The “good” laser cutting machine balances cutting precision, speed, reliability, ease of use, and long-term affordability. It’s a holistic package, where every component and service matters. This framework is essential for assessing whether Chinese machines measure up to global standards.
Over the past decade, China’s laser-cutting industry has exploded in both scale and global relevance. Once known for producing only entry-level or budget equipment, Chinese manufacturers have rapidly advanced, closing the gap with Western, Japanese, and South Korean competitors. Today, China is not just following trends—it’s setting them.
China dominates the global laser equipment market by volume. In terms of unit sales, Chinese brands make up the majority of new laser cutting machine purchases worldwide, especially in small and mid-range segments. While European and Japanese manufacturers still lead in ultra-high-end applications (like aerospace and semiconductor), Chinese machines have captured significant ground in general manufacturing, signage, automotive, and furniture industries. The performance-to-price ratio offered by Chinese models has made them especially attractive to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) globally.
The perception of Chinese laser cutting machines has shifted dramatically. What was once viewed as “cheap but unreliable” is now increasingly seen as “affordable and competitive.” This change is driven by real improvements in build quality, component integration, and software sophistication. Chinese brands are investing heavily in R&D, smart factory automation, AI-driven systems, and global certifications. At international trade shows like LASER World of PHOTONICS and FABTECH, Chinese manufacturers are now key players, not just budget alternatives.
China’s laser-cutting industry has matured rapidly, on a scale unmatched by any other country. It offers a full spectrum of machines from hobby-grade to high-end industrial, and its market share continues to grow globally. With improved reliability, better branding, and rising technical standards, Chinese manufacturers are no longer the underdogs. They’re now serious contenders—and in many segments, they’re leading the charge.
Chinese laser cutting machine manufacturers have significantly expanded their technology portfolios in recent years, moving well beyond basic models to offer a diverse and increasingly sophisticated lineup. Today, their offerings include everything from conventional fiber and CO2 systems to advanced ultra-high-power and multi-axis automation platforms. This breadth of capability is a key reason why Chinese machines are gaining traction globally, not just in entry-level markets, but in serious industrial environments.
Chinese manufacturers have also embraced complexity. Bevel laser cutting machines, which can cut edges at precise angles (up to ±45°), are now offered for advanced fabrication needs in shipbuilding, construction, and automotive. These machines integrate tilting heads and dynamic path planning software.
5-axis laser cutting systems—traditionally seen in aerospace and automotive sectors—are also emerging from China. These machines can perform complex three-dimensional cuts on formed parts, tubes, or irregular surfaces. While not as widespread as 2D models, their presence signals a push toward high-tech applications.
Automation is another area of rapid development. Leading Chinese companies now offer full turnkey systems with robotic arms, auto-loading/unloading, conveyor integration, and centralized control dashboards. Smart features like remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and real-time production analytics are becoming standard in higher-end models.
The performance and longevity of a laser cutting machine depend heavily on the quality of its core components. Even a well-designed frame or sleek interface can’t compensate for poor parts under the hood. In the case of Chinese laser cutting machines, component quality has long been a point of scrutiny, but the landscape is changing fast. Today, many Chinese manufacturers source or develop high-grade components that rival international standards. Here’s how they measure up across the board:
The laser source is the heart of any laser cutting machine. Chinese brands offer a range of options—from cost-effective domestic sources to premium imported ones. Companies like Raycus, Maxphotonics, and JPT dominate the local market and have made significant strides in power stability, beam quality, and service life. While they’re more affordable than Western sources like IPG Photonics or nLIGHT, their reliability has improved year after year. For mission-critical or export-grade machines, many Chinese manufacturers still offer IPG lasers as an upgrade option, giving users flexibility depending on budget and performance needs.
The laser beam’s delivery depends on the cutting head and optics, components that must be both precise and durable. Brands like WSX, RayTools, and PRECITEC (used in some Chinese laser cutting machines) are widely deployed. High-end models now include autofocus, real-time height sensing, anti-collision protection, and automatic nozzle cleaning. These features enhance cut quality and reduce downtime. Optics made from high-reflection-resistant materials and with advanced coatings help improve energy efficiency and extend lifespan.
Precision motion is what turns laser energy into a clean, accurate cut. Chinese laser cutting machines increasingly use components from top-tier suppliers such as HIWIN (linear guides), Yaskawa or Fuji (servo motors), and Panasonic or Beckhoff (controllers). High-performance CNC systems—either proprietary or sourced from industry leaders—are becoming the norm, especially in mid-to-high-end machines. These systems ensure tight tolerances, smooth acceleration, and repeatable positioning even under demanding workloads.
Compliance is critical for global competitiveness. The best Chinese laser cutting machines now carry international certifications such as CE (Europe), FDA (U.S.), ISO 9001 (quality management), and sometimes UL or CSA for North America. Machines targeting global markets are increasingly built to meet these regulatory standards, ensuring not just legal eligibility for export but also a basic threshold of safety, environmental responsibility, and production quality.
The quality of core components in Chinese laser cutting machines has dramatically improved over the past decade. With options ranging from budget parts to globally recognized brands, buyers can now select machines that meet their performance and certification requirements without compromising on cost. Supply chains are more mature, and integration of high-end optics, motion systems, and laser sources is becoming standard in mid- and high-tier models. While not all Chinese laser cutting machines are built equal, the top manufacturers are closing the quality gap—and in some cases, leading the charge in innovation and value.
To answer whether Chinese laser cutting machines are truly “good,” we need to look beyond specs and price tags and focus on real-world performance. This includes cutting precision, handling of demanding materials, consistency over time, and how they fare under industrial conditions.
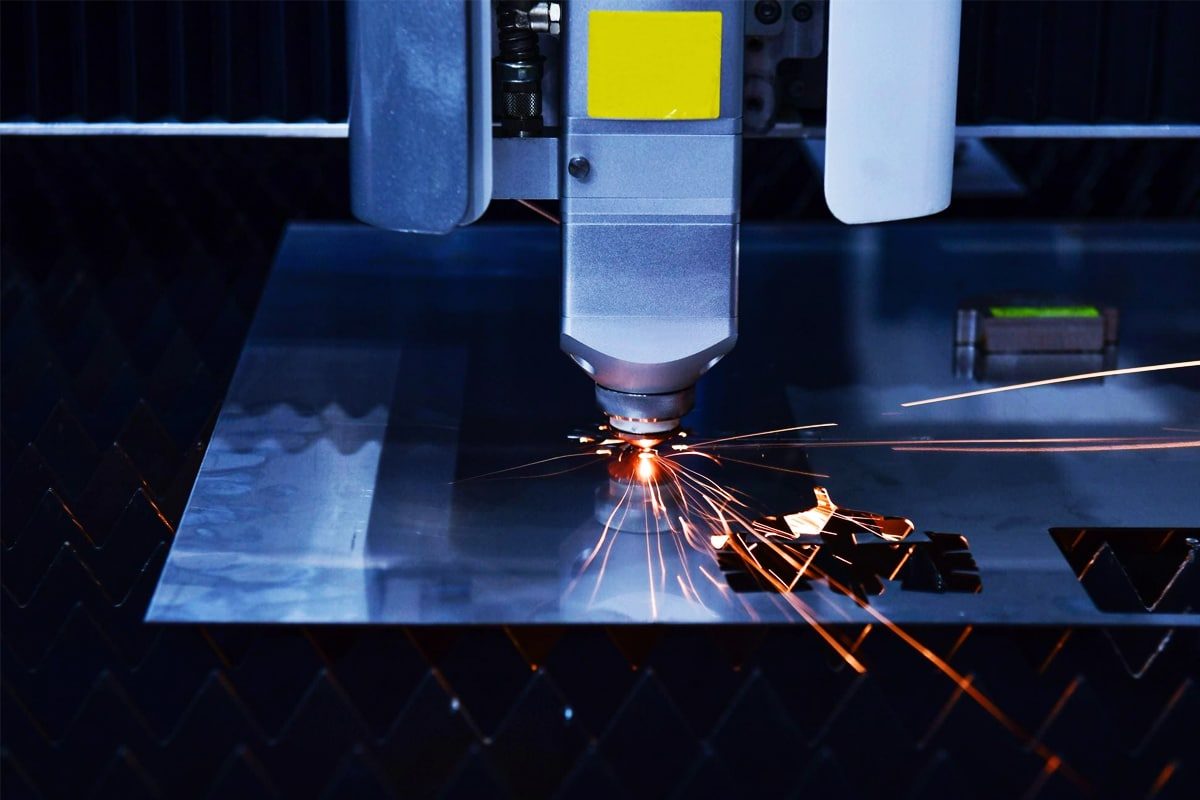
Modern Chinese laser cutting machines, especially those equipped with high-end motion systems and advanced CNC controls, offer impressive cutting precision, often within ±0.02 mm. Features like autofocus heads, capacitive height sensors, and real-time positioning correction have brought repeatability to levels suitable for high-tolerance applications. While ultra-high-end European machines may still lead in micron-level control, Chinese systems now easily meet the precision needs of industries like metal fabrication, signage, and automotive components.
Chinese manufacturers have scaled up power capabilities dramatically. Fiber laser models now range from 1kW to 40kW, allowing users to cut anything from thin sheet metal to 50mm+ carbon steel. Advanced high-power systems also feature intelligent piercing, cut monitoring, and edge smoothing technologies—helping reduce slag, deformation, and taper even on thick or reflective materials. These enhancements are crucial for heavy-duty industries like shipbuilding, construction equipment, and large-format fabrication.
Consider a mid-size sheet metal factory in Turkey that switched from a European-built 6kW laser to a 12kW laser cutting machine from a leading Chinese brand like HSG. The company reported a 35% increase in cutting speed and a 20% reduction in maintenance costs, without sacrificing edge quality. Similar results have been observed in India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, where cost-sensitive industries need high throughput but can’t compromise on cut precision or reliability. While anecdotal, these cases underline the growing trust in Chinese-built equipment in real-world production environments.
A common concern with Chinese laser cutting machines is durability. But improvements in component quality, better thermal management, and stronger frames are extending operational lifespans. Machines with robust build quality, sourced from reliable brands, are now logging 20,000–30,000 hours of runtime with proper maintenance. Predictive maintenance software and improved cooling systems also contribute to reduced downtime and longer machine life. Importantly, many manufacturers now offer warranties of 2–3 years and local service partnerships, addressing previous gaps in long-term support.
Chinese laser cutting machines have reached a level where their performance and reliability often match the needs of serious industrial users. With tight tolerances, high power options, and increasingly durable designs, they’re proving themselves capable not just in theory, but in production environments around the world. While not all machines are created equal, those from top-tier Chinese manufacturers are no longer just “good enough”—they’re genuinely competitive.
When evaluating the value of laser cutting machines, cost isn’t just about the sticker price—it’s about what you pay over the machine’s lifetime versus what it delivers in return. Chinese laser cutting machines stand out in this equation, often offering a compelling financial case for businesses trying to balance performance with budget constraints. Let’s break down the economic picture into three key elements: acquisition cost, running cost, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
One of the strongest selling points of Chinese laser cutting machines is their affordability. For the same power level and working area, a Chinese-built fiber laser cutting machine can cost 30–50% less than a comparable model from Europe, Japan, or the U.S. Entry-level desktop CO2 laser cutting machines start as low as $2,000, while industrial 6kW fiber systems can be had for under $80,000—often including features like auto-focus heads, cooling units, and basic automation. This lower upfront cost lowers the barrier to entry for small to mid-sized manufacturers, job shops, and startups.
Chinese laser cutting machines are increasingly efficient in daily operation. Fiber lasers, in particular, consume significantly less power than older CO2 systems and require fewer consumables. Domestic laser sources like Raycus or Maxphotonics offer competitive lifespans (up to 100,000 hours), and many laser cutting machines now include built-in diagnostics to reduce unplanned maintenance. However, maintenance intervals, part quality, and local support availability can vary by brand. Still, day-to-day costs for electricity, gas assistance, and labor are often on par with or lower than non-Chinese systems.
TCO looks at the big picture: initial investment + running costs + maintenance + downtime + resale value. A low-cost machine that breaks down frequently or lacks local support can end up costing more in the long run. That’s where brand selection becomes critical. Reputable Chinese manufacturers now offer global support networks, multi-year warranties, and remote troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and boosting overall value. While ultra-premium machines from Western brands might last longer or retain more resale value, a well-chosen Chinese laser cutting machine can often deliver a faster return on investment (ROI), especially for businesses with high throughput or tight capital budgets.
Chinese laser cutting machines offer a strong value proposition: lower acquisition costs, competitive running expenses, and solid long-term economics when sourced from trusted manufacturers. For many buyers, especially those focused on ROI and short payback periods, they’re not just affordable—they’re financially smart. Choosing wisely can mean cutting costs without cutting corners.
No matter how powerful or affordable laser cutting machines are, their true value shows when something goes wrong or when your team needs help getting the most out of them. After-sales service is the ultimate stress test for any equipment supplier, and it’s an area where Chinese manufacturers have made real progress, though some gaps remain. From technical support to parts availability and operator training, here’s how the picture looks today.
A decade ago, after-sales service was one of the biggest drawbacks of buying a Chinese laser cutting machine. Language barriers, time zone delays, and inconsistent communication made technical support frustrating. But that’s changing fast. Leading manufacturers like Bodor, HSG, Han’s Laser, and G.WEIKE now operate international service centers, provide multilingual support, and offer remote diagnostics via apps or cloud dashboards. Many have expanded their footprints in Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia with local partners or dedicated offices.
That said, not all brands are equal. Smaller or no-name manufacturers may still offer limited service, relying on email-only support or slow response times. Buyers need to assess the strength of the brand’s global presence, not just the specs of the laser cutting machine.
Reliable access to replacement parts and consumables (like lenses, nozzles, belts, and filters) is critical to minimizing downtime. Top-tier Chinese suppliers now stock common components in overseas warehouses or through local distributors. Some even offer next-day delivery for critical parts in key regions.
However, compatibility issues can arise if the laser cutting machine uses proprietary parts or unbranded components. That’s why laser cutting machines built with standard, globally sourced parts (e.g., HIWIN guides, RayTools heads, IPG or Raycus lasers) are often a smarter choice—they’re easier to service, and replacement parts are more readily available.
Operator skill directly affects laser cutting machine performance, safety, and lifespan. The best Chinese manufacturers now offer detailed manuals, online training modules, and on-site commissioning support as part of their sales packages. Some also conduct overseas training events or partner with local technicians to deliver hands-on instruction.
Still, the quality of training can vary. Some companies provide robust support with multi-language materials and video walkthroughs; others may fall short, offering little beyond a PDF manual. For first-time buyers, especially in regions without local service agents, this can be a critical consideration.
After-sales service is where the gap between top-tier and budget-tier Chinese laser cutting machine makers becomes most apparent. While industry leaders are building solid international service networks and improving support quality, lesser-known brands still pose risks. Buyers should look beyond price tags and prioritize brands with proven support infrastructure, reliable parts availability, and clear training programs. Because in the long run, good service isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity.
Safety and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable when it comes to industrial equipment, and laser cutting machines are no exception. Between high-power lasers, moving parts, and harmful emissions, these systems pose real risks if not properly engineered. Chinese laser cutting machine manufacturers have made clear strides in this area, especially those aiming for international markets. Still, buyers must stay sharp and verify whether a machine meets all relevant standards for their region and industry.
The top Chinese brands now build machines that meet or exceed key global safety and quality certifications. This includes CE marking for the European Union, FDA compliance for the U.S., ISO 9001 for quality management, and sometimes even UL or CSA certification for North America. These certifications signal that the machines have been inspected for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, structural integrity, and operator protection.
However, not every machine carrying a certification label is necessarily compliant in practice. Some lower-end manufacturers may affix fake or unverified CE or FDA markings without undergoing proper third-party audits. It’s essential to verify certifications with documentation and, if possible, choose suppliers who offer transparency and traceability for their compliance processes.
Laser cutting—especially of metals, plastics, or composites—produces hazardous byproducts: smoke, dust, and potentially toxic fumes. Effective fume extraction and filtration are critical not only for worker health but also for laser cutting machine longevity and cutting accuracy.
Leading Chinese laser cutting machines now incorporate enclosed cutting beds with built-in fume extraction ports, multi-zone vacuum systems, and optional air filtration units. Some also offer smart airflow control that adjusts suction based on the laser’s location. These systems help comply with workplace safety regulations such as OSHA standards in the U.S. or HSE guidelines in the U.K
However, not all systems come standard with proper ventilation or filters, particularly at the lower price end. In some cases, buyers must invest in separate extraction units or upgrade to compliant filtration systems themselves. This adds to the total cost and complexity if not considered upfront.
Compliance and safety are improving rapidly among top Chinese laser cutting machine manufacturers, especially those competing in regulated international markets. Machines now often meet global safety standards and include features like enclosures, emergency stops, and fume extraction. But buyers must do their due diligence: check certifications, assess fume control capabilities, and avoid cutting corners on essential safety systems. Because when it comes to laser cutting machinery, the cost of non-compliance can far outweigh any initial savings.
At the end of the day, the real test of any laser cutting machine lies in the hands of those who use it daily. User experiences with Chinese laser cutting machines are as diverse as the machines themselves, ranging from glowing endorsements to cautionary tales. While many buyers report exceptional value and strong performance, others warn about reliability gaps, communication issues, or inconsistent quality control. Here’s a balanced look at what users around the world are saying.
Owners of brands like Bodor, HSG, and Thunder Laser often mention responsive support, solid construction, and ease of use, especially in models aimed at export markets.
Technical support can be hit or miss depending on the brand and region. If local service infrastructure is lacking, even small issues can lead to long downtimes.
These users aren’t dismissing Chinese laser cutting machines—in fact, many are satisfied—but they stress that buyers must research, budget for accessories, and not expect premium-tier polish for entry-level prices.
User experiences with Chinese laser cutting machines are largely positive, but only when expectations are managed and choices are made wisely. The success stories are real, especially with top-tier manufacturers. But friction points exist, mainly around support, part availability, and quality consistency in the lower market tiers. For prospective buyers, the message is clear: do your research, don’t go for the cheapest option blindly, and plan for support just as much as specs.
As Chinese laser cutting machines continue to mature, the question many businesses face is no longer if they’re usable, but how they compare to Western models in real-world performance, quality, and long-term value. While there are still differences—some subtle, others significant—Chinese laser cutting machines are increasingly closing the gap. Here’s a detailed side-by-side look across four key areas: performance, build quality, software, and pricing.
In terms of raw cutting capabilities—speed, power, and accuracy—many modern Chinese laser cutting machines now operate at levels similar to Western brands like Trumpf, Bystronic, and Amada. Fiber laser systems from top-tier Chinese manufacturers (e.g., HSG, Bodor) can cut stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, brass, and even copper with clean edges and competitive speeds. Features like autofocus, adaptive piercing, and high-speed motion control have become standard in higher-end Chinese systems.
However, Western laser cutting machines tend to edge ahead in ultra-high-tolerance applications, especially where micron-level consistency or extreme material diversity is required. For the majority of general manufacturing use cases, though, the performance difference is now minimal.
Western laser cutting machines still lead when it comes to precision engineering, chassis rigidity, and long-term mechanical durability. They’re often overbuilt to withstand decades of continuous use in harsh environments. Attention to detail—such as cable routing, protective housing, and user interface ergonomics—is typically higher.
Chinese laser cutting machines, while vastly improved, can still show variation in build consistency between brands and models. Some budget-tier systems may feel “light” or lack refinement in components like enclosures or wiring. But mid- to high-end Chinese models are catching up quickly, with increasingly solid frames, industrial-grade components, and tighter assembly standards.
Western laser systems often come with proprietary, deeply integrated software platforms that offer robust CAD/CAM functionality, job scheduling, diagnostics, and factory automation tools. Brands like Trumpf’s TruTops or Bystronic’s BySoft are tightly coupled with machine hardware and provide a polished, high-end user experience.
Chinese software has improved substantially, especially with newer interfaces that support multi-language environments, cloud connectivity, and nesting algorithms. Some laser cutting machines are now compatible with popular third-party platforms like LightBurn, CypCut, or NCStudio. Still, Western platforms tend to offer deeper automation features and smoother user workflows—an advantage for high-throughput or smart factory environments.
This is where Chinese laser cutting machines still dominate. The price gap can be substantial, often 30–60% lower for comparable power and specs. A 6kW industrial fiber laser cutting machine from a Chinese manufacturer may cost around $70,000–$100,000, while a similar laser cutting machine from a Western brand could exceed $200,000. For many businesses, especially SMEs, this difference is game-changing, allowing them to access advanced laser cutting without crushing capital costs.
However, the lower price does come with trade-offs in terms of brand recognition, resale value, and in some cases, support coverage or lifespan. Still, the ROI from a Chinese laser cutting machine can be faster, especially in high-output environments.
Chinese laser cutting machines are no longer just cheap alternatives—they’re serious competitors. While Western machines still set the bar for engineering precision, software depth, and brand assurance, Chinese laser cutting machines offer surprisingly close performance at a much lower cost. For many buyers, the decision comes down to priorities: if cutting-edge automation, ultra-high precision, and long-term legacy support are critical, Western brands still lead. But if you’re focused on performance-per-dollar, scalability, and fast ROI, Chinese laser cutting machines now make a very strong case.
Beyond performance and price, Chinese laser cutting machines operate in a global landscape shaped by trade policy, tariffs, and geopolitical tension. These external forces can directly impact the total cost, availability, and long-term viability of purchasing Chinese equipment, especially for buyers in regions like the U.S., Europe, and Australia. Understanding how tariffs and supply-chain security factor into the equation is essential for making an informed investment.
Tariffs and import duties on Chinese-made machinery can significantly raise the final landed cost, sometimes by 10% to 25% or more, depending on the destination country. For example, the U.S. has imposed Section 301 tariffs on a wide range of Chinese industrial products, including laser equipment and components. These taxes can erode the initial cost advantage and must be factored into total budget planning.
Some buyers attempt to work around this by purchasing through intermediary countries or breaking shipments into parts (e.g., sourcing the machine frame and laser source separately). However, such strategies carry risks, including customs penalties, delayed shipping, and service complications. Ultimately, while Chinese laser cutting machines remain cost-effective in many cases, tariffs can narrow the gap.
Geopolitical tensions also raise concerns about supply-chain stability. Disruptions in international logistics—whether due to political conflict, trade restrictions, or pandemic-related slowdowns—can affect the availability of spare parts, consumables, and technical support. This is especially important for machines that rely on proprietary or brand-specific components from Chinese factories.
Businesses in strategic or defense-adjacent industries may also face restrictions or heightened scrutiny when importing Chinese-made equipment, due to national security concerns. In some regions, compliance requirements or industrial policy incentives may actively favor domestic or allied-manufacturer machines over Chinese imports.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should work with suppliers that offer strong overseas support infrastructure, localized warehousing, and contingency plans for parts and service continuity. Choosing laser cutting machines that use globally sourced components—like IPG laser sources or HIWIN guides—can also help reduce dependency on a single supply channel.
Tariffs and geopolitical uncertainty have become key variables in the cost and risk profile of Chinese laser cutting machines. While the value proposition remains strong, buyers must look beyond base price and evaluate long-term exposure to trade disputes, import duties, and supply-chain disruptions. With careful planning and a smart sourcing strategy, these risks can be managed—but they shouldn’t be ignored.
Buying a Chinese laser cutting machines can be a smart move—but only if you approach it with diligence and a checklist like this. By verifying certifications, auditing components, testing performance, and locking in service and logistics details, you can reduce risks and maximize long-term value. The best deals aren’t just about the lowest price—they’re about getting the right machine, with the right support, from the right partner.
So, are Chinese laser cutting machines good? The answer is increasingly yes, but with important caveats. Top-tier Chinese brands have made major strides in technology, performance, and global competitiveness. They now offer machines with impressive cut quality, high power output, automation options, and real-world reliability. In many cases, they deliver performance comparable to Western counterparts at a fraction of the cost, making them highly attractive for small and mid-sized manufacturers.
However, the market is broad and uneven. While leading Chinese manufacturers back their machines with certifications, solid support, and high-quality components, low-cost or no-name models can still come with serious trade-offs, ranging from weak build quality to nonexistent service.
Buyers must look beyond specs and price. Careful evaluation of certifications, core components, after-sales support, and software is essential. Import considerations like tariffs and service coverage can also affect the true cost and value over time.
In short, Chinese laser cutting machines can be an excellent investment—if you choose the right brand and plan carefully. With due diligence, businesses can access industrial-grade laser technology at unmatched value, but cutting corners in the selection process can lead to costly setbacks. The potential is real, but so is the need to buy smart.