operation in case of any malfunctions or safety hazards.
- Safety Interlocks: Laser marking machines should have safety interlocks that prevent the machine from operating if the cover or enclosure is open, reducing the risk of accidental exposure to the laser beam.
- Training and Supervision
- Operator Training: Operators must receive proper training on the safe operation of the laser marking machine. This includes understanding how to handle the equipment, how to respond in case of an emergency, and how to maintain the laser system.
- Supervision: For new operators or during training periods, supervision is essential to ensure that safety protocols are followed.
- Stone-Specific Considerations
- Stone Composition: Some stones, particularly certain types of granite, may contain trace amounts of harmful materials (e.g., radioactive minerals like radon) that could pose a risk when marked with a laser. It’s important to know the composition of the stone and assess any potential hazards.
- Proper Waste Disposal: After marking, the stone waste (dust, debris, etc.) should be disposed of properly. Use appropriate waste disposal methods to handle stone dust and laser-engraved materials, especially if they contain harmful substances.
How Should I Maintain Stone Laser Marking Machines?
- Cleaning and Dust Removal
- Regular Cleaning: Stone laser marking produces dust and debris that can accumulate in the machine. Clean the machine regularly to prevent dust buildup on critical components like the laser lens, mirrors, and cooling system. Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove dust from hard-to-reach areas.
- Laser Lens and Mirrors: The laser lens and mirrors are essential for directing the laser beam. Clean them frequently to maintain beam quality and avoid interference with the laser path. Use specialized lens cleaning wipes or cloths, and avoid touching the lens directly with your fingers.
- Air Assist Nozzle: The air assist system helps blow away debris from the marking area. Ensure the air assist nozzle is clean and free of obstructions to allow efficient airflow and prevent particles from affecting the marking quality.
- Cooling System Maintenance
- Water-Cooled Lasers: Many stone laser marking machines are equipped with a water-cooling system to keep the laser tube cool during operation. Regularly check the water level in the cooling tank and ensure it is clean. Replace the water periodically to prevent contamination and overheating of the laser tube.
- Clean the Water Chiller: The water chiller should be cleaned regularly to prevent debris and scale buildup that can reduce its efficiency. Use clean, distilled water and check the chiller’s filter for any blockages.
- Air Assist System Maintenance: The air assist system should be checked for leaks and cleaned regularly. Replace any worn-out tubing or components to ensure the system operates at peak efficiency.
- Laser Tube and Power Supply Care
- Inspect the Laser Tube: The laser tube generates the laser beam, and its condition directly impacts the machine’s performance. Check for signs of damage, such as discoloration or physical wear. If you notice any drop in marking power or quality, the laser tube may need maintenance or replacement.
- Power Supply Monitoring: Regularly check the laser power supply for signs of wear or malfunction. Ensure that all connections are secure and that the power supply operates smoothly. A malfunctioning power supply can lead to inconsistent laser performance.
- Focus Lens and Focusing System
- Focusing Lens: Ensure the focusing lens is in good condition. If it gets dirty or scratched, it can affect the quality of your marks. Clean it gently with a soft cloth and replace it if necessary.
- Adjust the Focus: Regularly check and adjust the focusing system of the laser to ensure that the laser beam is focused correctly on the stone’s surface. This is crucial for precise, clean markings.
- Mechanical Components
- Check the Gantry and Motors: Inspect the gantry, rails, and motors for any wear or misalignment. Clean the rails and lubricate moving parts with appropriate lubrication to ensure smooth movement.
- Belt and Pulley Inspection: Check the belts and pulleys for wear. Replace any damaged components to maintain precise movement and avoid tracking errors.
- Check the Guide Rails: Ensure that the guide rails are free from debris and properly aligned. Lubricate the rails to maintain smooth operation and reduce wear on the machine.
- Air Filtration System
- Clean Filters: If your machine is equipped with an air filtration system to remove harmful fumes, regularly clean or replace the filters. Dirty filters can cause a buildup of dust and fumes inside the machine, potentially affecting performance and safety.
- Check Ventilation: Ensure that the ventilation system is working properly. Poor airflow can result in overheating, reduced marking efficiency, and the accumulation of dangerous fumes.
- Software and Control System
- Update Software: Ensure that the control software is up-to-date to maintain compatibility with your machine and improve operational efficiency. Regularly check for software updates or patches from the manufacturer.
- Backup Settings and Data: Periodically back up the machine’s settings, calibration data, and design files to prevent data loss in case of system crashes.
- Test Calibration: Regularly check the machine’s calibration to ensure that the markings are accurate. If the laser output appears inconsistent, recalibrate the machine to restore precision.
- Safety Systems
- Check Safety Features: Regularly inspect the safety features of the machine, including the emergency stop buttons, safety interlocks, and warning signs. Ensure that the laser enclosure and other protective barriers are in place and functioning properly.
- Fume Extractor Maintenance: If the machine uses a fume extractor, make sure it is properly maintained. Clean the fan and replace the filters to ensure optimal airflow and filtration.
- General Checks
- Inspect Cables and Wiring: Over time, cables and wiring may become worn or damaged, affecting the functionality of the machine. Periodically inspect all cables and connectors for wear, fraying, or loose connections.
- Check for Vibrations: Excessive vibrations can lead to inaccurate markings and damage to the machine’s components. Ensure that the machine is on a stable, level surface and that vibration-damping measures are in place if necessary.
- Professional Maintenance
- Schedule Regular Servicing: While regular cleaning and basic maintenance can be done in-house, schedule professional servicing at regular intervals, especially if the machine is used extensively. A trained technician can thoroughly inspect the machine, perform in-depth maintenance, and replace any worn-out components.
What Training is Required to Operate Stone Laser Marking Machines?
- Basic Laser Safety Training
- Laser Safety Awareness: Operators must understand the basic principles of laser safety, including the risks associated with exposure to laser beams and how to mitigate them. This includes the use of laser safety goggles and the importance of ensuring that the machine’s safety enclosure is always in place.
- Safety Protocols: Operators should be trained on emergency stop procedures, how to respond to emergencies (such as fire or equipment malfunctions), and how to handle hazardous materials, including laser fumes and dust.
- Protective Gear: Training should include the correct usage of personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection if necessary.
- Machine Setup and Operation
- Machine Assembly and Setup: Operators must be trained on how to properly set up the laser marking machine, including ensuring the laser tube, cooling system, and air assist are properly installed and functioning.
- Loading and Securing Stones: Operators need to know how to properly load and secure the stones or materials in the machine’s work area to ensure accurate and safe marking. This includes aligning the stone and adjusting the Z-axis for precise focusing of the laser.
- Focal Length Adjustment: Proper training is required on how to adjust the focal length of the laser, which is crucial for achieving clean and sharp markings on the stone’s surface.
- Software and Control Systems
- Software Operation: Operators should be proficient in using the laser marking software, which controls the design, settings, and operation of the laser machine. This includes tasks such as importing design files (e.g., AI, DXF, PDF), setting laser parameters (power, speed, frequency), and calibrating the machine.
- Design Software Integration: Operators should know how to use design software (like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW) in conjunction with the laser system to create and modify marking designs.
- Machine Parameter Settings: Training should include how to set the correct laser parameters (such as power, speed, and frequency) based on the stone type and the desired marking result.
- Material Knowledge and Compatibility
- Understanding Stone Types: Operators should be trained to understand the different types of stone (e.g., granite, marble, limestone) and how they interact with the laser. Knowledge of laser material compatibility will help operators adjust settings to avoid damaging the stone or producing poor-quality markings.
- Surface Preparation: Training should cover how to prepare the surface of the stone (e.g., cleaning and ensuring it’s free from dust or oil) before marking to achieve optimal results.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Basic Maintenance: Operators should receive training on basic maintenance procedures, such as cleaning the laser lens, checking the cooling system, and replacing consumables like the focusing lens or air filters.
- Troubleshooting Skills: Operators should know how to troubleshoot common issues (e.g., inconsistent marking, misalignment) and take corrective actions to ensure the machine runs efficiently.
- Calibration and Quality Control
- Calibration: Operators must be trained to calibrate the machine regularly, ensuring that the laser beam is correctly aligned and focused to produce high-quality markings.
- Quality Control Checks: Operators should be trained to visually inspect the quality of the markings on the stone, checking for clarity, depth, and precision. They should also be able to identify any defects or issues that might arise during the marking process (such as uneven marking, incomplete engraving, or burn marks).
- Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Fume Management: Operators must be trained to use the fume extraction system to prevent harmful fumes from accumulating in the workspace. This includes knowing when to clean or replace filters and ensuring proper ventilation.
- Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of stone dust and debris is important for safety and cleanliness. Operators should be trained on how to collect and dispose of waste in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Compliance with Regulations: Training should also include awareness of any local regulations regarding laser equipment use, such as noise levels, emissions, and safety standards.
- Advanced Techniques and Applications
- Advanced Marking Techniques: For operators who will be performing advanced tasks, such as deep engraving or cutting stone, additional training on how to adjust the laser settings for different depths and types of stone is necessary.
- Multi-material Marking: In cases where stones are combined with other materials (e.g., stone and metal), operators should understand how to adjust the laser settings to accommodate multiple materials for precise marking.
- Operator Certification (Optional)
- Depending on local regulations and company policies, some operators may be required to complete a laser marking certification program. This certification ensures that operators have met the necessary safety standards and have the expertise to operate the machine safely and effectively.
What Are the Environmental Requirements for Using Stone Laser Marking Machines?
- Proper Ventilation and Airflow
- Fume Extraction System: Laser marking produces fumes and dust, particularly when engraving or cutting stone. A fume extraction system is essential to remove harmful particles and fumes from the air. This system should be equipped with filters to capture dust and particles and prevent them from entering the workspace.
- Ventilation: Proper room ventilation is crucial to maintain airflow and disperse heat generated by the machine. Adequate ventilation ensures that the workspace is free from accumulated fumes and reduces the risk of respiratory issues for operators.
- Air Assist: For some stone marking processes, air assist (compressed air) helps blow away debris from the engraving area and prevents the stone from overheating. Ensuring proper airflow is essential for both fume removal and cooling.
- Temperature Control
- Stable Temperature: Laser marking machines, especially high-powered ones, require a stable ambient temperature to operate effectively. Temperature fluctuations can affect the precision and consistency of laser marking. Ideally, the temperature should be maintained between 18℃ (64℉) and 25℃ (77℉) to ensure the machine operates within its optimal parameters.
- Cooling System: The machine should be equipped with a water-cooling system (for CO2 lasers) or an air cooling system to prevent overheating during extended operations. Regular maintenance of the cooling system is necessary to ensure it is functioning properly and to prevent the laser tube from overheating.
- Humidity Control
- Optimal Humidity Range: Excessively high or low humidity can interfere with the machine’s operation and affect the material being marked. The ideal humidity range for laser marking machines is typically between 40% and 60%.
- Condensation Risks: If the humidity is too high, there may be a risk of condensation inside the machine, especially near electrical components, which could cause damage or malfunction. Low humidity, on the other hand, could generate static electricity, affecting both the machine and the materials being marked.
- Clean and Dust-Free Environment
- Dust Control: Stone laser marking produces significant dust, particularly from harder stones like granite. A clean, dust-free environment is essential to prevent the dust from settling on sensitive machine parts such as lenses, mirrors, and cooling systems, which could degrade the laser’s performance.
- Regular Cleaning: The workspace should be cleaned frequently to remove any dust or debris, and the machine should be regularly inspected and cleaned. An automated air filtration system is often used in conjunction with the laser to ensure the air quality remains at a safe level.
- Flooring and Surface Conditions
- Stable Surface: The flooring and work surface should be level and stable to prevent vibrations, which could negatively impact the precision of the laser marking. Uneven floors or surfaces may lead to misalignments in the laser path, affecting the accuracy of markings.
- Vibration Dampening: In some cases, vibration-dampening pads or systems may be necessary to reduce external vibrations from nearby machinery or heavy traffic, especially in industrial environments.
- Lighting Conditions
- Controlled Lighting: Bright lights or direct sunlight can affect the visibility of the markings during or after the engraving process. It’s important to have controlled lighting in the workspace, such as LED lights that are positioned away from the laser marking area, to ensure that the operator has proper visibility for setup, monitoring, and quality control.
- Laser Beam Visibility: Ensure the machine’s laser safety enclosure is fully transparent or has a sufficient window to allow the operator to safely monitor the process while also ensuring the beam is not exposed to unnecessary ambient light that could interfere with its focus and performance.
- Noise Control
- Noise Levels: While laser marking machines generally operate quietly, certain models may generate noise, especially during high-power operations or when cooling systems are in use. The workspace should be set up with noise control measures, such as soundproofing or acoustic panels, to reduce noise pollution for workers in the vicinity.
- Hearing Protection: In environments where high noise levels are expected, operators should wear hearing protection to avoid long-term hearing damage.
- Power Supply and Electrical Requirements
- Stable Power Source: The machine requires a stable electrical supply to function efficiently. Voltage fluctuations or inconsistent power can affect the performance of the laser, especially in machines with high-powered lasers. Ensure that the electrical system can support the machine’s power requirements.
- Grounding: Proper grounding of the machine is necessary to prevent electrical shocks and ensure the safety of the operator. Grounding systems should be checked periodically for integrity.
- Workplace Safety Standards
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure that the workspace complies with local health, safety, and environmental regulations, including OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards in the U.S. or other regional safety requirements.
- Fire Prevention: Since laser marking machines can produce heat, ensure the workspace is equipped with fire suppression systems, such as extinguishers or an automatic fire suppression system, to respond to any emergency.
- Space Requirements
- Sufficient Workspace: The machine should be installed in a location that provides sufficient space for proper operation, including adequate clearance around the machine for maintenance, ventilation, and safe operation.
- Room for Material Handling: Ensure there is enough space for operators to load, unload, and move stone materials safely. This includes having a stable surface to place the stones and tools for measuring and adjusting the material.








