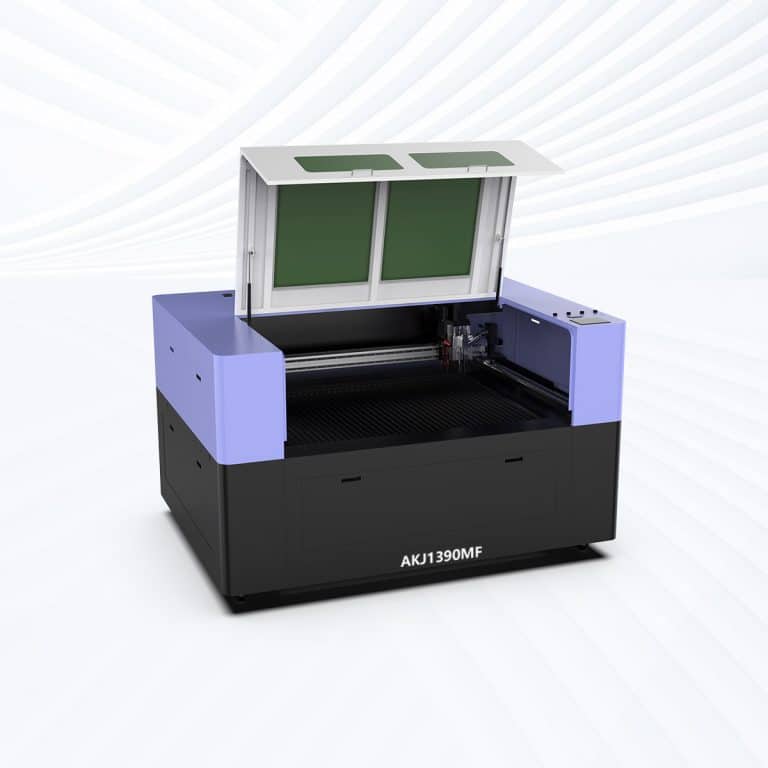
Product Introduction
Benefits of Laser Cutting Rubber
Clean, Precise Edges
CO2 lasers cut rubber with high accuracy, creating sharp, sealed edges without fraying or distortion. This eliminates the need for secondary trimming or finishing and ensures tight tolerances for gaskets, seals, and precision parts.
Non-Contact Cutting Process
The laser beam cuts rubber without physically touching it, avoiding pressure or deformation. This is especially important for soft or compressible rubber materials that are prone to warping or distortion when using mechanical cutting tools.
Supports Complex Shapes and Details
CO2 lasers can cut intricate geometries, tight curves, and small holes with ease. This enables the production of detailed gaskets, logos, stamps, and technical components that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional cutters.
No Tool Wear or Blade Replacement
Unlike mechanical systems, CO2 lasers don’t rely on physical blades. This means no dulling, no replacements, and consistent performance over time—ideal for high-volume operations with repeatable designs.
Minimal Material Waste
Laser cutting allows for tight nesting of parts, reducing offcuts and maximizing material usage. Combined with its precision, this lowers production costs and improves overall efficiency, especially for expensive or specialty rubber materials.
Compatible with Many Rubber Types
CO2 laser cutting machines can process natural rubber, silicone, EPDM, SBR, and engrave rubber sheets. This flexibility makes them ideal for diverse applications in automotive, industrial, medical, and creative sectors.
Compatible Rubber Materials
- Natural Rubber
- Silicone Rubber
- EPDM Rubber
- SBR
- Neoprene Rubber
- Nitrile Rubber
- Viton Rubber
- Buna-N Rubber
- Butyl Rubber
- Latex Rubber Sheets
- Foam Rubber
- Rubberized Cork
- Rubberized Fabric
- Conductive Rubber
- Anti-Static Rubber
- Laser-Engraving Rubber Sheets
- Stamp Rubber
- Rubber Gaskets
- Rubber Seals
- Rubber Mats
- Rubber Insulation Sheets
- High-Temperature Silicone Sheets
- Dense Rubber Sheets
- Soft Rubber Sheets
- Open-Cell Foam Rubber
- Closed-Cell Foam Rubber
- Colored Rubber Sheets
- Rubber with Textile Backing
- Weather Stripping Rubber
- Rubber Rollers
- Rubber Padding
- Rubber Tape
- Perforated Rubber Sheets
- Rubber Spacers
- Oil-Resistant Rubber
- UV-Resistant Rubber
- Fire-Retardant Silicone
- Recycled Rubber Sheets
- Rubber Floor Tiles
- Rubber Diaphragms
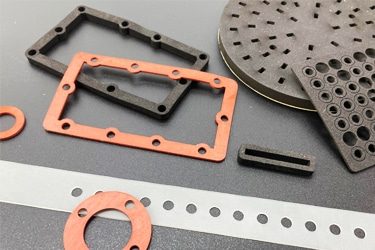
Application of Rubber Laser Cutting Machines







Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Cutting Technologies
| Comparison Item | Laser Cutting | CNC Routing | Knife Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitability for Rubber Materials | Highly suitable | Limited | Very suitable | Suitable |
| Cutting Precision | Very high | Medium | Medium | High |
| Edge Quality | Clean, smooth edges | Rough edges | Clean but uneven | Clean but wet |
| Material Deformation | None (non-contact) | High risk | Medium | None |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Small and controllable | None | None | None |
| Kerf Width | Very narrow | Medium | Narrow | Wide |
| Cutting Speed | High | Moderate | High | Slow |
| Thickness Capability | Thin to medium rubber | Medium | Thin to medium | Thin to thick |
| Tool Wear | No tool wear | High tool wear | Blade wear | Nozzle wear |
| Material Waste | Very low | Medium | Medium | High |
| Setup and Changeover Time | Very fast | Moderate | Fast | Long |
| Design Flexibility | Excellent | Good | Limited | Good |
| Automation and Repeatability | Excellent | Good | Good | Good |
| Operating Cost | Moderate | Moderate | Low | High |
| Overall Efficiency for Rubber Processing | Excellent | Fair | Good | Good |
Why Choose Us
Advanced Technology
Our laser cutting machines feature high-speed, precision cutting with the latest laser technology, ensuring smooth edges, minimal waste, and superior efficiency across various materials and thicknesses.
Reliable Quality
Each machine undergoes rigorous quality control and durability testing to ensure long-term stability, low maintenance, and consistent high performance, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Comprehensive Support
We provide full technical support, including installation guidance, operator training, and after-sales service, ensuring smooth machine operation and minimal downtime for your business.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Our machines offer high performance at competitive prices, with customizable options to fit different production needs, helping businesses maximize their investment without compromising on quality.
Related Resources

Understanding The Odors Associated With Laser Cutting
This article provides a comprehensive guide to laser cutting odors, explaining the causes of odors, material-specific odors, health risks, and practical strategies for effectively controlling odors and ensuring safer operation.

What Safety Measures Should Be Taken When Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article teaches the basic safety measures for operating a laser cutting machine, including hazard awareness, engineering controls, PPE, fire prevention, ventilation, training, and emergency response drills.

Addressing the Challenges of Fiber Laser Cutting: Common Problems and Solutions
This article explores common challenges in fiber laser cutting, including material-related issues, machine performance, and operator-related problems, offering practical solutions to optimize cutting quality and efficiency.

Precautions for Operating Laser Cutting Machines
This article provides a detailed overview of basic precautions for operating laser cutting machines, covering safety risks, proper setup, operating guidelines, maintenance procedures, and emergency preparedness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can It Cut Rubber Without Melting?
Does It Produce Burnt Smells When Laser Cutting Rubber?
Does It Require Special Ventilation For Laser Cutting Rubber?
What Is The Price Range For Rubber Laser Cutting Machines?
How Does Laser Power Affect Rubber Cutting Quality?
- Low Laser Power: When power is too low for the rubber’s thickness or density, the beam won’t fully penetrate the material. This leads to incomplete cuts, ragged edges, and potential tearing when removing parts. The laser may also leave melted or sticky residue along the cut path because the material absorbs heat unevenly without reaching full vaporization.
- Optimal Laser Power: At the correct power level, the beam cleanly vaporizes the cut path without excessive melting or burning. This produces smooth, sealed edges with minimal residue. The cut is consistent throughout, even on curves or intricate shapes, and the part can be removed from the sheet without manual trimming.
- Excessive Laser Power: Too much power can overheat the rubber, causing excessive charring, edge deformation, and widening of the kerf (cut width). In some cases, the heat may create a strong burnt odor or damage surrounding material, especially on thin or soft rubber types. High power can also shorten laser tube life unnecessarily and waste energy.
- Material Safety Considerations: Only laser-safe, non-chlorinated rubbers should be cut, as some formulations (like those with PVC content) release toxic chlorine gas when heated. Proper ventilation and fume extraction are essential at all power levels.
- Thickness Guidelines: Thicker rubber requires more power and slower cutting speeds for clean results, while thin sheets benefit from lower power and faster speeds to prevent burning. Testing on sample pieces is the best way to fine-tune settings before a production run.
Does Laser Cutting Rubber Produce Hazardous Fumes?
- Natural and Laser-Safe Synthetic Rubbers: Some rubbers are specifically formulated for laser processing, such as laser-grade natural rubber or certain EPDM blends. These materials can be cut with minimal hazardous output, producing mostly particulate smoke and manageable organic vapors. However, even “safe” rubber types release strong odors and fine particulates that require fume extraction.
- Rubbers Containing Chlorine or Other Hazardous Additives: Many industrial rubbers, such as neoprene or PVC-based compounds, contain chlorine. When laser cut, these materials release hydrogen chloride gas — a highly toxic, corrosive fume that can damage lungs, eyes, and the laser machine itself. Chlorinated rubbers also leave behind acidic residues that can corrode optics and metal components. Cutting these materials without specialized filtration is unsafe.
- Other Hazardous Emissions: Depending on the formulation, rubber cutting may release sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions can be harmful in both the short term (irritation, breathing difficulty) and long term (respiratory disease risk).
- Ventilation and Filtration Requirements: An active exhaust system is essential, even for laser-safe rubber. Industrial setups often use activated carbon filters in combination with particulate filters to capture both solid particles and gaseous emissions. Without proper ventilation, harmful fumes can accumulate quickly in enclosed spaces.
- Material Verification: Before cutting, check the manufacturer’s safety data sheet (SDS) for the rubber’s composition. If chlorine or other hazardous additives are listed, the material should not be cut on CO2 lasers unless you have specialized equipment for neutralizing toxic gases.
What PPE Should The Operator Wear When Laser Cutting Rubber?
- Eye Protection: While most CO2 laser cutting machines are enclosed and have protective viewing windows that block the laser wavelength, safety glasses rated for infrared protection should still be worn when working with open-bed systems or during maintenance. This helps guard against accidental beam exposure and irritation from airborne particulates.
- Respiratory Protection: Cutting rubber — even laser-safe types — can generate fine particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). An N95 or P100 respirator can protect against particulates, but for maximum safety, a respirator with activated carbon filters is recommended to absorb gases and odors. This is especially important when cutting materials of uncertain composition or when ventilation is limited.
- Hand Protection: Operators handling rubber sheets, scrap pieces, or freshly cut parts should wear heat-resistant gloves. Rubber can retain heat after cutting, and charred or melted edges may stick to skin or clothing. Gloves also protect against any soot or residue that may contain irritants.
- Skin and Clothing Protection: A flame-resistant lab coat or work apron is recommended when working with laser equipment. While direct flame is rare, rubber is flammable under certain conditions, and sparks or molten particles can cause burns. Clothing should be non-synthetic when possible to reduce the risk of melting in case of exposure to hot debris.
- Hearing Protection (If Applicable): Most CO2 laser cutting machines operate quietly, but in industrial environments with multiple machines, background noise can exceed safe limits. Ear protection may be required in such cases.
How To Reduce Burnt Marks On Rubber Edges?
- Optimize Laser Power and Speed: Using more power than necessary increases heat buildup, which deepens burn marks and widens the kerf. Reducing power while increasing speed helps the laser move through the material before excess heat has time to spread. Test small samples to find the lowest power setting that still achieves a clean cut.
- Use Air Assist Effectively: A constant stream of compressed air or nitrogen directed at the cut helps clear away debris and cool the cutting zone. This reduces scorching and prevents residue from fusing to the edges. Air assist also helps suppress small flames that can occur when cutting rubber.
- Choose the Right Focus and Lens: Keeping the laser beam precisely focused on the material’s surface ensures maximum energy efficiency and reduces the amount of heat spreading to surrounding areas. For thicker rubber, slightly offsetting the focus into the material can help maintain cut quality while limiting edge charring.
- Masking and Surface Protection: Applying a low-adhesive masking tape to the rubber surface before cutting can act as a thermal barrier, catching soot and vaporized particles before they settle back onto the material. This is especially effective for smooth rubber sheets used in decorative or precision applications.
- Multiple Passes for Thick Rubber: For dense or thick sheets, making several lower-power passes instead of one high-power pass reduces the thermal load and prevents excessive burning. This approach is slower but can significantly improve edge appearance.
- Post-Processing Techniques: If light burn marks remain, edges can be cleaned with mild solvents (safe for rubber) or light mechanical abrasion, such as fine-grit sanding. However, prevention through optimized cutting is preferable to heavy post-cleaning.





