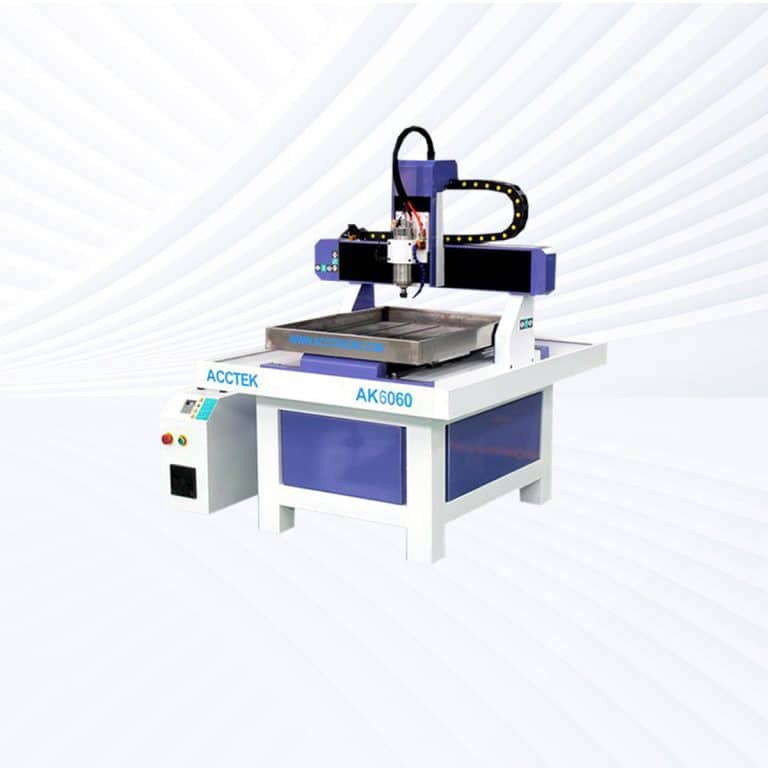
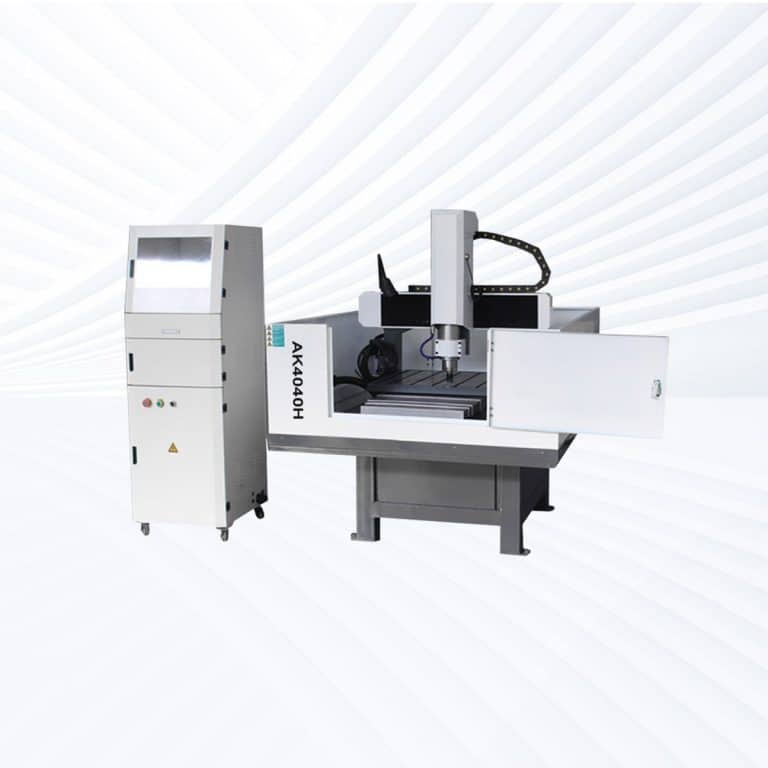
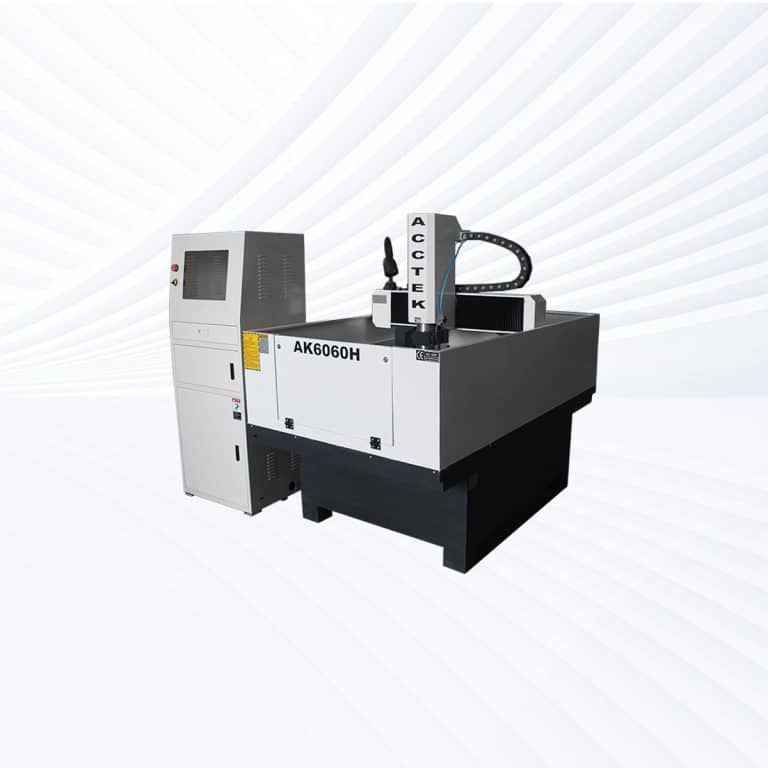
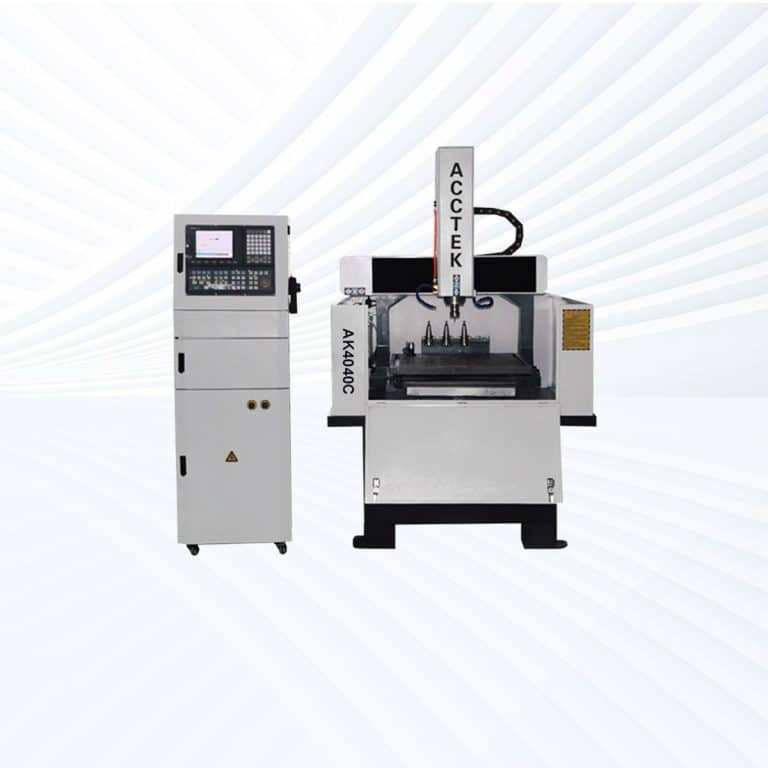
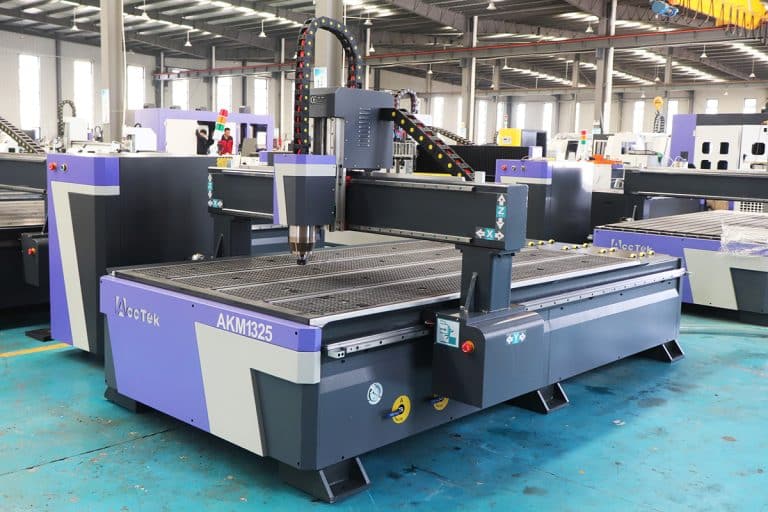
Product Introduction
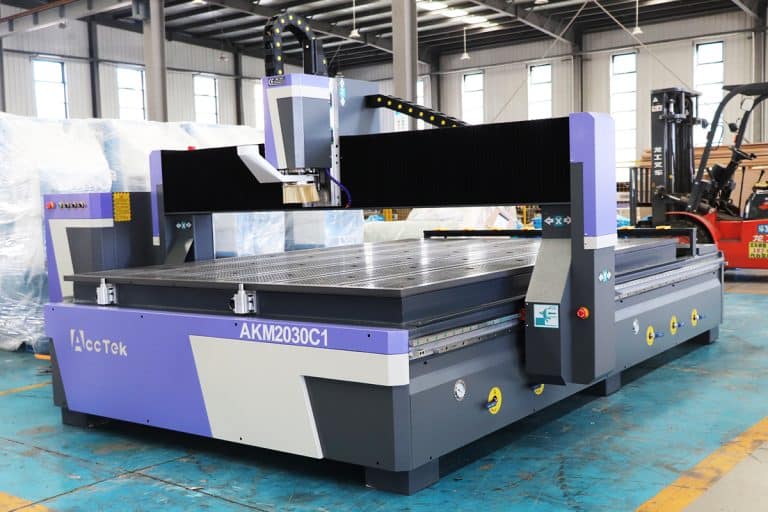
Types of Plywood CNC Routers
Material Routing Capability
| Material Type | 1.5 kW | 2.2 kW | 3.0 kW | 3.2 kW | 3.5 kW | 4.5 kW | 5.5 kW | 6.0 kW | 7.5 kW | 9.0 kW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood | Light Cutting | Standard Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Speed Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Heavy-Duty Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Hardwood | Light Duty | Standard Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Plywood/MDF | Basic Cutting | Smooth Cutting | Fast, Clean Cutting | Fast Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Smooth Cuts | High-Volume Cutting | High-Volume Cutting |
| HDF/Particle Board/Melamine | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Clean Cuts | Clean Cuts | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Acrylic(PMMA) | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Fast, Clean Edges | High Clarity | High Clarity | Smooth Finishing | Smooth Finishing | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity | Industrial Clarity |
| Polycarbonate/PETG | Thin Sheets | Clean Cutting | Stable Cutting | Stable Cutting | Precision Cutting | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ABS/PVC Foam Board | Light Duty | Standard | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | High Stability | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| HDPE/LDPE/PP/Nylon | Light Cuts | Standard Cuts | Stable Cuts | Stable Cuts | Deep Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | High-Torque | Industrial | Industrial |
| Delrin/UHMW | Light Duty | Standard | Accurate Routing | Accurate Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Solid Surface (Corian) | Very Light | Standard | Strong Cutting | Clean Cutting | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting | Industrial Cutting |
| Fiberglass/Carbon Fiber Sheet | Light Trimming | Standard | Precise Routing | Precise Routing | High-Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Phenolic/Bakelite | Limited | Standard | Clean Routing | Clean Routing | Precision Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Foam(EVA, XPS, EPS, PU) | Very Easy | Very Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | High-Speed | High-Speed | High-Speed |
| Rubber/Leather/Cork | Light Duty | Standard | Clean Edges | Clean Edges | Faster Routing | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| Cardboard/Paperboard | Easy | Easy | Fast Cutting | Fast Cutting | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Ultra-Fast | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
| ACP/ACM (Surface Routing Only) | Very Light | Standard | Clean Grooves | Clean Grooves | High Precision | Heavy-Duty | Heavy-Duty | Industrial | Industrial | Industrial |
Compatible Materials
- Softwood Plywood
- Hardwood Plywood
- Birch Plywood
- Poplar Plywood
- Pine Plywood
- Maple Plywood
- Oak Plywood
- Walnut Plywood
- Beech Plywood
- Ash Plywood
- Bamboo Plywood
- UV-Coated Plywood
- Film-Faced Plywood
- Phenolic Plywood
- Marine-Grade Plywood
- Exterior Plywood
- Interior Plywood
- Structural Plywood
- Pressure-Treated Plywood
- Fire-rated Plywood
- MDF-Core Plywood
- Particleboard-Core Plywood
- LVL (Laminated Veneer Lumber)
- LVB (Laminated Veneer Board)
- HDF-Laminated Plywood
- Veneer-Faced Plywood
- Decorative Plywood Panels
- Cabinet-Grade Plywood
- Furniture-Grade Plywood
- Acoustic Plywood
- Flexible/Bendable Plywood
- Lightweight Plywood Panels
- Radiata Plywood
- Luan Plywood
- Paulownia Plywood
- Okoume Plywood
- Teak Plywood
- Mahogany Plywood
- Cherry Plywood
- Multi-Ply Engineered Plywood
Application of Plywood CNC Routers




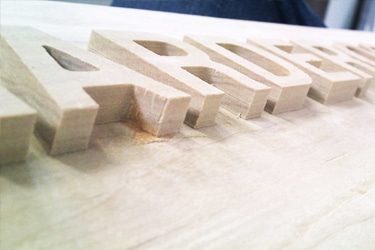



Customer Testimonials
Comparison VS Other Engraving Technologies
| Comparison Item | Plywood CNC Routing | Laser Engraving | Chemical Etching | EDM Engraving |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Mechanical cutting with rotating bits | Surface burn/vaporization | Chemical reaction removes material | Electrical discharge erodes material |
| Suitable Materials | Plywood, wood panels, MDF | Wood, acrylic, coated metals | Metals, glass, ceramics | Conductive metals only |
| Cutting Ability | Full-depth cutting and profiling | Limited cutting on wood | No cutting ability | High-precision cutting but slow |
| Engraving Depth | Deep engraving + pockets | Mostly shallow | Very shallow | Deep but slow |
| Speed | Fast for routing and shaping | Fast for fine engraving | Medium | Slowest |
| Detail Resolution | High detail; dependent on bit size | Extremely high | Moderate | Extremely high |
| Precision | High repeatability | Very high | Moderate | Ultra-high |
| Design Complexity | Supports 2D, 2.5D, and some 3D | Excellent for intricate 2D | Good for patterns | Excellent for complex metal parts |
| Edge Quality | Clean with correct tooling | Charred edges on wood | Smooth after cleaning | Very clean edges |
| Tool Wear & Cost | Low-cost bits; predictable wear | Laser tubes degrade over time | Requires chemicals & masks | High electrode/tool wear |
| Setup Time | Medium (fixtures + tooling) | Low (mostly software) | Medium (chemical prep) | High (tooling & setup) |
| Safety Concerns | Noise, chips, dust | Fumes, laser radiation | Chemical burns & fumes | High voltage & sparks |
| Operating Cost | Low | Low–medium | Medium–high | High |
| Best Applications | Cutting plywood panels, signs, furniture parts | Fine marking, shallow engraving | Serial numbers, surface textures | Precision metal molds & parts |
| Ideal Use Case | Plywood fabrication & woodworking | Detailed engraving on many materials | Uniform shallow metal patterns | High-precision conductive material machining |
Why Choose Us
High Precision & Efficiency
AccTek CNC routers deliver fast, accurate results with minimal errors, supporting intricate designs and mass production across the woodworking, plastic, and metal industries.
Robust and Durable Design
Our machines are built with high-quality frames and components, ensuring long service life, high load-bearing capacity, and stability during high-speed operations.
Intelligent Control Systems
Equipped with user-friendly interfaces and smart controllers, our routers offer smooth motion control, automatic toolpath optimization, and easy integration with various CAD/CAM software.
Flexible Customization
From machine size to spindle power and motor type, we offer flexible configurations to suit different production needs, budgets, and material requirements.
Related Resources

How Do CNC Routers Work
This article explains the working principle of CNC routers, from the motion system and cutting tools to the software workflow, materials, precision, and actual machining principles.

How To Maintain CNC Routers
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to maintain CNC routers, covering essential tasks, troubleshooting tips, upgrades, and best practices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

What Is The Accuracy Of CNC Routers
This article is a comprehensive guide that explains the precision of CNC routers, the key factors affecting precision, expected performance, and how to improve machining results.

How to Choose the Right Router Bits for CNC Routers
This article explains how to select the right router bit for your CNC router, including cutter type, material, coating, and tip, to achieve precise, efficient, and durable cutting performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Price Of Plywood CNC Routers?
What Is The Working Range Of Plywood CNC Routers?
- Small and Medium Working Sizes: Compact formats such as 700mm×900mm and 900mm×1500mm are ideal for small workshops, sign-making studios, and craft applications. These sizes handle partial plywood sheets or smaller components, offering excellent flexibility for furniture parts, decorations, and custom woodworking projects without requiring a large workshop footprint.
- Standard Full-Sheet Sizes: Popular models like 1300mm×2500mm and 1500mm×3000mm are specifically designed for standard 4×8 ft or 5×10 ft plywood sheets. These sizes are widely used in cabinetry, furniture manufacturing, and panel processing. They allow full-sheet loading without trimming, making them efficient for continuous production and nested-based manufacturing workflows.
- Large-Format Industrial Sizes: Larger working ranges such as 2000mm×3000mm, 2000mm×4000mm, and 2000mm×6000mm support heavy-duty industrial tasks, allowing the processing of oversized plywood panels, architectural components, and specialty construction materials. These machines offer extended cutting paths for long structural parts or large-scale nested layouts.
- Ultra-Large Custom Sizes: Very large models like 3000mm×6000mm accommodate exceptionally large plywood sheets used in construction, marine applications, stage design, or prefabricated building systems. These machines deliver expansive working surfaces for multi-panel cutting, structural layout work, and high-volume industrial production.
- Customizable Working Dimensions: For manufacturers with unique production flows or oversized plywood requirements, custom working sizes are available upon request. Custom CNC routers can be built to match specific sheet dimensions, conveyor-type loading systems, or integrated automation lines.
What Is The Accuracy Of Plywood CNC Routers?
- Positioning Accuracy: Most plywood CNC routers achieve a positioning accuracy of ±02mm to ±0.05mm, depending on the build quality and motion system. This level of precision is suitable for cabinetry, panel processing, joinery components, and detailed plywood carving. High-end machines equipped with servo motors and heavy-duty frames achieve the tightest tolerances.
- Repeatability Accuracy: Repeatability is often even more important in production environments. Plywood CNC routers typically offer ±02mm repeatability, ensuring that identical parts can be produced consistently across large batches. This makes them ideal for furniture manufacturers, cabinet door makers, and nesting-based production lines where accuracy must remain stable over long shifts.
- Structural Rigidity and Frame Stability: Welded steel frames, linear guide rails, and helical racks help maintain accuracy under load. A rigid machine prevents vibration or deflection when cutting dense plywood, ensuring clean edges on deep cuts or high-speed passes. Machines with enhanced gantry strength maintain precision across large working areas.
- Servo, Easy Servo, and Stepper Systems: Accuracy can vary slightly depending on the drive system. Servo motors deliver the highest precision and smoothest movement. Easy servo motors offer near-servo accuracy with improved stability. Stepper systems are suitable for most plywood applications but may show slight accuracy reductions at high speeds or heavy loads.
- Toolpath Smoothness and Edge Quality: High accuracy contributes directly to cleaner contours, smoother curves, and well-aligned joints. When combined with sharp carbide bits and proper feed rates, the CNC router produces tight-fitting components requiring minimal sanding or edge refinement.
- Application Suitability: Whether for intricate carving, fine patterns, cabinet joinery, or precision hole drilling, plywood CNC routers maintain a high level of dimensional accuracy across all major woodworking tasks.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Plywood CNC Routers?
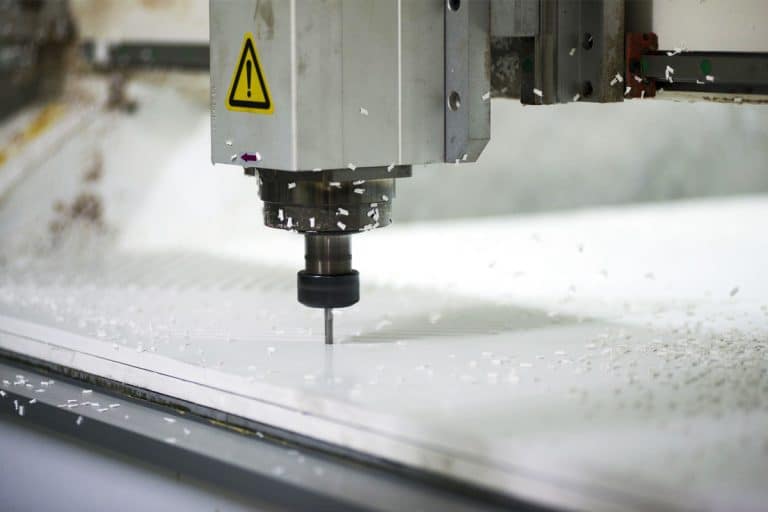
- Material Tear-Out on Lower-Grade Plywood: Plywood with voids, weak core layers, or inconsistent glue lines can cause chip-out or edge splintering during cutting. Even high-quality CNC routers cannot fully compensate for defects in low-grade sheets. Compression bits help reduce tear-out, but material inconsistency remains a common issue.
- Dust Production and Extraction Requirements: Plywood machining generates large amounts of fine dust that can accumulate inside machine components or spread throughout the workshop. Proper dust extraction systems are essential for maintaining cutting quality, operator safety, and clean workshop conditions. Inadequate dust management may reduce machine lifespan.
- Tool Wear on Dense or Resin-Rich Panels: Some plywood types, especially those with dense hardwood veneers or resin-heavy glue layers, can accelerate tool wear. Frequent bit changes increase operational cost. Carbide tools handle plywood well, but high-volume production environments may still experience rapid wear on cutting edges.
- Noise and Vibration: High-speed cutting of plywood—particularly on large-format CNC routers—can generate noticeable noise levels. Without a rigid machine frame or stable workshop floor, vibration may occur, impacting edge quality and long-term precision.
- Learning Curve for New Operators: CNC routers require proper programming, toolpath planning, and material setup to achieve professional results. Incorrect feed rates, spindle speeds, or tool selections can cause burning, misalignment, or tool breakage. New operators may need time to master CAD/CAM workflows.
- Large Space Requirements: Full-sheet plywood CNC routers, such as 1300mm×2500mm or 1500mm×3000mm models, require significant workshop space for loading, unloading, and safe movement around the machine. Smaller workshops may find space management challenging.
- Higher Upfront Investment: Compared to manual woodworking tools, CNC routers involve a higher initial cost for the machine, control system, dust extraction, and tooling. Although they improve efficiency and accuracy, the upfront investment can be a barrier for small workshops.
What Is The Spindle Power Of Plywood CNC Routers?
- 3.0kW Spindles: Suitable for small to medium workshops, these spindles handle standard plywood sheets, light carving, and moderate-depth cuts. They offer a good balance of affordability and performance, making them ideal for signage, cabinetry prototypes, and custom furniture parts.
- 3.5kW Spindles: A slight upgrade in power, 3.5kW spindles improve cutting stability and support deeper passes on hardwood-faced plywood. These spindles are commonly used in light production environments where higher torque is beneficial but industrial-level power is not required.
- 4.5kW Spindles: One of the most popular choices for full-sheet plywood processing, 4.5kW spindles provide strong torque and smooth high-speed cutting. They handle nested-based manufacturing, detailed carving, and continuous plywood cutting with reliable performance.
- 5.5kW Spindles: Designed for heavier workloads, these spindles support deeper cuts, larger bits, and higher feed rates. They are ideal for furniture factories and workshops processing large volumes of multi-layer plywood or mixed wood materials.
- 6.0kW Spindles: These high-performance spindles deliver strong, stable power for industrial operations. They maintain consistent torque during long production cycles, allowing fast and clean cutting on dense or thick plywood panels.
- 9.0kW Spindles: The most powerful option, 9.0kW spindles are built for heavy-duty CNC routers used in continuous, high-volume production. They excel in deep pocketing, large-format panel cutting, and demanding industrial applications where speed and durability are essential.
What Type Of Worktable Do Plywood CNC Routers Use? Vacuum and T-Slot Worktable
- Vacuum Worktable: Vacuum tables are the most efficient clamping solution for plywood sheet processing. They use vacuum pumps to create strong suction across the table surface, holding full plywood sheets firmly in place without mechanical clamps. This system ensures fast material loading, stable cutting at high speeds, and excellent edge accuracy. Vacuum zones can be controlled independently, allowing operators to secure small plywood pieces after nesting cuts. For large-format and high-volume plywood production, vacuum tables provide superior convenience and productivity.
- T-Slot Worktable: T-slot tables use aluminum tracks to accommodate mechanical clamps, making them flexible for irregularly shaped plywood pieces, thicker materials, or specialty fixtures. They offer a reliable holding force for operations that require heavy cutting or deep carving. T-slot worktables are especially useful for custom woodworking, jig mounting, or parts that cannot be easily sealed on a vacuum surface. Although they require more setup time than vacuum systems, they remain a durable and versatile choice for general plywood routing.
- Hybrid Vacuum + T-Slot Design: Some plywood CNC routers combine both systems, offering vacuum suction for full-sheet processing and T-slots for clamping small or uniquely shaped components. This hybrid design increases flexibility, supporting a wider range of production tasks while maintaining strong material stability.
What Are The Environmental Requirements For Plywood CNC Routers?
- Stable Temperature Conditions: Plywood CNC routers perform best in environments with temperatures between 10℃ and 35℃. Extreme cold can cause lubrication thickening and motor instability, while excessive heat may affect electronics, reduce spindle efficiency, and increase the risk of overheating. A consistent temperature helps preserve machine calibration and cutting accuracy.
- Controlled Humidity Levels: Ideal workshop humidity is around 40–70%. High humidity can affect plywood sheets, causing expansion, warping, or surface swelling, which results in inconsistent cutting quality. Excess moisture may also lead to corrosion on metal components. Very low humidity creates static buildup that can attract dust to sensitive electronics.
- Adequate Ventilation and Airflow: Proper airflow prevents heat accumulation around the spindle, motors, and control cabinet. Good ventilation also helps disperse airborne dust and ensures a comfortable working environment. Workshops without sufficient airflow may experience increased machine wear due to heat buildup.
- Effective Dust Extraction: Plywood machining produces fine dust that accumulates quickly. A reliable dust-collection system is essential to prevent clogging, maintain cutting accuracy, and prolong machine life. Dust can interfere with linear rails, ball screws, and sensors if not managed properly.
- Clean and Organized Workspace: A clean floor and surrounding area help prevent debris from entering machine components. Clutter-free spaces allow operators to move safely while loading plywood sheets, minimize fire hazards, and reduce the risk of toolpath errors caused by accidental obstructions.
- Stable Power Supply: CNC routers require a steady voltage to operate motors, drives, and controllers. Voltage fluctuations may cause spindle errors, motor alarms, or sudden shutdowns. Using a voltage regulator or UPS system ensures stable performance.
- Low-Vibration Setting: Although CNC routers generate some vibration, placing the machine in a structurally stable workshop prevents external vibrations from affecting cutting quality. Avoid installing the CNC router near heavy machinery that causes frequent floor vibration.
What Training Is Required To Operate Plywood CNC Routers?
- Basic CNC Operation Training: Operators must learn the fundamentals of machine startup, homing, axis movement, spindle control, and emergency stop procedures. This includes understanding how to load plywood sheets, secure workpieces, and verify work offsets before cutting.
- CAD/CAM Software Training: Proper training in CAD design and CAM toolpath generation is essential. Operators learn how to create vectors, assign toolpaths, select bits, and set cutting parameters such as feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut. Knowledge of nesting software is especially useful for plywood panel optimization.
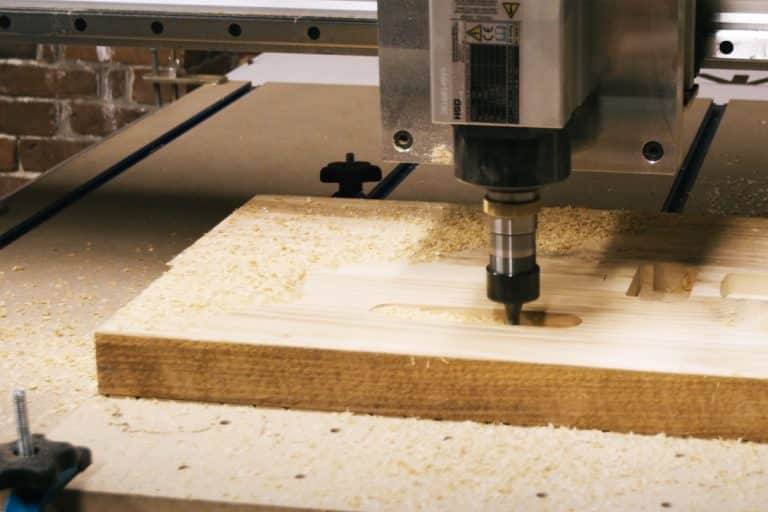
- Tool Selection and Setup: Training includes identifying different router bits (compression, up-cut, down-cut, engraving bits) and understanding how they affect plywood edge quality. Operators must learn how to install bits, tighten collets, set tool lengths, and perform Z-axis calibration accurately.
- Material Characteristics and Cutting Techniques: Operators need to understand plywood density, veneer orientation, and glue layers to choose the correct cutting parameters. Training covers how to prevent tear-out, reduce burning, and maintain clean edges through proper toolpaths and machine settings.
- Safety Procedures and Emergency Protocols: Operators must follow safety standards, including proper use of dust extraction, hearing protection, eye protection, and a safe distance during machine operation. Training also covers emergency stop usage, handling unexpected vibrations, and managing tool breakage safely.
- Maintenance and Daily Checks: Routine tasks such as cleaning dust from rails, checking lubrication points, inspecting belts or racks, and monitoring spindle cooling systems are essential for long-term reliability. Operators are taught how to perform basic troubleshooting for common issues like motor errors or inconsistent cutting depth.
- Quality Inspection and Workflow Management: Training includes verifying part dimensions, adjusting toolpaths when needed, and organizing production schedules for high-volume plywood cutting.








